Executive Dysfunction Test
Explore our Executive Dysfunction Test Template, designed for mental health professionals to assess and address executive functioning challenges in clients.


What are a person's executive functions?
Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes necessary for the cognitive control of behavior. These functions help us manage our thoughts, actions, and emotions to achieve our goals. Here are some essential executive functions:
Working memory
Working memory allows us to hold and manipulate information in our minds over short periods. It's crucial for tasks like following multi-step instructions, solving problems, completing tasks requiring more than one skill, and completing multiple tasks simultaneously. It also includes visual working memory and verbal working memory.
Cognitive flexibility
Cognitive flexibility, or mental flexibility, is the ability to switch between thinking about two or multiple concepts simultaneously. It's essential for adapting to new situations and tasks requiring attention to more than one thing at a time.
Inhibition control
Inhibition control is the ability to control impulsive responses and resist distractions. It's essential for staying focused on a task and for behaviors that require self-control.
Planning and organization
Planning and organization involve creating a roadmap to reach a goal or complete a task and making the necessary arrangements or preparations. It's crucial for tasks requiring multiple steps or managing time effectively.
Task initiation
Task initiation is the ability to begin tasks without undue procrastination. It's essential for productivity and initiating functions that may be challenging or uninteresting.
Emotional regulation
Emotional regulation is the ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences healthily. It's crucial for maintaining emotional stability and for coping with stress.
Self-monitoring
Self-monitoring is the ability to monitor and evaluate one's behavior and performance. It's important to recognize when adjustments are needed to improve effectiveness or to stay on track toward a goal.
Each of these executive functions plays a vital role in our daily lives, and difficulties in any of these areas can lead to challenges in managing tasks and achieving goals.
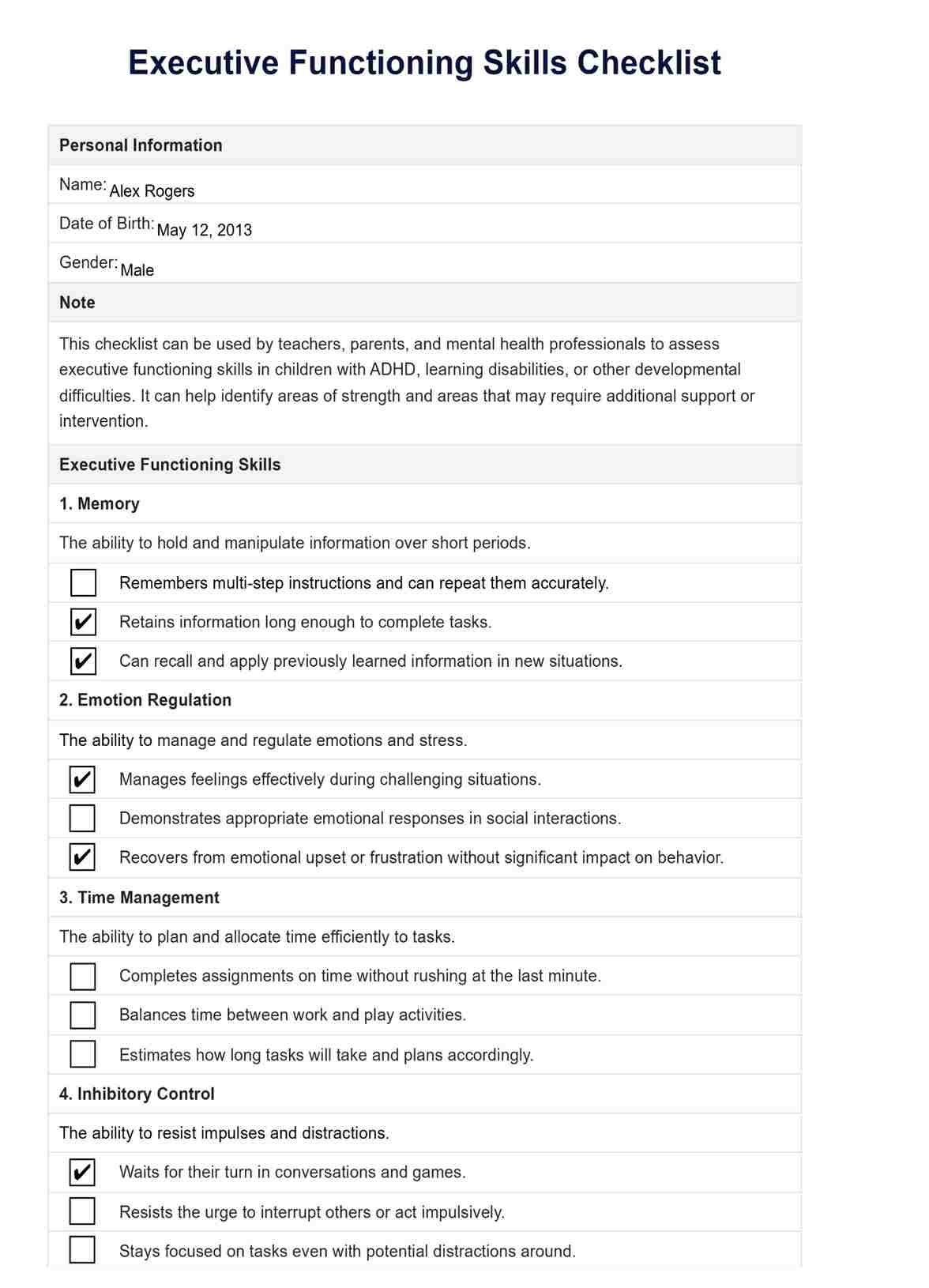
Executive Dysfunction Test Template
Executive Dysfunction Test Example
What is executive dysfunction?
Executive dysfunction, or executive function disorder, refers to difficulties using executive functions effectively. It is often associated with various neurological and psychiatric conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorder, depression, and brain injuries. Executive dysfunction can manifest in various ways, including:
- Poor impulse control and decision-making
- Difficulty organizing and prioritizing tasks
- Struggles with starting and completing tasks
- Challenges in adapting to new situations
- Problems with working memory and recalling information
Consequences of executive dysfunction, or executive functioning issues, can significantly impact an individual's daily life, affecting their ability to perform at work or school, manage personal relationships, and maintain overall well-being. Executive function tests are often used to assess the extent of these difficulties and guide interventions and support strategies.
In summary, executive dysfunction involves challenges in using executive function skills, leading to difficulties in managing tasks, emotions, and behaviors. Understanding and addressing these issues is crucial for improving an individual's quality of life and helping them achieve their potential.
How does this Executive Dysfunction Test work?
Our Executive Dysfunction Test is designed to help mental health professionals assess their patients' executive functioning skills. Here's how to use it effectively:
Step 1: Access the template
First, access the Executive Dysfunction Test template through the Carepatron app or website. This ensures you have a standardized and comprehensive tool for assessment.
Step 2: Explain the template
Introduce the template to your patient and explain its purpose. It contains statements about various executive functions, such as planning, organization, impulse control, and cognitive flexibility. Each statement is designed to reflect common challenges individuals with executive dysfunction face.
Step 3: Administer the test
Ask your patient to rate each statement based on their experiences, using a scale from 1 to 5, where 1 = Never and 5 = Always. Their responses provide insights into the areas of executive functioning that may be problematic for them.
Step 4: Calculate the scores
Total the scores for each executive function area to get an overall picture of the patient's executive dysfunction. Higher scores indicate greater difficulties in that particular area.
Step 5: Interpret the results
Use the scores to identify executive dysfunction patterns and understand the patient's challenges. This can inform the development of targeted interventions and support strategies.
Step 6: Reflect and discuss
Encourage the patient to reflect on their answers and discuss areas they want to explore or improve their executive functioning skills.
By following these steps, mental health professionals can use our Executive Dysfunction Test to assess and understand their patients' executive functioning challenges, aiding in therapeutic approaches and personal development.
How do you interpret the results of this test?
Interpreting the results of the Executive Dysfunction Test involves analyzing the scores from the questions to gain insights into the individual's executive functioning. To do this, add the scores from each question to obtain a total score. The maximum score for each section (Overt and Covert) is 75, with a combined maximum score of 150.
In the Overt section, higher scores suggest better executive functioning, indicating strengths in planning, organization, and inhibition control. Conversely, in the Covert section, lower scores tell better executive functioning, meaning fewer challenges with impulsivity, emotional regulation, and task initiation.
A higher combined score indicates more vital executive functioning skills, while a lower combined score suggests potential areas of executive dysfunction that may require further exploration and intervention. It's important to note that this test is not a diagnostic tool. The results should be used as a starting point for discussions about executive function deficits, potential strategies for improvement, and possible ways to treat executive dysfunction disorder.
Combine these results with other assessments and clinical evaluations to comprehensively understand the individual's executive functioning.
What are the benefits of this test?
The Executive Dysfunction Test offers several benefits for individuals and mental health professionals. Some key advantages include:
- Improved understanding of executive functioning: The test provides insights into an individual's executive functioning skills, such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibition control. This understanding can help identify specific areas of difficulty and guide targeted interventions.
- Early detection of executive dysfunction: Administering the test can help detect signs of executive dysfunction early, allowing for timely intervention and support to prevent further challenges in daily functioning and completing tasks.
- Personalized treatment planning: The test results can inform personalized treatment plans that address each individual's unique executive functioning issues, leading to more effective management and improvement of symptoms.
- Monitoring progress: The test can monitor changes in executive functioning over time, allowing mental health professionals to assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
- Supporting diagnosis: While the test is not a diagnostic tool, it can provide valuable information to support the diagnosis of conditions that often involve executive dysfunction, such as ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, and brain injuries.
By leveraging the benefits of the Executive Dysfunction Test, mental health professionals can enhance their understanding of executive functioning, provide more targeted support, and improve outcomes for individuals with executive dysfunction.
How to treat or manage executive dysfunction
Managing executive dysfunction requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual's unique challenges. Here are some effective strategies to help individuals cope with and improve their executive functioning:
Behavioral and psychological interventions
Behavioral and psychological interventions focus on developing coping mechanisms and enhancing mental resilience. These strategies can help individuals better manage their symptoms and improve their overall functioning:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps individuals develop coping strategies, improve organizational skills, and learn techniques to enhance focus and self-control.
- Mindfulness and stress reduction: Mindfulness meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and improve focus.
Medical and therapeutic interventions
Medical and therapeutic interventions may involve medication or therapy to address underlying conditions contributing to executive dysfunction. Working with healthcare professionals can help determine the most suitable options:
- Medication: For conditions like ADHD, medication can be effective in managing symptoms of executive dysfunction. Stimulant and non-stimulant medications may improve attention, impulsivity, and working memory.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists can work with individuals to develop strategies for managing daily tasks, improving time management, and enhancing problem-solving skills.
Educational and technological support
Educational and technological support can provide individuals with tools and resources to overcome challenges related to executive dysfunction. These supports can be particularly beneficial in academic and professional settings:
- Educational support: For students with executive dysfunction, individualized education plans (IEPs) or 504 plans can provide accommodations and support to help them succeed academically.
- Assistive technology: Tools like planners, reminder apps, and organizational software can help individuals with executive dysfunction stay organized and manage their time more effectively.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact overall well-being and may help alleviate some symptoms of executive dysfunction. Incorporating healthy habits into daily routines can improve brain function and quality of life:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can improve overall brain function and may help alleviate some symptoms of executive dysfunction.
- Healthy diet and sleep: A balanced diet and adequate sleep are crucial for maintaining optimal brain health and managing symptoms of executive dysfunction.
Working with a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate treatment and management plan based on the individual's specific challenges and needs is important.
Commonly asked questions
Mental health professionals use assessments like the Executive Dysfunction Test to test for executive dysfunction, which evaluates crucial executive functions such as working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibition control.
Various factors, including neurological disorders like ADHD, brain injuries, mental health conditions, and developmental disorders, can cause poor executive functioning.
Breaking out of executive dysfunction involves implementing strategies to improve executive functioning skills, such as using planners, setting reminders, breaking tasks into smaller steps, and seeking support from mental health professionals.




















-template.jpg)






























































































