Level of Consciousness Assessment
Enhance patient care in neurology with this guide for medical practitioners on conducting a Level of Consciousness Assessment.


Introduction to levels of consciousness
Understanding and assessing the level of consciousness is fundamental for medical practitioners in neurology. This aspect of patient evaluation provides critical insights into the functioning of the central nervous system.
The level of consciousness reflects the patient's overall neurological status, encompassing their responsiveness, orientation, and cognitive functioning. This guide aims to equip medical practitioners with a comprehensive approach to conducting an effective neurological assessment, ensuring a thorough understanding of a patient's neurological condition.
Level of Consciousness Assessment Template
Level of Consciousness Assessment Example
The importance of documenting the level of consciousness
Accurate documentation of the level of consciousness holds significant implications for patient care in neurology. It serves as a cornerstone for making informed clinical decisions by providing a baseline for comparison over time.
Neurological conditions can be dynamic, and changes in consciousness may indicate improvement or deterioration. Therefore, meticulous and consistent documentation enables medical practitioners to track these changes, formulate appropriate treatment plans, and communicate effectively with interdisciplinary teams. Documenting the level of consciousness is not merely a record-keeping task but a crucial component in ensuring optimal and tailored patient care.
Patient assessment
Evaluate the patient's response to stimuli
During this assessment, clinicians carefully observe how the patient reacts to verbal and tactile stimuli. A quick and appropriate response is indicative of a higher level of consciousness. Whether responding to a spoken question or a gentle touch, the patient's ability to engage with stimuli provides valuable insights into the integrity of their neurological functions.
Observe for signs of confusion, lethargy, or agitation
Behavioral cues play a crucial role in gauging a patient's mental state and can serve as indicators of changes in consciousness. Observing signs of confusion, lethargy, or agitation provides clinicians with qualitative information about the patient's cognitive functioning. Changes in behavior may suggest alterations in neurological or altered mental status itself, prompting further investigation and intervention.
Evaluate orientation
To assess orientation, clinicians determine the patient's awareness of their surroundings, including person, place, time, and situation. An oriented patient demonstrates intact and normal cognitive functioning, accurately recognizing themselves, their location, the current time, and an understanding of the situation. This evaluation is essential for establishing a baseline cognitive state and monitoring deviations over time.
Identify any disorientation or memory deficits
Clinicians must be attentive and alert to any disorientation or memory deficits during patient assessment. Disorientation, where patients may appear confused about their surroundings or exhibit memory lapses, could indicate underlying neurological issues. Identifying such deficits helps guide further diagnostic evaluation and appropriate interventions.
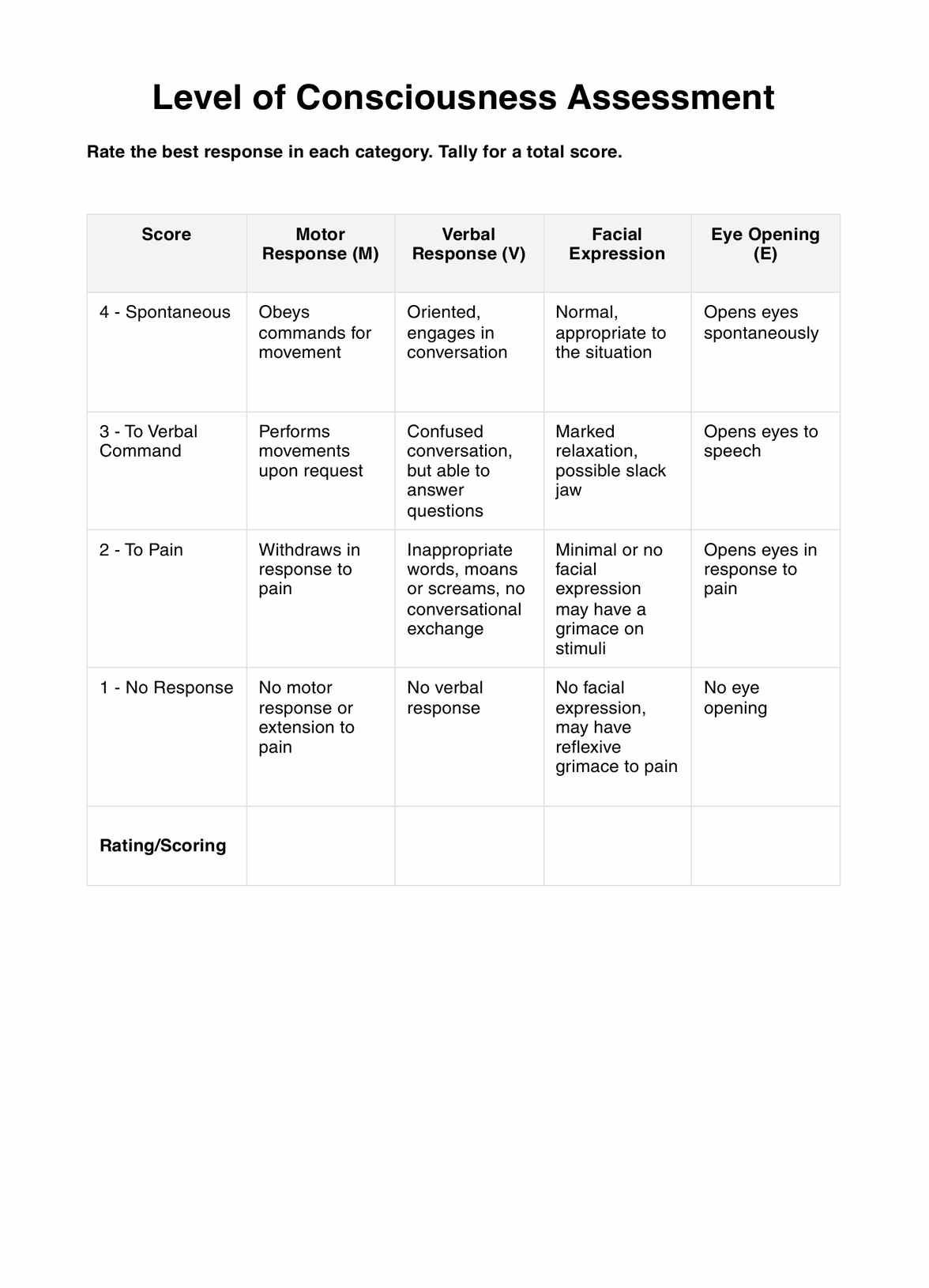
Utilize Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
The Glasgow Coma Scale serves as a standardized tool for quantifying the level of consciousness based on eye, verbal, and motor responses. By applying the GCS, clinicians assign a numerical score that aids in categorizing the severity of impairment. This systematic evaluation assists in objectively assessing a patient's neurological status, facilitating communication among healthcare providers, and guiding treatment decisions.
Apply the GCS
Breaking down the GCS, clinicians assess the patient's eye response, evaluating their ability to open their eyes spontaneously or respond to stimuli. The patient's verbal response is then analyzed, considering the appropriateness and coherence of the patient's verbal interactions. Finally, the motor response is observed, including the patient's ability to follow commands or exhibit purposeful movements. This comprehensive evaluation using the GCS provides a structured and quantitative approach to understanding the patient's level of consciousness.
How to use this level of consciousness evaluation
Step 1: Incorporate into routine patient examinations
Begin by seamlessly integrating the Level of Consciousness Evaluation into routine patient examinations. Whether conducting initial assessments or follow-up visits, consistency is key. Ensure that the evaluation becomes a standard component of your clinical practice.
Step 2: Begin the assessment
Start the assessment by evaluating the patient's responsiveness. Observe their reactions to both verbal and tactile stimuli. A prompt and appropriate response indicates a higher level of consciousness. Note any signs of confusion, lethargy, or agitation as behavioral indicators that provide insights into their mental state.
Step 3: Assess orientation
Move on to assessing the patient's orientation. Determine their awareness of person, place, time, and situation. An oriented patient demonstrates intact cognitive functioning. Identify any disorientation or memory deficits, which could indicate underlying neurological issues.
Step 4: Utilize the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Apply the Glasgow Coma Scale as a standardized tool to quantify the level of consciousness based on eye, verbal, and motor responses. Assign numerical scores to each component to categorize the severity of impairment. This systematic approach ensures a comprehensive evaluation.
Step 5: Document findings systematically
Document the findings of the Level of Consciousness Evaluation systematically in the patient's medical records. Record observations related to responsiveness, orientation, and GCS scores. Accurate and detailed documentation is a reference point for future assessments and facilitates communication among healthcare providers.
Understanding the results
Interpreting the assessment results is crucial to gaining insights into the patient's neurological status. Gauge the severity of impairment or improvement by carefully analyzing the documented neurological examination findings. Collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, nurses, and therapists, to derive comprehensive insights. The collective expertise of a multidisciplinary team enhances the accuracy of interpretation and ensures a holistic approach to patient care.
Next steps
Based on the assessment findings, the following steps involve outlining appropriate interventions and treatment plans to address any issues related to the patient's level of consciousness.
Collaborate with the healthcare team to tailor interventions to the specific needs identified during the assessment. This may include medication adjustments, therapeutic interventions, or referrals for further diagnostic evaluations. A proactive, collaborative approach ensures timely, targeted interventions for optimal patient outcomes.
Benefits of using this assessment
Early detection
Identifying neurological issues, including altered consciousness, promptly is a key benefit of this assessment. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which is crucial in preventing the progression of neurological conditions such as drug overdose and minimizing potential complications.
Treatment tailoring
One of the significant advantages of the Level of Consciousness Assessment is its ability to tailor treatments based on the patient's specific level of consciousness. This personalized approach ensures that interventions align with each patient's needs and neurologic function, optimizing the treatment plan's effectiveness, especially in cases of internal rotation or drug overdose.
Monitoring progress
The assessment is a valuable tool for tracking changes in consciousness over time. Regular evaluations allow healthcare practitioners to monitor progress and gauge the effectiveness of implemented treatments. This ongoing assessment helps make informed decisions about adjusting interventions and ensures that the patient progresses toward improved neurological functioning. Clinical findings related to altered consciousness, internal rotation, or drug overdose can be closely monitored and addressed through this comprehensive assessment.
Commonly asked questions
The Level of Consciousness Assessment is a systematic evaluation used by medical practitioners to gauge a patient's neurological status. It includes components such as responsiveness and orientation, and it applies the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) to quantify the level of consciousness based on eye, verbal, and motor responses.
The assessment is crucial for early detection of neurological issues, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of the progression of conditions. It helps tailor treatments based on the patient's specific level of consciousness, ensuring a personalized approach to care. Additionally, the assessment is valuable for monitoring progress over time, guiding intervention adjustments, and promoting improved neurological functioning.
Interpretation of assessment results involves analyzing findings related to responsiveness, orientation, and GCS scores. Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, including neurologists and therapists, enhances comprehensive insights into the patient's neurological status.




















-template.jpg)