CBT for Psychosis Worksheets PDF
Click here for PDFs of CBT for psychosis worksheets you can incorporate into your patient's treatment plan to help them manage their symptoms better.


What is psychosis?
Psychosis is a mental health experience characterized by a detachment from reality. People with psychosis may experience hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren't there) and delusions (fixed, false beliefs). These experiences can be accompanied by trouble thinking, social withdrawal, and difficulty with daily tasks.
Psychosis can occur in various mental health conditions, including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. External factors like trauma, sleep and exercise deprivation, medical conditions, certain medications, and substance use can also trigger it.
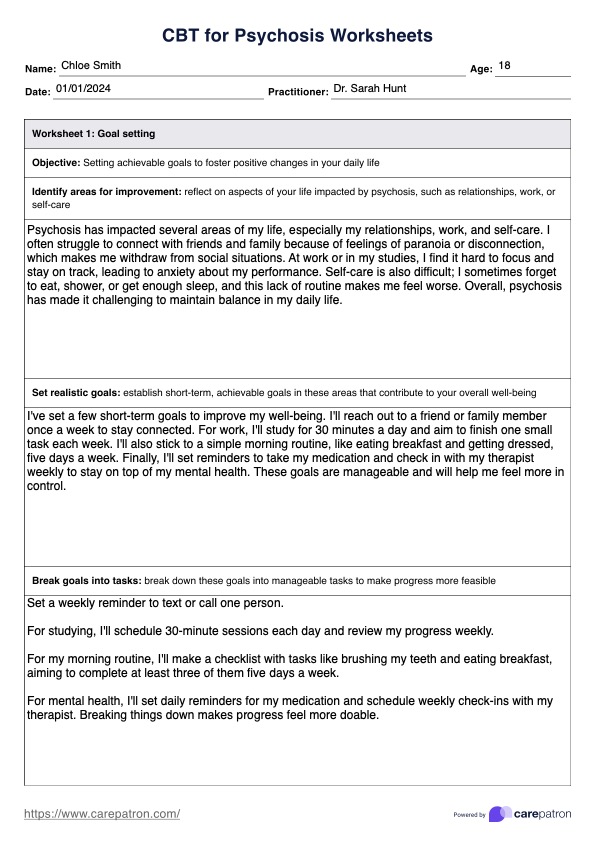
CBT for Psychosis Worksheets PDF Template
CBT for Psychosis Worksheets PDF Example
What are examples of psychotic symptoms?
Psychosis can cause a variety of symptoms that generally fall into two categories: positive and negative.
Positive symptoms
Positive symptoms are experiences that seem real to the person dealing with psychosis but aren't based on reality. They can be very distressing and disruptive.
- Delusions: These are false beliefs that someone holds onto even when presented with evidence to the contrary. Examples include believing someone is spying on them or that a celebrity is in love with them.
- Hallucinations: These are sensory experiences that seem real but aren't. They can involve hearing voices, seeing things that aren't there, or feeling sensations that don't exist.
- Disorganized speech: This speech is difficult to follow because it jumps from topic to topic or doesn't make sense. Someone with disorganized speech might repeat words or phrases or makeup words.
- Disorganized behavior: This can include acting out of character, being impulsive, or behaving in a way that seems odd or unusual.
Negative symptoms
Negative symptoms are a decrease in experiencing symptoms or in a person's normal abilities. They can make it difficult for someone to function in daily life.
- Social withdrawal: People with this symptom lose interest in spending time with others and may withdraw from friends and family.
- Loss of motivation: This can show up as a decline in school or work performance, a lack of interest in hobbies, or difficulty concentrating.
- Poor hygiene: Someone with this symptom may neglect their personal hygiene and stop caring for themselves.
- Catatonia: This is a rare but serious symptom that can cause someone to become motionless or unresponsive.
How is psychosis diagnosed?
Diagnosing psychosis involves a careful assessment and evaluation by a mental health professional. There is no single test, but mental health professionals and clinicians use a combination of approaches:
- Clinical interview: This is a conversation where the doctor asks about symptoms, medical history, drug and alcohol use, and medications.
- Medical tests: Blood tests can check for physical conditions or infections that might be contributing to psychosis. Drug tests can rule out substance-induced psychosis.
- Imaging scans: In some cases, brain scans may be used to look for abnormalities, but these are not routinely done and wouldn't be used to diagnose psychosis on their own.
Remembering that understanding the goal is to understand the whole picture and rule out other explanations for the symptoms is essential.
How can cognitive behavioural therapy help people with psychosis?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can be helpful for people with psychosis. CBT for psychosis (CBTp) is a more developed, specific kind of CBT designed to address the challenges and consequences of psychosis.
Here's how CBTp can help:
- Increase self-awareness: CBT helps people understand how their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are connected.
- Change unhelpful thinking patterns: CBT teaches people how to identify and challenge distorted thinking patterns that can worsen psychosis symptoms.
- Manage delusions and hallucinations: CBT provides strategies for healthily coping with delusions and hallucinations.
- Improve negative symptoms: CBT can also help improve negative symptoms of psychosis, such as social withdrawal and lack of motivation.
- Build coping skills: CBT teaches people skills for managing stress, identifying triggers, and maintaining healthy relationships.
CBT is a collaborative process that involves working with a therapist to develop and practice these skills. It's important to note that CBT is often used in conjunction with medication to achieve the best results. CBT can also be helpful for relapse prevention planning.
What are psychosis worksheets, and how can they help?
Psychosis worksheets are tools used in CBT to help you manage your psychosis. They provide a structured and supportive way to learn about your condition, identify triggers, develop coping skills, and track your progress.
Here's how psychosis worksheets can benefit you:
- Learn about psychosis: Worksheets can teach you about the symptoms, causes, and management. This knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions about your treatment.
- Identify your triggers: Worksheets can help you identify things that worsen your symptoms, like stress or lack of sleep. Once you know your triggers, you can learn to avoid them or healthily manage them.
- Develop coping skills: Worksheets can teach you specific strategies for coping with symptoms like hallucinations, delusions, and stress. These skills might include relaxation techniques, thought-challenging exercises, or problem-solving strategies.
- Track your progress: Worksheets can help you keep track of your symptoms over time. This can help you see how you're doing and identify areas for improvement.
- Set goals: Some worksheets can help you set personal goals for recovery. This can give you a sense of purpose and motivation to stick with your treatment plan.
- Improve social connections: Some worksheets offer strategies to improve social skills and rebuild connections.
Remember, psychosis worksheets are most effective when used with therapy. A therapist can help you choose the proper worksheets and teach you how to use them with therapists most effectively.
Other treatment options for psychosis
In addition to CBT and medication, several other treatments can be helpful for people with psychosis. The best treatment plan will vary depending on the individual's needs. Here are some alternatives:
- Inpatient treatment: If someone is a danger to themselves or others, they may need to stay in a hospital for a short time until their symptoms are under control.
- Medication: Medications called antipsychotics are the primary treatment for psychosis. Other medications like antidepressants, anti-anxiety meds, or anti-seizure meds may also be used. In some cases, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be an option.
- Psychotherapy: This type of therapy can help people understand their psychosis, develop coping skills, and manage their symptoms. There are many different types of psychotherapy, including family therapy and substance abuse counseling.
- Arts therapies: Art, music, and other creative activities can be used to help people with psychosis express themselves and cope with their symptoms.
- Family intervention: This type of therapy helps family members understand psychosis and learn how to support their loved one.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have psychosis can be a great source of support and encouragement. Support groups can help people feel less alone and learn from each other's experiences.
Remember, with proper treatment and support, many people with psychosis disorders can live fulfilling and productive lives.
Commonly asked questions
Yes, it is, since it can be a symptom of schizophrenia.
The recommended number of sessions of CBT for psychosis is at least 16 over six months.
You can either print the worksheets and have your client answer them with a pen or send them a copy and have them answer it digitally on any PDF editing software.

















-template.jpg)