Defense Mechanisms Worksheet
Explore the intricacies of defense mechanisms with our comprehensive guide. Learn how these strategies impact mental health, relationships, and personal growth.


What are defense mechanisms?
Defense mechanisms are psychological strategies that individuals unconsciously employ to protect themselves from anxieties, threats, and uncomfortable feelings like guilt and shame. These mechanisms, first conceptualized by Sigmund Freud and later developed by his daughter, Anna Freud, are a fundamental part of human psychology. They serve as filters for our emotional responses to challenging situations.
Understanding defense mechanisms requires delving into the complexities of the human psyche. At their core, these ego defense mechanisms are a form of self-deception; they distort or deny reality to make it less threatening. For instance, a person who is in denial about a serious health issue might convince themselves that their symptoms are due to a less severe cause, thereby avoiding the anxiety of facing the illness.
There are numerous defense mechanisms, each serving a different purpose. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial because they influence our behavior and emotional well-being. Overreliance on certain defense mechanisms, especially the more primitive ones, can lead to mental health issues. For example, consistent denial of problems can prevent individuals from addressing and resolving underlying issues, leading to exacerbated stress and anxiety.
In therapy, recognizing and understanding one’s defense mechanisms is vital to emotional healing and growth. It allows individuals to start confronting their fears and anxieties more directly and healthily, improving their mental health and well-being.
Defense Mechanisms Worksheet Template
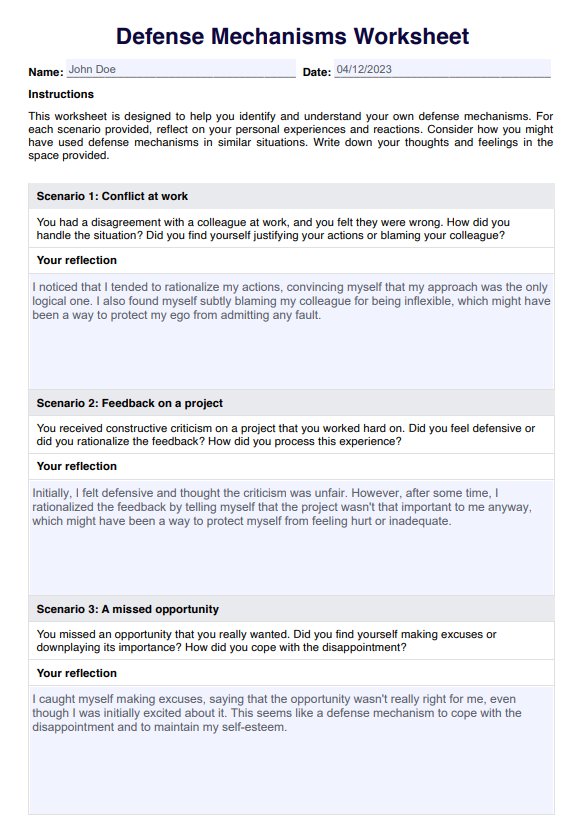
Defense Mechanisms Worksheet Example
Understanding defense mechanisms psychology
Defense mechanisms psychology is a field that studies how these subconscious processes protect the ego from anxiety, internal stress, and perceived threats. This area of psychology is rooted in the theories of Sigmund Freud and has evolved with contributions from various psychologists.
Defense mechanisms operate unconsciously, meaning people are generally unaware of their use. These defense mechanisms included here can range from simple denial, where a person refuses to acknowledge the reality of a situation, to passive aggression, to more complex processes, like sublimation, where unacceptable impulses are transformed into socially acceptable actions.
Understanding these mechanisms is essential for mental health professionals as it helps in diagnosing and treating various psychological issues. For instance, people who frequently use projection – attributing their unacceptable feelings to others – might struggle with personal relationships. Recognizing this pattern can be the first step in addressing deeper emotional conflicts.
Moreover, defense mechanisms are not inherently negative. They can be adaptive and help individuals cope with life’s stresses. For example, humor is a defense mechanism that can diffuse tension and lighten difficult situations. The key is balance; overreliance on any one mechanism, especially in avoiding reality, can be detrimental to mental health.
Understanding a client’s primary defense mechanisms can guide the therapeutic process in therapy. It helps in tailoring interventions that address the root causes of emotional distress. For example, if a client primarily uses denial, therapy might focus on gently confronting reality and developing healthier coping strategies.
How to identify denial defense mechanisms
Denial is one of the most basic and common defense mechanisms. It involves refusing to accept reality or facts, avoiding a potentially distressing truth. Identifying denial can be challenging, as it operates on a subconscious level and is often deeply ingrained in an individual’s coping strategies.
To identify denial, mental health professionals look for signs like refusing to acknowledge a problematic situation, minimizing the seriousness of circumstances involved, or avoiding conversations about specific issues. For example, a person might consistently dismiss concerns about their excessive drinking habits or avoid discussing the consequences of a failing relationship.
In therapy, addressing denial involves creating a safe and supportive environment where the individual can gradually confront and accept reality. This process requires patience and empathy, as directly confronting someone in denial can lead to increased resistance and emotional shutdown.
Understanding and moving past denial is crucial for mental health and well-being. It allows individuals to face and address issues head-on rather than avoiding them, which can lead to more significant problems in the long run. Overcoming denial leads to greater self-awareness, healthier coping mechanisms, and improved emotional resilience.
How to identify repression defense mechanisms
Repression is a defense mechanism that unconsciously blocks distressing thoughts and feelings from conscious awareness. Unlike denial, where a person refuses to acknowledge reality, repression involves completely pushing uncomfortable thoughts out of conscious thought.
Identifying repression can be complex, as it operates on an unconscious level. Signs of repression include having difficulty recalling specific events or periods of life, experiencing unexplained emotions or reactions, or having recurring dreams or themes in dreams related to the repressed content.
Techniques like free association, dream analysis, and exploration of physical symptoms without a clear medical cause can help uncover repressed memories and feelings in therapy. The goal is to bring these repressed thoughts into consciousness, where they can be addressed and processed.
Repression is often linked to traumatic events related feelings or experiences. When these repressed memories are not dealt with, they can manifest in various psychological symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, or phobias. Addressing repression in therapy can lead to significant breakthroughs and emotional healing, as it allows individuals to process and integrate previously hidden aspects of their experiences.
How to identify displacement defense mechanisms
Displacement is a defense mechanism where an individual redirects their emotions or feelings from the original source to a safer or more acceptable target. It often occurs when expressing emotions directly to the source is too threatening or risky.
To identify displacement, mental health professionals look for patterns where clients consistently redirect their emotional responses. For example, a person who is angry with their boss but is unable to express it might come home and take out their anger and frustration on their family. Another sign of displacement is an overreaction to minor irritations, which might be a redirection of more significant, unaddressed emotions.
In therapy, recognizing and addressing displacement involves helping the client become aware of this pattern and understanding the underlying emotions and conflicts. Techniques like role-playing or exploring reactions to recent conflicts can be useful in identifying displacement.
Understanding and managing displacement is important as it can lead to strained relationships and inappropriate emotional responses. Therapy can help individuals learn to express their emotions more directly and appropriately, leading to healthier interpersonal dynamics and better emotional regulation.
How to recognize reaction formation defense mechanisms
Reaction formation is a defense mechanism where an individual unconsciously converts unwanted or dangerous thoughts, feelings, or impulses into their opposites. This mechanism often results in exaggerated or overly opposite behaviors and attitudes.
Identifying reaction formation involves observing behaviors that are excessively the opposite of what one would expect. For example, a person who is struggling with homosexual desires might become overly critical of homosexuality or adopt a strong homophobic stance.
Exploring these exaggerated attitudes and behaviors in therapy can reveal underlying conflicts and anxieties. The therapist might gently challenge these attitudes or explore the origins of these feelings, helping the client to confront and accept their true feelings and desires.
Understanding and addressing reaction formation is crucial as it can lead to a life of contradiction and internal conflict. Therapy can help individuals reconcile their true feelings with their outward behaviors, leading to a more integrated and authentic self.
How to identify projection defense mechanisms
Projection is a defense mechanism where individuals attribute their unacceptable thoughts, feelings, or motives to someone else. It is a way of externalizing one’s internal conflicts.
To identify projection, mental health professionals look for patterns where clients consistently attribute their negative qualities or feelings to others. For example, a person who is unfaithful in a relationship might accuse their partner of being unfaithful.
Helping clients recognize projection in therapy involves exploring these accusations or attributions and examining their basis in reality. Techniques like reflecting on past and present, relationships or analyzing recurring conflicts can be helpful.
Understanding and addressing projection is important as it can lead to misunderstandings, damaged relationships, and a lack of self-awareness. Therapy can help individuals take responsibility for their feelings and behaviors, leading to healthier relationships and a more accurate self-view.
Recognizing avoidance defense mechanisms
Avoidance is a defense mechanism where an individual consciously or unconsciously avoids facing certain painful or uncomfortable thoughts, feelings, or situations. This mechanism can manifest in various forms, such as physical avoidance, distraction, or emotional detachment.
Identifying avoidance involves observing behavior patterns where a person consistently steers clear of specific topics, people, or situations likely to cause distress. For example, a person might avoid social situations due to underlying social anxiety or consistently change the subject when discussing certain topics.
In therapy, addressing avoidance can involve gradually exposing the client to the feared situation or topic in a controlled and supportive environment. This process helps the individual confront and process the underlying emotions or fears.
Understanding and managing avoidance is crucial for emotional growth and well-being. Avoidance can lead to a restricted life and unaddressed emotional issues. Therapy can help individuals face their fears and develop healthier coping strategies, leading to a more fulfilling and engaged life.
How to use this worksheet
To use our Printable Defense Mechanisms Worksheet, individuals must read through each scenario and reflect on their life experiences. They should consider whether they have exhibited similar behaviors or reactions and, if so, what underlying emotions or conflicts might be driving these defense mechanisms.
The worksheet can of course be used independently for self-reflection or as part of therapy. In a therapeutic setting, the therapist can guide the client through the worksheet, providing insights and facilitating deeper exploration of emotional responses.
The goal of using this worksheet is to increase self-awareness and understanding of one’s defense mechanisms. This can lead to more adaptive coping strategies and improved emotional well-being.
Benefits of understanding your defense mechanisms
Gaining insight into one's defense mechanisms is a transformative process with far-reaching benefits for mental health and emotional well-being:
- Enhanced self-awareness and insight: Recognizing personal defense mechanisms is akin to uncovering a map of one's subconscious landscape. This heightened self-awareness illuminates why certain reactions or behaviors occur, particularly under stress or conflict. It allows individuals to see beyond surface emotions and understand deeper motivations and fears.
- Improved emotional regulation: A clear understanding of defense mechanisms equips individuals with the tools to manage their emotions more effectively. Recognizing when one is employing mechanisms like projection or denial enables one to pause and reassess one's response. This leads to more balanced emotional reactions and reduced impulsive behaviors driven by unacknowledged feelings.
- Healthier relationships: Awareness of one's defense mechanisms can profoundly improve interpersonal dynamics. Individuals can break miscommunication, projection, and misunderstanding cycles by understanding how these mechanisms play out in relationships. This leads to more authentic interactions, where both parties can express their feelings and needs without distorting subconscious defenses.
- Effective stress and anxiety management: Understanding defense mechanisms is a powerful tool in managing stress and anxiety. When individuals recognize that subconscious defenses might exacerbate their anxiety, they can adopt more adaptive coping strategies. This shift from avoidance to confrontation and from repression to expression can significantly alleviate psychological distress.
- Facilitated emotional healing in therapy: In therapeutic settings, an understanding of defense mechanisms can lead to breakthroughs in treatment. Therapists can guide clients to uncover and work through these mechanisms, addressing deep-seated emotional wounds and unresolved conflicts. This process is often pivotal in healing from trauma, anxiety disorders, and depression.
- Promotion of personal growth and development: The journey of understanding and working through defense mechanisms is inherently a journey of personal growth. It challenges individuals to confront uncomfortable truths, reassess their self-image, and develop greater emotional maturity. This growth often leads to increased resilience, self-confidence, and a more nuanced understanding of oneself and others.
- Enhanced decision-making abilities: With greater emotional clarity comes improved decision-making. Individuals who understand their defense mechanisms are less likely to make choices based on unresolved emotional issues or subconscious fears. Instead, their decisions align more with their desires, values, and objectives.
- Increased authenticity and self-expression: Individuals who work through their defense mechanisms often find a greater sense of authenticity. They become more in tune with their true feelings and can better express themselves. This authenticity fosters a sense of integrity and unity in life choices and relationships.
- Improved coping with life transitions and stressors: Life is replete with changes and stressors. A deep understanding of defense mechanisms provides a robust framework for navigating these challenges. Individuals become better equipped to handle life transitions, stress, and adversity, adapting more healthily to changing circumstances.
Understanding one's defense mechanisms is critical to psychological health and personal development. It empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills to navigate their emotional world more effectively, leading to improved relationships, better mental health, and a more fulfilling life.
Research and evidence
The study of defense mechanisms in psychology has a substantial and rich history, marked by significant research and theoretical advancements. Originating from Freud's psychoanalytic theory, the concept of defense mechanisms has evolved over the years, with contemporary research offering a more nuanced understanding of these mechanisms and their impact on mental health.
In his seminal work, "The Ego and the Id", Freud laid the foundation for defense mechanisms. Published in 1923, this book introduced the idea that unconscious processes significantly influence behavior and mental health. Freud's theories have been pivotal in psychology, particularly in understanding how individuals unconsciously protect themselves from psychological distress (Freud, 1923).
Expanding on Freud's theories, McWilliams' "Psychoanalytic Diagnosis, Second Edition: Understanding Personality Structure in the Clinical Process" published by Guilford Press in 2011, provides a modern perspective on how defense mechanisms manifest in personality and psychopathology. This text is instrumental in understanding the contemporary applications of Freud's initial concepts, offering insights into how these mechanisms play out in various mental disorders and everyday life (McWilliams, 2011).
Furthermore, the American Psychiatric Association's "Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.)" published in 2013, acknowledges the role of defense mechanisms in various mental disorders, highlighting their relevance in clinical practice. The DSM-5 is a cornerstone in psychiatric diagnosis and underscores the importance of defense mechanisms in mental health. This manual reflects the consensus in the psychiatric community about the critical role these mechanisms play in psychological functioning (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
Contemporary research continues to explore the role of defense mechanisms in mental health. Studies have shown that certain defense mechanisms, such as repression and denial, are linked to specific mental health issues. In contrast, others, like sublimation and humor, are associated with healthier psychological outcomes.
This review of ongoing research emphasizes the importance of understanding and managing defense mechanisms to improve mental health and well-being, highlighting the need for continued exploration and understanding of these subconscious processes to enhance therapeutic practices and promote mental health.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.) American Psychiatric Publishing.
Freud, S. (1923). The Ego and the Id. W. W. Norton & Company.
McWilliams, N. (2011). Psychoanalytic Diagnosis, Second Edition: Understanding Personality Structure in the Clinical Process. Guilford Press.
Commonly asked questions
Defense mechanisms are subconscious psychological strategies used to protect oneself from anxiety, stress, and internal conflicts. They are important because they influence our behavior, emotional well-being, and relationships. Understanding these eight defense mechanisms helps in managing mental health issues, reducing anxiety, and promoting healthier coping strategies.
While defense mechanisms are a normal part of healthy psychological functioning, overreliance on certain mechanisms, like denial or repression, can lead to mental health issues. They can prevent individuals from addressing underlying problems, increasing stress and emotional difficulties.
Mental health professionals help individuals recognize and understand their defense mechanisms. They use various tools, including defense mechanisms worksheets, to facilitate self-awareness and teach healthier coping strategies. This process is crucial in therapy for addressing mental health issues and promoting emotional growth.

.jpg)

















-template.jpg)