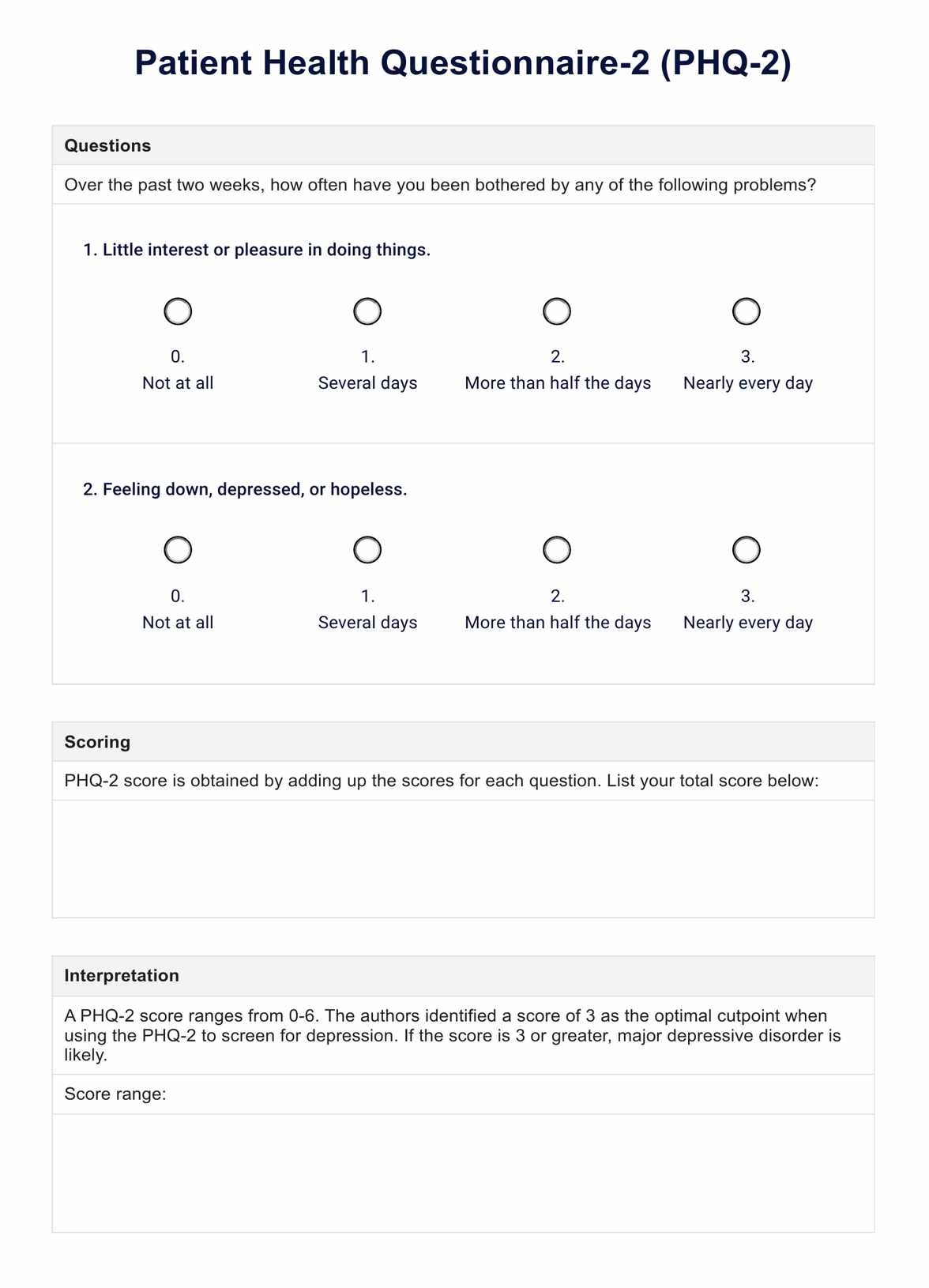
The search results do not specify a recommended frequency for administering the PHQ-2 screening tool. However, the PHQ-2 is often used as an initial screening step, followed by the more comprehensive PHQ-9 for those who screen positive on the PHQ-2 when diagnosing depression.
PHQ 2
Get a quick depression screening with PHQ-2. Compare it with PHQ-9, track symptoms, and streamline care. Administer regularly in primary care.
PHQ 2 Template
Commonly asked questions
The PHQ-2 has been found to be good at detecting depression compared to diagnostic interviews. However, depending on the cutoff used, the PHQ-2 alone may result in lower sensitivity and specificity than the PHQ-9.
The PHQ-2 is a brief 2-item screening tool that assesses the frequency of depressed mood and anhedonia over the past two weeks. In contrast, the PHQ-9 is a more comprehensive 9-item depression severity measure that aligns with DSM-5 criteria for major depressive disorder. Using the PHQ-2 first, followed by the PHQ-9 for those who screen positive, can efficiently identify individuals at risk for depression while minimizing the number who need to complete the full PHQ-9.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











