Narcissism Test
See our Narcissism Test template, designed for mental health professionals to assess narcissistic traits and guide patients toward self-awareness and growth.


What is narcissism?
Narcissism is a personality trait characterized by an inflated sense of self-importance, a deep need for excessive attention and admiration, and a lack of empathy for other people's feelings. In its extreme form, narcissism can manifest as Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD), a mental disorder that significantly impacts an individual's relationships and overall functioning (Grapsas et al, 2020).
The concept of narcissism has its roots in Greek mythology, where a young man named Narcissus fell in love with his own reflection. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the term began to be used in psychology to describe self-centeredness and self-admiration. Research on narcissism has evolved over the years, with the introduction of various theories and assessment tools, including the Narcissistic Personality Inventory (NPI), which measures narcissistic traits on a continuum.
Narcissism is considered one of the dark triad personality traits, along with Machiavellianism and psychopathy, which are associated with a lack of morality, empathy, and a tendency to manipulate others for personal gain. While everyone may exhibit narcissistic traits to some degree, individuals with NPD have a grandiose sense of self that permeates their thoughts and behaviors, often leading to dysfunctional relationships and difficulties in various areas of life (Holtzman et al., 2010).
Narcissism Test Template
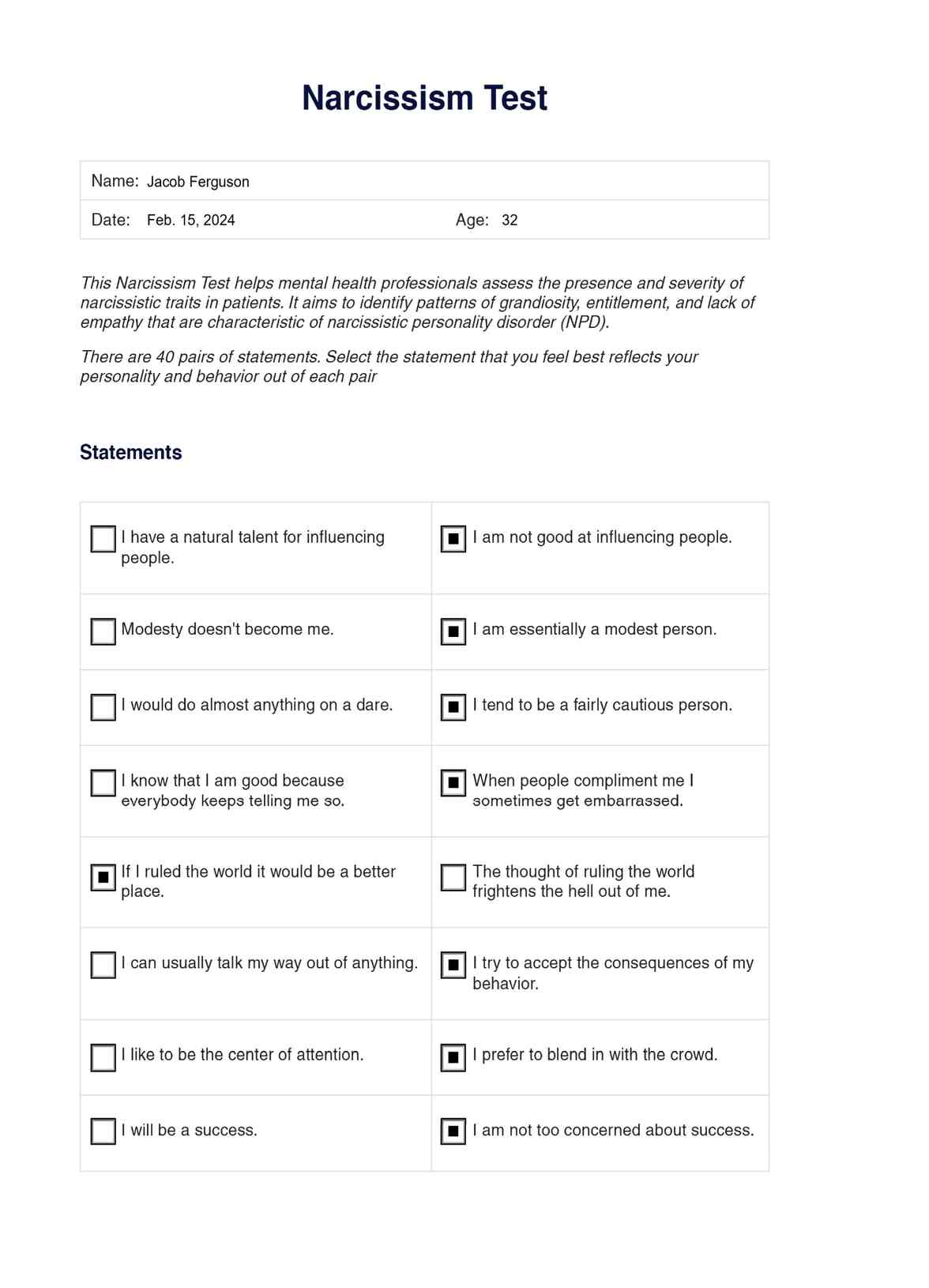
Narcissism Test Example
Common narcissistic personality traits
Narcissistic personality traits can vary in intensity and manifestation, but there are several common characteristics that are often observed in individuals with narcissistic tendencies. Here's a list of some of these traits:
- Grandiosity: An exaggerated sense of self-importance and superiority over others.
- Need for admiration: A constant craving for attention, validation, and praise.
- Sense of entitlement: Believing that one deserves special treatment and that rules or norms do not apply to them.
- Exploitative behavior: Taking advantage of others to achieve personal goals without regard for their feelings or well-being.
- Lack of empathy: Difficulty or unwillingness to recognize and consider other people's emotions and needs.
- Envy and jealousy: Feeling envious of others' success or possessions, or believing that others are envious of them.
- Arrogance and haughtiness: Displaying snobbish, disdainful, or patronizing attitudes toward others.
- Fantasies of success and power: Preoccupation with fantasies of unlimited success, power, brilliance, beauty, or ideal love.
- Fragile self-esteem: Despite the outward appearance of confidence, having a fragile sense of self-worth that is easily threatened by criticism or failure.
It's important to note that having some of these traits does not necessarily mean that an individual has Narcissistic Personality Disorder. NPD is diagnosed when these traits are pervasive and persistent and significantly impair an individual's functioning and relationships.
What problems can narcissism cause?
Narcissism, especially when it reaches the level of narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), can lead to a variety of problems in an individual's personal and professional life. Here are some of the common consequences:
Conflict in interpersonal relationships
Narcissists often struggle to maintain healthy relationships due to their lack of empathy, tendency to manipulate, and need for constant admiration. Relationships with narcissists tend to go through the narcissstic abuse cycle. This can lead to conflicts, broken friendships, and strained family dynamics.
Problems in the workplace
In the workplace, narcissistic traits can result in difficulties with teamwork, conflicts with colleagues, and challenges with authority figures. While some narcissists may achieve superficial success, their arrogance and entitlement can ultimately hinder long-term career growth.
Poor mental health
Narcissism is often associated with underlying mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse. The constant pursuit of validation and fear of criticism can lead to emotional instability and stress.
Low self-esteem
Despite their outward appearance of confidence, narcissists often have fragile self-esteem. They may rely heavily on external validation to feel good about themselves, leading to a cycle of seeking admiration and feeling empty when it's not forthcoming.
Stunted emotional growth
A lack of empathy can prevent narcissists from forming deep, meaningful connections with others. This can result in isolation and hinder personal growth and emotional maturity.
Understanding the potential problems caused by narcissism is crucial for mental health professionals when assessing and treating individuals with narcissistic traits or NPD.
How do mental health professionals diagnose narcissistic personality disorder?
Mental health professionals diagnose Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) based on criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). The diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
- Clinical interview: A mental health professional conducts a detailed interview to gather information about the individual's symptoms, behaviors, and personal history.
- Assessment of criteria: The professional assesses whether the individual meets the specific criteria for NPD as defined in the DSM-5. These criteria include a pervasive pattern of grandiosity, need for admiration, and lack of empathy, with at least five specific narcissistic traits present.
- Differential diagnosis: The clinician must rule out other mental disorders that may have similar symptoms, such as borderline personality disorder or antisocial personality disorder.
- Personality tests: In some cases, standardized personality tests or questionnaires, such as the Narcissistic Personality Inventory (NPI), may be used to assess narcissistic traits and behaviors.
- Evaluation of impact: The professional evaluates the extent to which the narcissistic traits impact the individual's functioning in various areas of life, including work, relationships, and overall well-being.
It's important to note that a diagnosis of NPD should only be made by a qualified mental health professional after a thorough evaluation. Treatment typically involves psychotherapy, with the goal of helping the individual develop healthier self-esteem and more empathetic relationships.
How does our Narcissism Test work?
Our Narcissism Test is modeled on the Narcissistic Personality Inventory (NPI-40), a widely used tool developed by Raskin and Terry in 1988 for assessing narcissistic traits. It's designed to help mental health professionals and their patients gauge the presence and severity of narcissistic characteristics. Here's how it works:
Step 1: Access the template
First, access the Narcissism Test template through the Carepatron app. This ensures that mental health professionals have a standardized and accessible tool for evaluating narcissistic traits.
Step 2: Explain the template
Explain the purpose and format of the test to the patient. Clarify that the test consists of 40 pairs of statements, and they should choose the statement in each pair that best reflects their personality and behavior.
Step 3: Monitor completion and assess honesty
As the patient completes the test, the mental health professional should observe their responses and demeanor. It's important to remember that patients may not always be honest or self-aware when answering. If inconsistencies or signs of dishonesty are noticed, this should be considered and addressed in the overall evaluation process.
Step 4: Score the test
Each choice corresponding to a narcissistic trait is tallied to obtain a total score. A higher score in the first column indicates a greater presence of narcissistic traits.
Step 5: Discuss the results
Review the results with the patient, discussing areas where narcissistic traits are prominent and exploring how these traits impact their daily life and relationships.
Step 6: Reflect and plan
Based on the test results, engage in a reflective conversation with the patient about their narcissistic tendencies. Develop a plan for addressing these traits through therapy or other interventions.
By following these steps, mental health professionals can effectively use the Narcissism Test to assess narcissistic traits and guide their patients toward greater self-awareness and personal growth.
What are the benefits of taking a Narcissism Test?
Taking a Narcissism Test can offer several advantages for both patients and mental health professionals:
- Increased self-awareness: The test helps individuals identify and understand their narcissistic traits, providing insights into their behavior and personality.
- Informed diagnosis: For mental health professionals, the test serves as a valuable tool in the diagnostic process, contributing to a more accurate assessment of narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) or other related conditions.
- Guided treatment planning: By identifying specific narcissistic traits, therapists can tailor their treatment approach to address the patient's unique needs and challenges.
- Improved interpersonal relationships: Understanding one's narcissistic tendencies can lead to better communication and empathy in relationships, reducing conflicts and fostering healthier connections.
- Personal growth: Recognizing and addressing narcissistic traits can facilitate personal growth, self-improvement, and a more balanced sense of self-esteem.
Overall, the Narcissism Test provides a structured way to explore and address narcissistic characteristics, leading to enhanced mental health and well-being.
How is narcissistic personality disorder treated?
Treating narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) can be challenging, but various strategies can help manage symptoms and improve functioning. Here are some common approaches:
Psychotherapy
Individual therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychodynamic therapy, is often the primary treatment for NPD. Therapy focuses on helping individuals understand the root causes of their narcissism, develop healthier self-esteem, and learn empathy and more adaptive coping mechanisms.
Group therapy
Participating in group therapy can provide individuals with NPD opportunities to practice social skills and empathy and learn from others' experiences.
Medication
While there are no specific medications for NPD, medications such as antidepressants or mood stabilizers may be prescribed to address co-occurring symptoms like depression or anxiety.
Self-help strategies
Encouraging patients to engage in activities that promote self-reflection, mindfulness, and stress reduction can be beneficial in managing narcissistic traits.
Family therapy
Involving family members in the treatment process can help improve communication and relationships within the family, providing support for both the individual with NPD and their loved ones.
It's important to note that progress in treating NPD can be slow and requires a long-term commitment. A strong therapeutic alliance and consistent, supportive care are crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
References
Grapsas, S., Brummelman, E., Back, M. D., & Denissen, J. J. A. (2019). The “why” and “how” of narcissism: A process model of narcissistic status pursuit. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 15(1), 174569161987335. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691619873350
Holtzman, N. S., Vazire, S., & Mehl, M. R. (2010). Sounds like a narcissist: Behavioral manifestations of narcissism in everyday life. Journal of Research in Personality, 44(4), 478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2010.06.001
Raskin, R., & Terry, H. (1988). A principal-components analysis of the Narcissistic Personality Inventory and further evidence of its construct validity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(5), 890–902. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.5.890
Commonly asked questions
If you consistently exhibit traits such as an inflated sense of self-importance, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others, you may have narcissistic tendencies.
Five main symptoms of narcissism include grandiosity, a constant need for admiration, a sense of entitlement, exploitative behavior, and a lack of empathy.
Good questions to ask a narcissist might include: "How do you feel when others receive attention?" or "Can you describe a time when you empathized with someone else's feelings?"




















-template.jpg)