Personal Psychology Test
Explore your psyche with personal psychology tests, revealing key insights into your personality, emotions, and behaviors.


What are Personal Psychology Tests?
Personality tests are tools used in psychological research to assess personality and describe individual differences in personality traits, characteristics, and behavioral patterns. These assessments aim to evaluate an individual's personality across various dimensions, such as the widely recognized Big Five personality traits: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and emotional stability. Some popular personality tests, like the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), employ a typology approach, categorizing individuals into specific personality types based on preferences in how they perceive and interact with the world. The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) is another widely used tool in clinical psychology, focusing on detecting psychopathology and personality disorders.
Projective tests, like the Rorschach inkblot test, delve into the individual's unconscious, revealing aspects of their personality through their interpretations of ambiguous stimuli. The Enneagram, a personality typing system, explores how individuals express and experience emotions, revealing insights into the factors behind their emotional responses and interpersonal dynamics.
Personality assessments play a crucial role in career development and team dynamics in professional settings. For instance, organizational psychology often uses the Big Five traits to predict success in various career paths. Emotional intelligence assessments, focusing on factors in an individual's ability to understand and manage their emotions, contribute to positive outcomes in both personal and professional life.
Personal Psychology Test Template
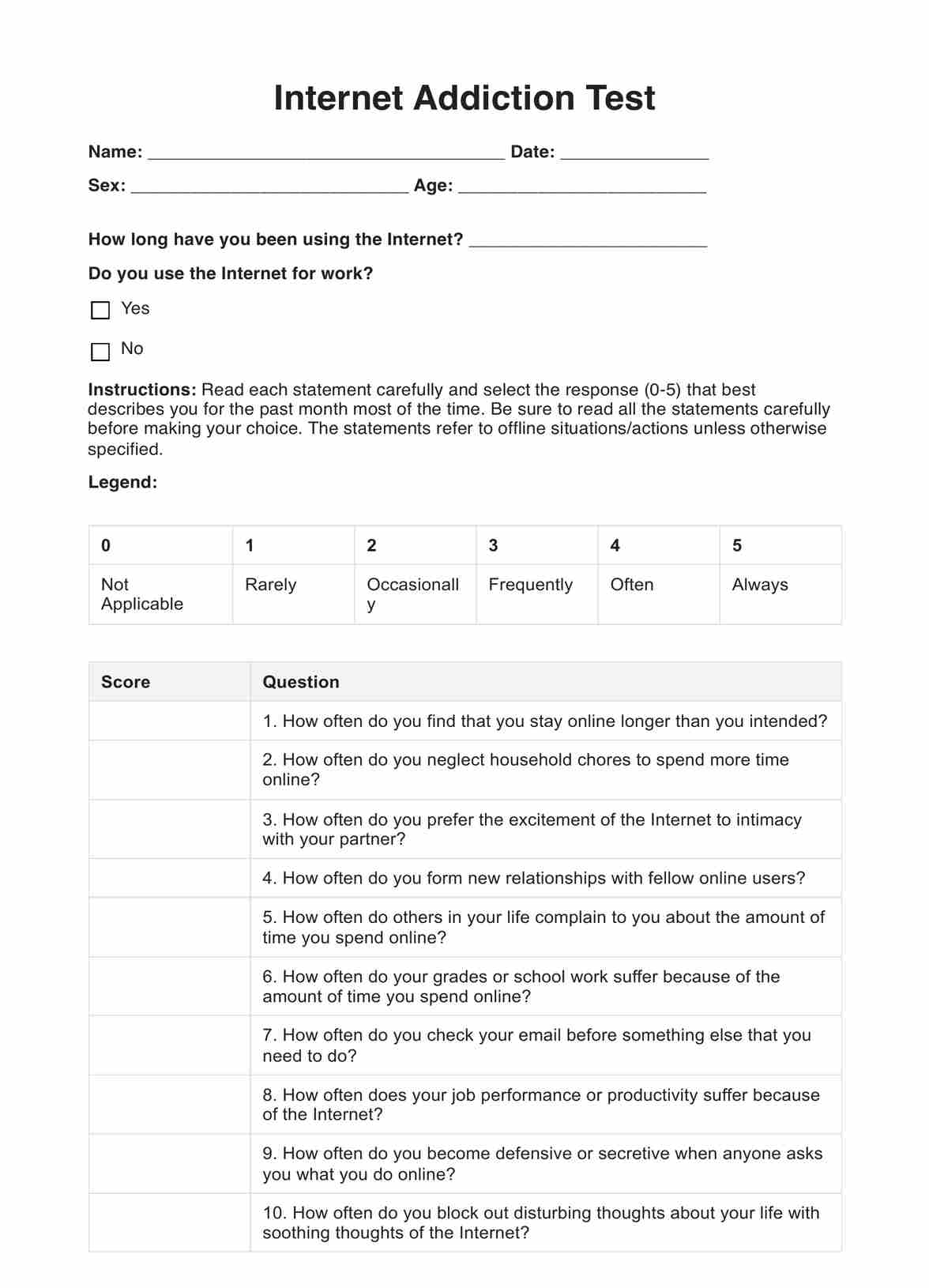
Personal Psychology Test Example
Different personality types
Personality types categorize individuals based on their thinking, feeling, and behaving patterns. Several prominent personality typing systems aim to capture the diversity of human personalities. Here are a few well-known frameworks:
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
This system identifies 16 personality types based on four dichotomies: extraversion vs. introversion, sensing vs. intuition, thinking vs. feeling, and judging vs. perceiving. For example, an individual might be categorized as an INFJ (Introverted, Intuitive, Feeling, Judging).
Big Five Personality Traits
Also known as the Five-Factor Model, this system measures five broad dimensions of human personality:
- Openness to experience
- Conscientiousness
- Extraversion
- Agreeableness
- Emotional stability (or Neuroticism)
Enneagram
This system identifies nine interconnected personality types, each associated with specific motivations, fears, and core beliefs. Individuals are categorized by their dominant types, such as the Perfectionist, Helper, Achiever, or Investigator.
DISC assessment
This model classifies individuals into four primary personality traits: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Conscientiousness. It is often used in organizational settings to enhance communication and teamwork.
Holland Code (RIASEC)
Primarily used in career counseling, this model categorizes individuals into six personality types based on their preferences for different work environments and tasks: Realistic, Investigative, Artistic, Social, Enterprising, and Conventional.
History of personality tests
The history of personality tests and questionnaires dates back to the early 20th century, marked by the emergence of pioneering psychological theories and the desire to understand and measure individual differences in various personality characteristics. One of the earliest attempts to categorize personality traits was by psychologist Gordon Allport in the 1930s, who identified thousands of traits and categorized them into three levels: cardinal, central, and secondary.
The projective test techniques, such as the Rorschach inkblot test and the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), gained popularity in the mid-20th century. Hermann Rorschach developed the inkblot test in 1921, involving participants interpreting ambiguous images and revealing unconscious thoughts and feelings. The TAT, created by Henry Murray and Christiana Morgan, presents individuals with ambiguous pictures to stimulate the creation of stories, providing insights into their personality dynamics.
The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI), introduced in 1943 by Starke Hathaway and John Charnley, marked a significant development. It aimed to assess psychopathology and mental health by measuring various personality traits and psychopathological symptoms. The MMPI became widely used in clinical and forensic settings.
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), a personality theory developed by Isabel Briggs Myers and Katharine Cook Briggs based on Carl Jung's theories, emerged in the 1940s. This personality test categorizes individuals into 16 personality types based on preferences related to extraversion/introversion, sensing/intuition, thinking/feeling, and judging/perceiving.
In the 1980s, the Five-Factor Model (Big Five) gained prominence, emphasizing five major personality traits: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and emotional stability. This model has become a dominant framework in contemporary personality psychology.
As technology advanced, online personality tests and assessments became more accessible, contributing to the widespread use of personality testing in various contexts, from career counseling to personal development. Despite ongoing debates about their validity and reliability, personality tests are valuable tools for understanding human behavior and enhancing self-awareness.
How does this Personal Psychology Test work?
Personal psychology tests employ various methodologies to assess and analyze different aspects of an individual's personality. These assessments provide insights into an individual's behavioral tendencies, emotional responses, and interpersonal characteristics. One common approach involves self-report measures, where individuals respond to questions designed to reveal their behavior, preferences, traits, and emotional states.
These tests often align with established psychological models, such as the Big Five Personality Traits, which include openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and emotional stability. Another example of a popular test is the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), which categorizes individuals into personality types based on preferences like introversion vs. extraversion and thinking vs. feeling.
Some tests, like projective assessments, use ambiguous stimuli to elicit responses that may uncover hidden aspects of a person's personality. The results of these tests can be instrumental in clinical psychology, career counseling, and other personal development articles, providing valuable insights for individuals and professionals to make informed decisions in various aspects of life.
The benefits of knowing your personality type
- Self-awareness: Understanding your personality type provides insights into your preferences, strengths, and areas for growth. This self-awareness is a foundation for personal development and can help you make informed decisions about various aspects of your life.
- Effective communication: Personality typing systems like the MBTI or DISC often highlight communication styles. Recognizing your own and others' communication preferences can improve interpersonal relationships, both personally and professionally.
- Career alignment: Many personality assessments, like the Holland Code, are used in career counseling. Knowing your personality type can guide you toward careers that align with your strengths and interests, increasing job satisfaction and success.
- Team dynamics: In a team or group setting, understanding the diversity of personality types contributes to effective collaboration. It allows team members to appreciate each other's strengths, mitigate conflicts, and work together more cohesively.
- Stress management: Some personality typing systems, including the Enneagram, show how individuals respond to stress. This awareness can empower you to develop healthy coping mechanisms and navigate challenges more effectively.
- Relationship insights: Whether in friendships, family dynamics, or romantic relationships, knowledge of personality types can enhance understanding. It helps individuals appreciate differences, fostering healthier and more empathetic connections.
- Goal setting: Personality assessments often provide insights into goal-setting strategies. For instance, individuals with a high conscientiousness score might benefit from detailed plans, while those with a high openness score may prefer more flexible and creative approaches.
Commonly asked questions
A personal psychology test is an assessment tool designed to measure various aspects of an individual's personality, behaviors, and emotional responses.
Personal psychology tests typically use standardized questions or scenarios to evaluate specific traits, behaviors, or emotional patterns, providing insights into an individual's psychological makeup.
Knowing your personality type can enhance self-awareness, improve interpersonal relationships, guide career choices, and offer valuable insights into personal strengths and areas for growth.





















-template.jpg)