CEA Blood Test
Learn about the CEA blood test, its significance, and how it's conducted. Get a free PDF example for reference your comprehensive guide to CEA testing.


What is a CEA Blood Test?
CEA tests, which measure carcinoembryonic antigen levels in a patient's blood, are essential in documenting patient records for several reasons. First and foremost, they aid in the early detection of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer, by identifying elevated CEA levels in the blood even before symptoms manifest, thereby enhancing the chances of successful treatment outcomes through early intervention.
Monitoring cancer patients during and after treatment can help healthcare providers assess treatment effectiveness; decreasing CEA levels can indicate a positive response, while rising levels may signal cancer recurrence.
These tests also play a pivotal role in assessing the risk of cancer recurrence in post-treatment patients, facilitating appropriate surveillance and preventive measures. Moreover, results inform individualized treatment plans, allowing healthcare providers to tailor therapies to each patient's needs.
Documenting CEA test results in a patient's medical records provides a comprehensive health status history, particularly crucial for oncologists and specialists tracking cancer history for informed decision-making. CEA test results foster communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, ensuring a coordinated approach to patient care. Lastly, these results contribute to research and clinical trials, advancing our understanding of cancer diagnosis and treatment while potentially leading to improved therapies and diagnostic tools.
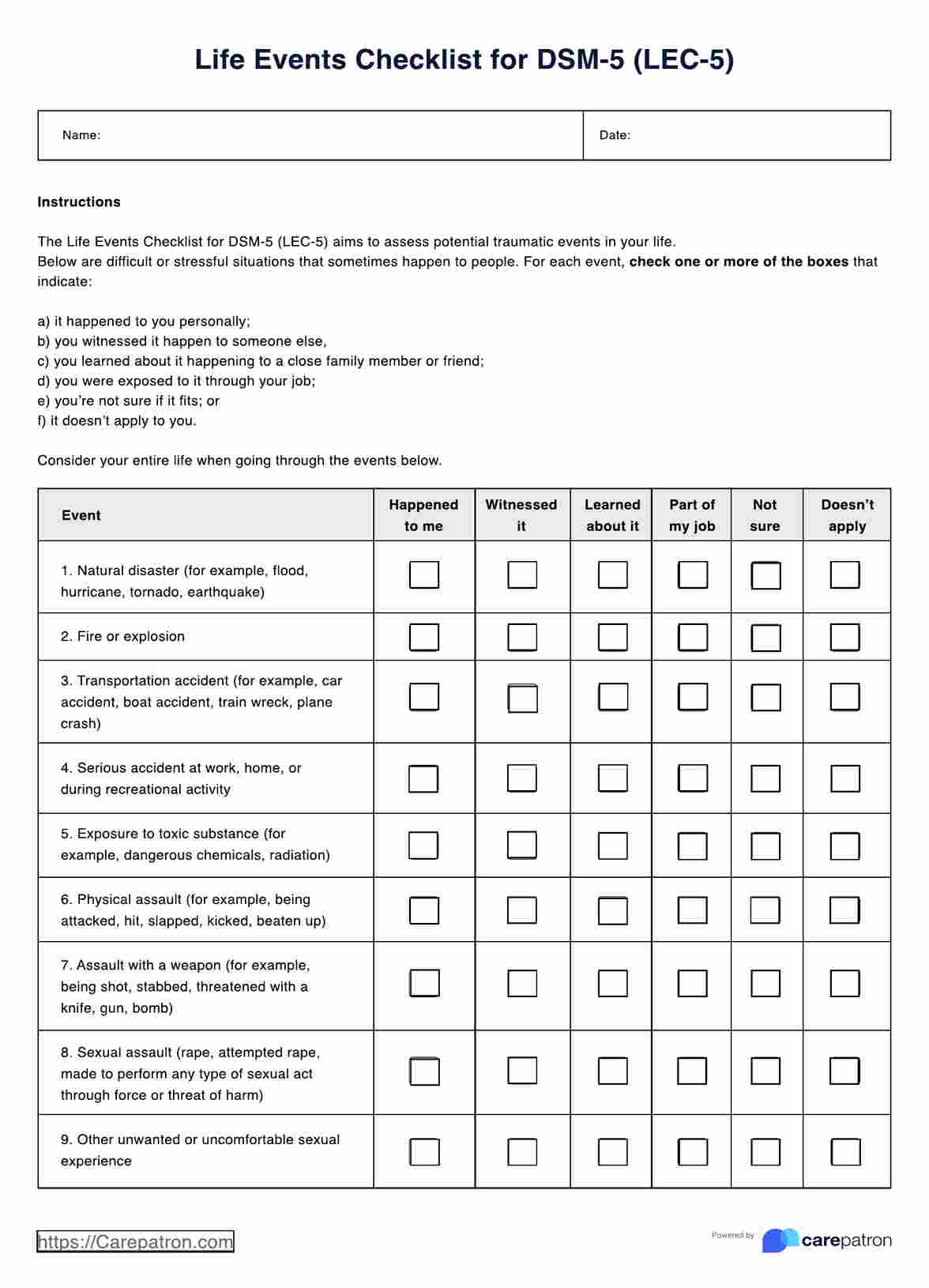
CEA Blood Test Template
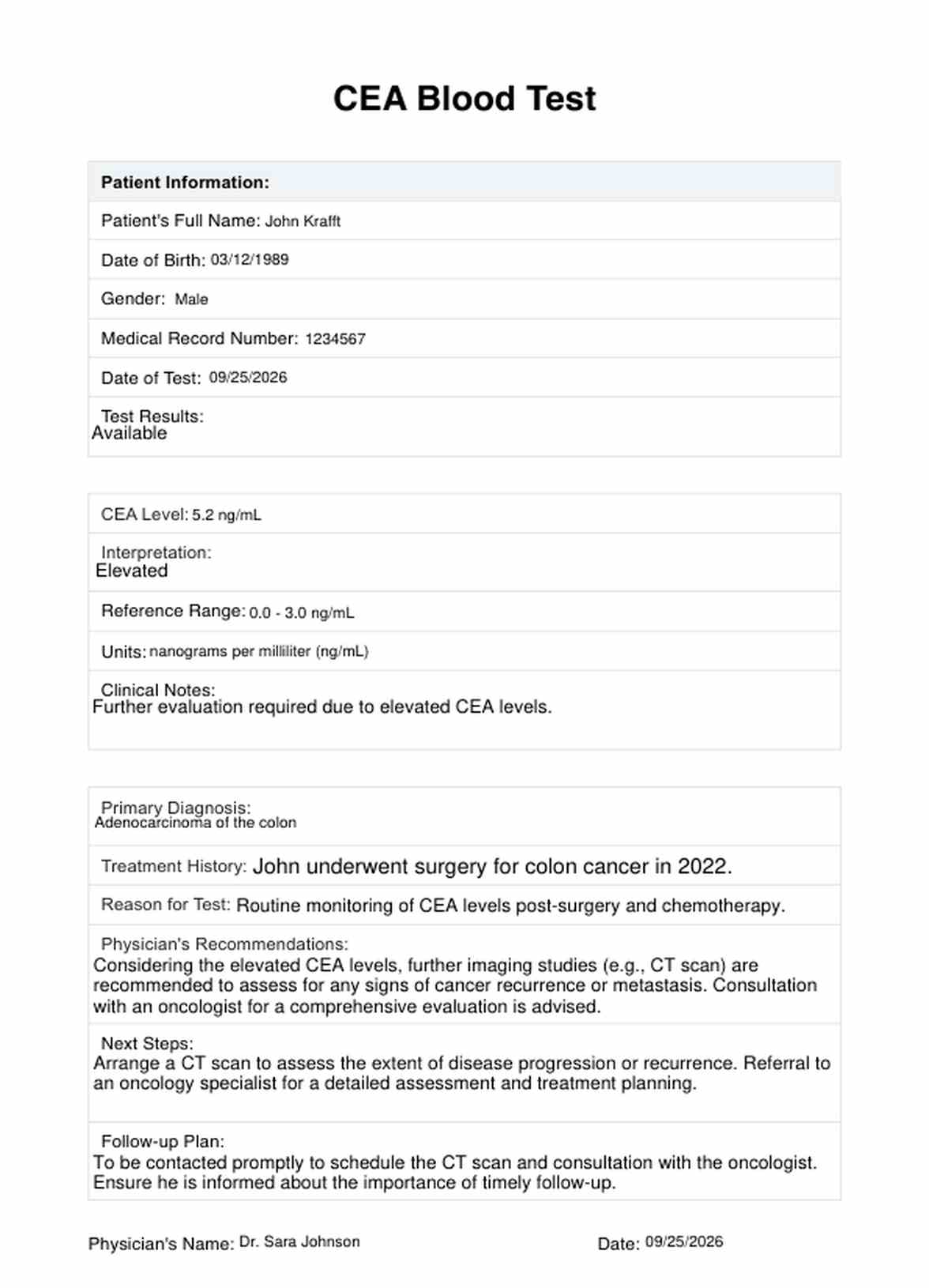
CEA Blood Test Example
How Does It Work?
Documenting medical information accurately and comprehensively is fundamental to providing quality healthcare. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use this Printable CEA Blood Test:
Step 1: Gather Patient Information
Begin by collecting essential patient information, including their full name, date of birth, gender, and medical record number (MRN). Ensure the accuracy of this data.
Step 2: Record CEA Blood Test Results
Enter the results of the CEA Blood Test into the template. Include the numeric CEA level, its interpretation (elevated, average, etc.), the reference range, and the units used for measurement (e.g., ng/mL).
Step 3: Document Clinical Context
Provide relevant clinical context by noting the patient's primary diagnosis (e.g., colorectal cancer), a brief treatment history (if applicable), and the reason for conducting the CEA Blood Test.
Step 4: Physician's Recommendations
Detail the physician's recommendations based on the CEA test results. This could include the next steps in the patient's care, such as scheduling follow-up appointments or ordering additional tests or treatments.
Step 5: Sign and Date
Ensure the document is signed and dated by the healthcare provider responsible for reviewing the CEA Blood Test results and making recommendations. This signature adds accountability and authenticity to the record.
When Would You Use This Test?
The CEA Blood Test is used in various medical scenarios to detect, monitor, and manage cancer. It serves as a diagnostic tool to aid in identifying cancer, particularly in gastrointestinal or related malignancies, such as colorectal, lung, breast, and pancreatic cancer.
It helps assess the effectiveness of cancer treatments and monitor post-treatment patients for cancer recurrence. These tests also evaluate treatment response and may be used in select high-risk individuals as part of cancer screening programs.
CEA tests are also utilized in some clinical scenarios to assess treatment response and guide therapeutic decisions. For instance, in cases where a patient's CEA levels remain elevated despite treatment, healthcare providers may consider alternative therapies or further diagnostic tests to tailor the treatment plan more effectively.
It's important to note that while CEA tests provide valuable insights, they are typically interpreted alongside other clinical data and trials to make informed medical decisions. The precise application of the CEA blood test depends on an individual's medical history, symptoms, and the judgment of their healthcare provider.
What Do the Results Mean?
Here's what different CEA blood test results may generally indicate:
- Low CEA Level (Before Cancer Treatment): A low CEA level may suggest that the tumor is relatively small and has not spread extensively. However, certain cancers may not produce significant amounts of CEA, particularly certain types. In such cases, healthcare providers may rely on additional tests, including this free CEA Blood Test, to assess the extent of cancer involvement.
- High CEA Level (Before Cancer Treatment): An elevated CEA level may indicate a larger tumor or the potential spread of cancer to other body areas. However, further tests are typically necessary to confirm the severity and extent of cancer.
- Monitoring During or After Treatment: When CEA tests are used to monitor cancer during or after treatment, your healthcare provider will compare current results with past ones:
- Decreasing CEA Levels: A consistent decrease in CEA levels over time is generally a positive sign, suggesting that the treatment effectively controls or reduces the cancer.
- Increasing or Persistently High CEA Levels: Conversely, elevated levels may indicate that the treatment is not having the desired effect. For instance, in the context of colorectal cancer surgery, this may suggest that the entire tumor wasn't successfully removed or that the cancer is regrowing.
- Decreasing CEA Followed by Increases: This pattern may suggest that the cancer has returned after an initial positive response to treatment. It's crucial to investigate further in such cases.
Research & Evidence
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a serum biomarker initially discovered in colon cancer cells by Freedman and Gold. Over time, research has revealed its presence in various other epithelial cells across the body, including those in the stomach, tongue, esophagus, cervix, and prostate.
CEA is a non-specific marker, and its levels can become elevated in several malignancies, such as colorectal cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, breast cancer, mucinous ovarian cancer, and more.
As our understanding of CEA and its association with different cancers has deepened, its clinical significance and utility in cancer diagnosis and management have evolved, making it an increasingly valuable tool in modern oncology.
Reference
- Kankanala VL, Mukkamalla SKR. Carcinoembryonic Antigen. [Updated 2022 Jan 26; cited 2022 Dec 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan
Commonly asked questions
Healthcare providers, particularly oncologists and surgeons, typically request CEA Blood Tests.
CEA Blood Tests are used for cancer diagnosis, staging, treatment monitoring, and post-treatment surveillance.
A blood sample is collected, and CEA levels are measured in a laboratory.
The test is quick, usually taking a few minutes for blood collection, but the overall process may vary based on laboratory turnaround times.





















-template.jpg)