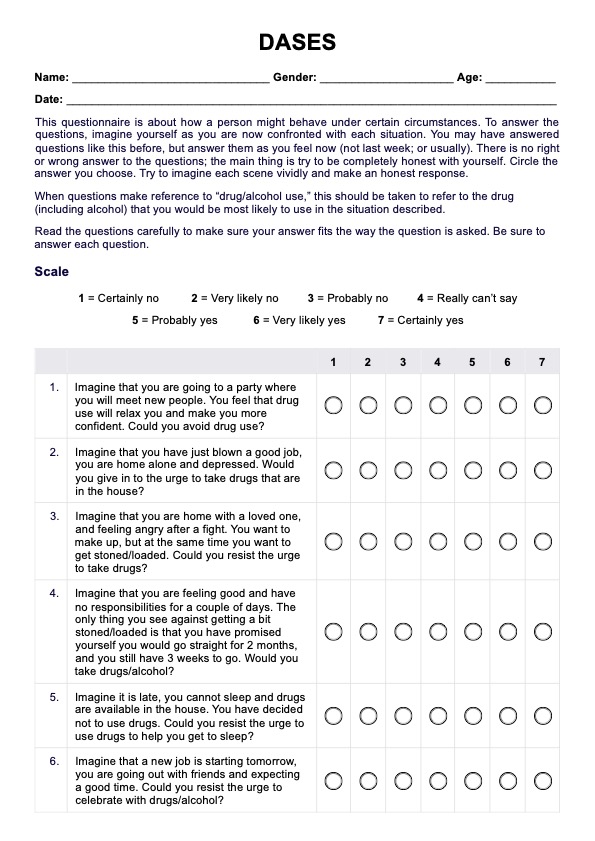
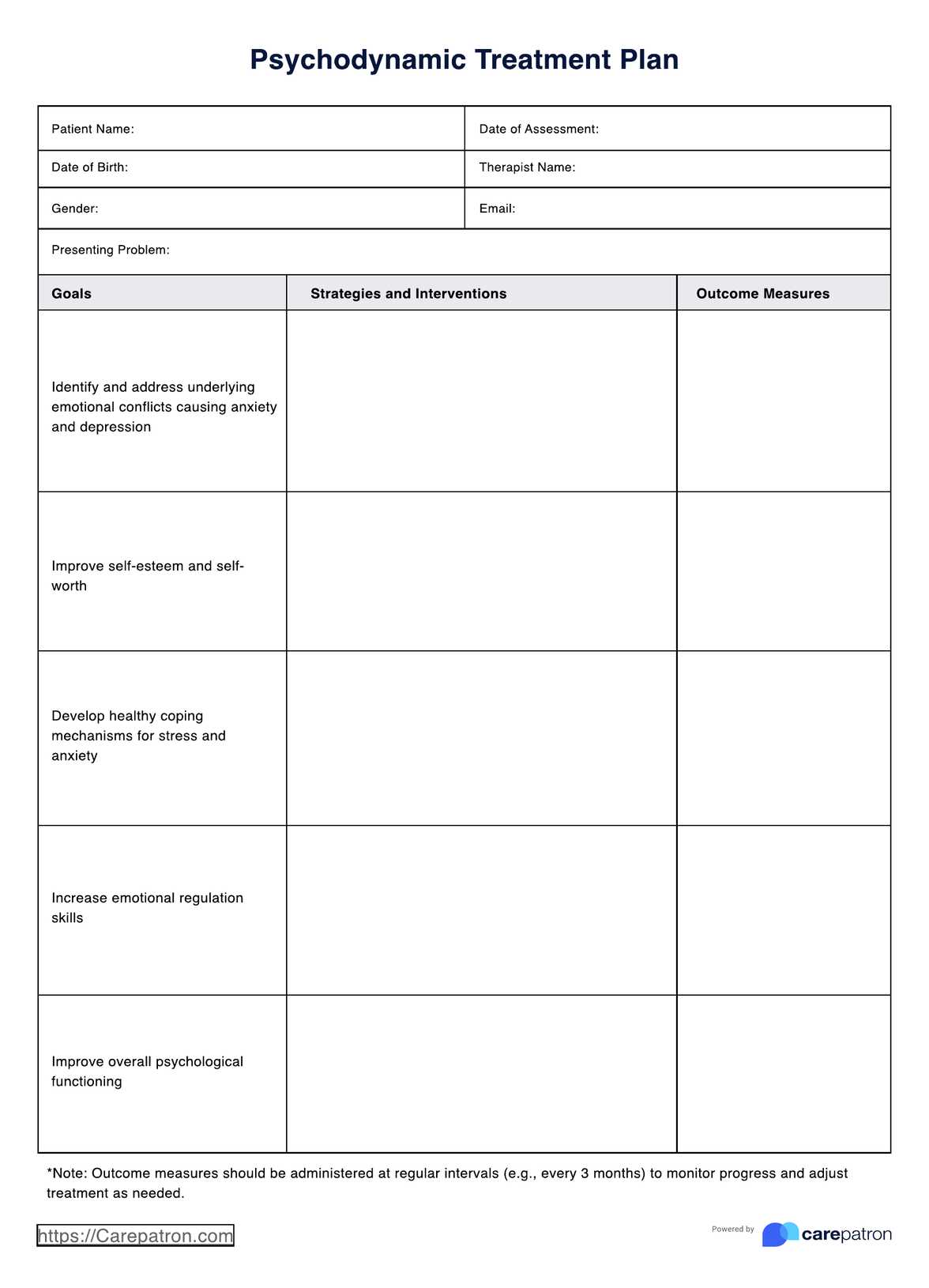
Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES)
Use the Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES) to evaluate readiness for change and customize interventions accordingly.


What is alcohol and substance addiction?
Addiction, often referred to as a substance use disorder, is a chronic and complex condition characterized by the compulsive use of alcohol or substances despite negative consequences. It affects not only the physical health of individuals but also their psychological well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. The link between genetics, brain chemistry, and environmental factors contributes to the development of addiction.
Alcohol addiction, specifically alcoholism, involves an uncontrollable urge to consume alcohol, leading to tolerance (needing more substance to achieve the same effects) and withdrawal symptoms when trying to quit. This form of addiction can result in serious health issues such as liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and cognitive impairment.
Substance addiction encompasses a range of illicit drugs, prescription medications, and other substances. It is characterized by losing control over usage, preoccupation with obtaining and using the substance, and continued use despite negative consequences. Opioids, stimulants, sedatives, and hallucinogens are among the substances that can lead to addiction. The opioid crisis, for instance, has highlighted the devastating impact of opioid addiction on individuals, families, and communities.
affects physical health and has profound psychological and social implications. It can lead to strained relationships, loss of employment, financial difficulties, and legal problems. Moreover, the brain's reward system becomes altered with prolonged substance abuse, making it exceedingly difficult for individuals to quit without proper intervention and support.
A comprehensive approach is necessary to address addiction effectively, involving medical treatment, therapy, counseling, and support groups. Electronic health records (EHRs) facilitate communication between healthcare providers and ensure accurate and up-to-date patient information. EHRs improve care coordination, enable early intervention, and help tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES) Template
Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES) Example
How to use the Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES)
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use this scale effectively:
Introduction to SOCRATES
Introduce the SOCRATES as a self-report questionnaire that measures individuals' perceptions of their motivation and readiness for change about substance use.
Selection of Appropriate Version
Choose the appropriate version of the SOCRATES based on the specific substance or behavior you're addressing. Different versions are available for alcohol, drugs, or other behaviors.
Administration
Administer the scale to the individual by providing clear instructions on completing it. The scale typically consists of a series of statements to which the individual responds on a scale, often ranging from 1 (Strongly Disagree) to 5 (Strongly Agree).
Scoring and Interpretation
Calculate the scores for each subscale (Recognition, Ambivalence, Taking Steps) by summing the individual item scores within each subscale. Higher scores on each subscale indicate greater readiness for change in that area.
Recognition
This subscale assesses the individual's recognition of the need to change their behavior. Higher scores suggest that the person acknowledges the negative consequences of their behavior.
Ambivalence
The Ambivalence subscale gauges the individual's mixed feelings about changing their behavior. Higher scores indicate a stronger internal struggle between the desire and resistance to change.
Taking Steps
This subscale measures the individual's belief in their ability to take steps toward change. Higher scores suggest greater self-efficacy and confidence in making positive changes.
Individualized Intervention
Use the scores to tailor interventions according to the individual's readiness level. Those with high recognition and taking steps scores may benefit from more action-oriented interventions, while individuals with high ambivalence scores may require more motivational enhancement techniques.
Monitoring Progress
Re-administer the SOCRATES periodically to track changes in motivation and readiness. Comparing scores over time can help gauge the effectiveness of interventions and adjustments in the treatment plan.
When would you use this Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES)?
Here are some key situations and contexts where the use of SOCRATES is particularly beneficial:
- Initial Assessment: During the initial assessment phase, healthcare professionals can administer the SOCRATES questionnaire to understand the individual's current mindset regarding substance use. This helps tailor the treatment plan to the individual's specific needs and level of motivation.
- Treatment Planning: As healthcare professionals work with individuals to create a treatment plan, the SOCRATES scale can guide decisions about the most appropriate interventions. It aids in identifying areas where the person is more open to change and where resistance might be present.
- Progress Monitoring: Periodic reassessment using SOCRATES allows healthcare providers to track individual motivation and readiness changes over time. This helps them adjust the treatment plan accordingly and celebrate progress.
- Intervention Tailoring: Based on SOCRATES scores, healthcare professionals can adapt their approach to match the individual's stage of change. Those with high recognition scores benefit from education and action-oriented interventions, while those with high ambivalence scores require more motivational enhancement techniques.
- Transition Points: SOCRATES can be useful when individuals transition from one phase of treatment to another, such as from detoxification to rehabilitation or inpatient to outpatient care. It informs the treatment team about the person's evolving readiness for treatment.
- Group Therapy and Counseling: Therapists and counselors in group settings can utilize SOCRATES to facilitate discussions about readiness for change among participants. It fosters peer support and shared insights.
- Collaborative Care: SOCRATES can be shared among healthcare professionals involved in an individual's care, ensuring a holistic approach and consistent communication.
- Behavioral Health Research: Researchers can use SOCRATES to assess readiness for change in various populations, contributing to advancing addiction treatment strategies.
What are the benefits of using this Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES)?
The Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale (SOCRATES) is a widely recognized tool in addiction treatment, offering valuable insights into an individual's readiness for change. Its benefits are numerous and impactful:
Personalized Treatment Planning
By assessing an individual's motivation and readiness for change, healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that align with the person's stage of change. This tailored approach enhances treatment effectiveness and increases the likelihood of positive outcomes.
Targeted Interventions
SOCRATES provides specific information about an individual's ambivalence, recognition of the need for change, and confidence in making changes. This data guides healthcare providers in selecting interventions that address the person's unique challenges and strengths.
Measurement of Progress
Regularly administering SOCRATES allows for the measurement of progress over time. This helps healthcare professionals track changes in motivation and tailor interventions accordingly. Research studies have shown that tracking motivation using tools like SOCRATES can predict treatment success.
Facilitation of Communication
SOCRATES facilitates open and honest communication between healthcare professionals and individuals seeking treatment. It encourages self-reflection and discussions about motivation, fostering a collaborative approach to recovery.
Enhanced Research and Evaluation
Researchers benefit from the structured nature of SOCRATES, which allows for standardized data collection. This enables the accumulation of evidence-based insights into motivation and treatment readiness, contributing to the advancement of addiction research.
Holistic Care and Team Collaboration
The use of SOCRATES supports interdisciplinary collaboration in addiction treatment. Healthcare professionals from various disciplines can share and interpret SOCRATES scores, enabling a holistic approach to care.
Commonly asked questions
Completing the SOCRATES questionnaire usually takes around 10-15 minutes. It consists of statements to which you respond based on your feelings and perceptions.
The SOCRATES questionnaire yields scores in three subscales: Recognition, Ambivalence, and Taking Steps. Higher scores in each subscale indicate greater readiness for change in that specific area. The recognition acknowledges the need for change, Ambivalence gauges mixed feelings, and Taking Steps measures confidence in making changes.
SOCRATES is used in various stages of addiction treatment and counseling. It is administered during initial assessments, treatment planning, progress monitoring, and transition points in treatment to assess an individual's readiness for change.
The SOCRATES scale is primarily used by healthcare professionals, including psychologists, counselors, doctors, nurses, and therapists. It aids in understanding an individual's motivation and tailoring interventions accordingly to support positive behavioral changes.


















-template.jpg)