Cognitive Processing Therapy Worksheets
Download our free CPT Worksheet to tackle traumatic beliefs and foster recovery with structured exercises for emotional well-being.


What is cognitive processing therapy?
Cognitive processing therapy (CPT) is a specialized type of cognitive-behavioral therapy aimed at helping individuals recover from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and related conditions. It is a type of evidence-based treatment that focuses on how a traumatic event is interpreted and remembered by the individual and how these patterns of thinking affect their emotional and mental health.
Cognitive processing therapy sessions guide individuals through a series of cognitive processing therapy exercises that teach cognitive skills designed to address and alleviate mental health disorders, mental health symptoms, and mental health concerns that those who have experienced trauma are dealing with. The goal is to help individuals understand and reinterpret their trauma, reducing the impact of mental health distress.
What are the core principles and theories that inform this therapy?
CPT is deeply rooted in cognitive-behavioral principles, focusing on the intricate link between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Central to CPT is the understanding that PTSD and related mental health challenges often arise from maladaptive interpretations and beliefs about traumatic experiences. The therapy is designed to address these core issues through several key principles:
- Interconnection of thoughts and emotions: CPT emphasizes the significant impact of thoughts on emotional responses, teaching clients to recognize and modify thought patterns that lead to distress.
- Challenging trauma-related beliefs: Clients are guided to critically evaluate and challenge their beliefs about the trauma, including feelings of guilt, shame, and responsibility.
- Reconstructing trauma narratives: A crucial aspect of CPT involves helping clients construct a new, healthier understanding of their traumatic event, facilitating a shift in perspective that can alleviate emotional pain.
These foundational principles of CPT not only aid in the alleviation of PTSD symptoms but also empower clients to reclaim control over their thoughts and emotions, leading to lasting changes in their mental health and overall outlook on life.
Why would a person take CPT therapy?
Choosing CPT therapy can be a pivotal step for individuals struggling with the aftermath of trauma. This therapeutic approach is particularly appealing for several reasons:
- Persistent PTSD symptoms: For those battling ongoing symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety, CPT offers a structured and evidence-based path toward relief.
- Seeking alternative therapies: Individuals with limited success with other treatment modalities may find CPT's structured and focused approach more effective in addressing their specific needs.
- Direct address of trauma: CPT is uniquely designed to confront and process trauma-related concerns head-on, making it an ideal choice for those ready to tackle their trauma in a supportive and structured environment.
What problems can CPT address?
CPT's versatility as a therapeutic approach allows it to address a broad spectrum of trauma-related challenges effectively:
- Beyond PTSD: While primarily known for its effectiveness in treating chronic PTSD, CPT is also adept at addressing anxiety disorders, depression, and emotional dysregulation.
- Emotional and cognitive struggles: It offers crucial support for individuals dealing with self-blame, guilt, or shame as a result of their trauma, providing strategies to challenge and redefine these harmful beliefs.
- Comprehensive trauma recovery: By focusing on both the emotional and cognitive components of trauma recovery, CPT facilitates a more holistic healing process, helping individuals to navigate the complexities of their experiences and emerge with a stronger, healthier mindset.
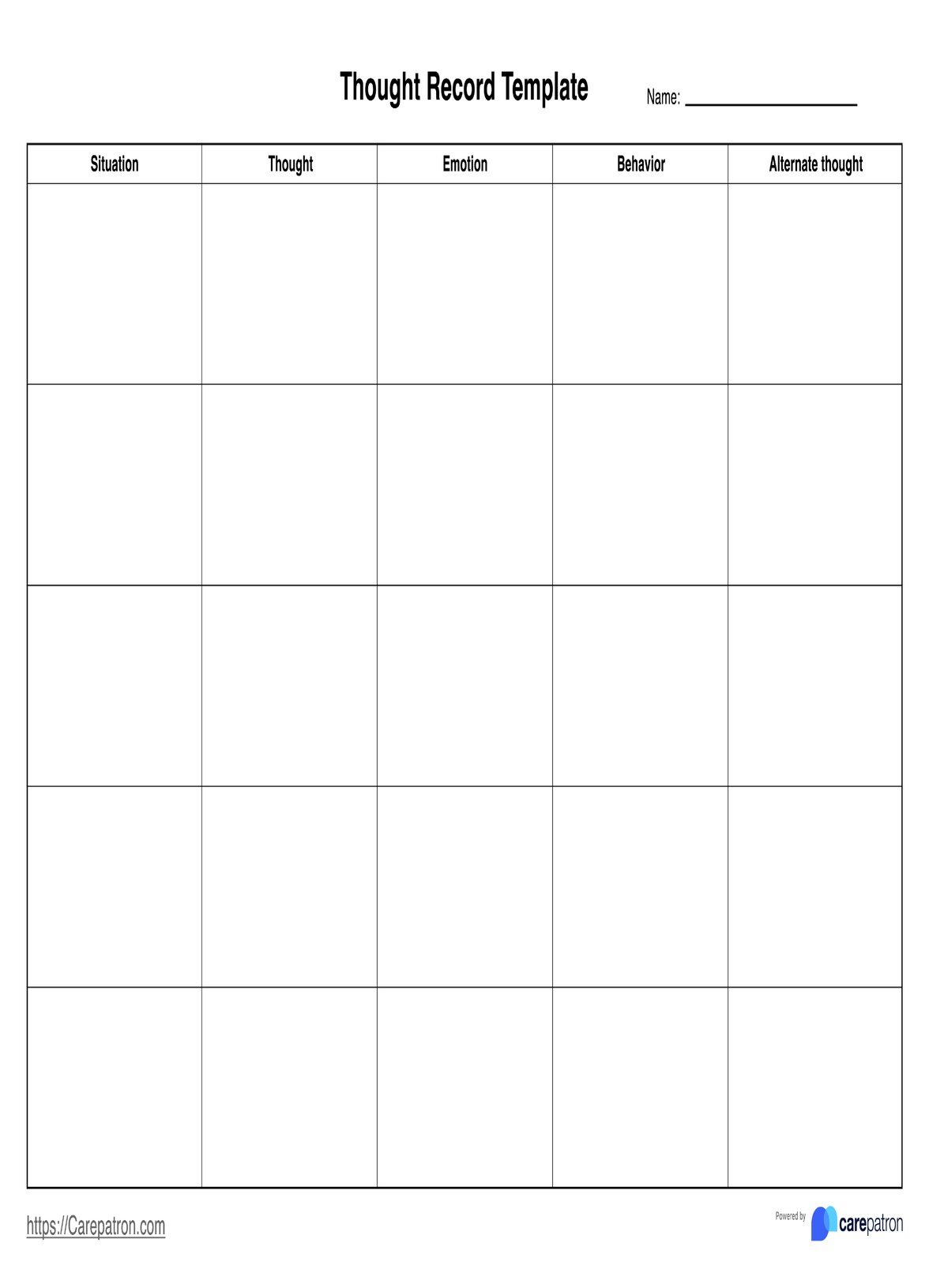
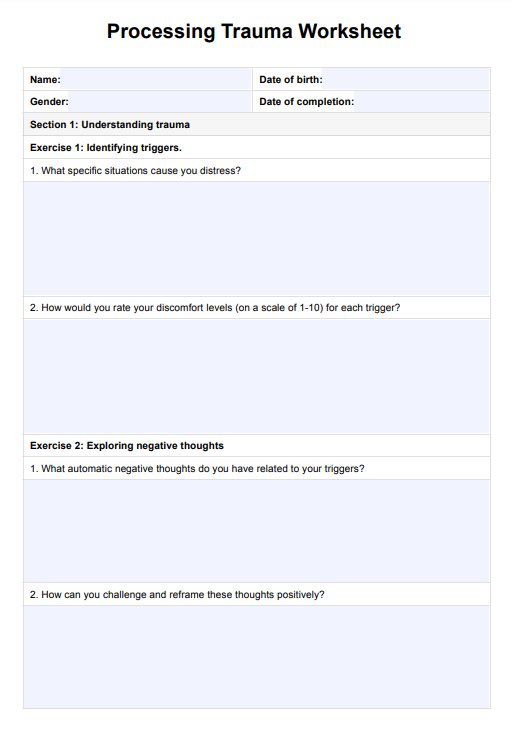
Cognitive Processing Therapy Worksheets Template
Cognitive Processing Therapy Worksheets Example
What are Cognitive Processing Therapy Worksheets?
CPT worksheets are tools used during therapy sessions to help clients actively engage with the therapy process. These worksheets facilitate the identification, examination, and challenge of unhealthy beliefs related to trauma. Examples include:
- Stuck point log: Helps clients identify and record specific thoughts that keep them stuck in unhelpful thinking patterns related to the trauma.
- Trauma impact questionnaire: Assists in exploring the effects of trauma on the client's current life.
- ABC worksheets: Guides clients in identifying the relationship between an event (A), beliefs (B), and consequences (C), helping to pinpoint cognitive distortions.
- Challenging beliefs worksheet: Used to challenge and reframe unhealthy beliefs about the trauma.
- Thought record: Encourages clients to record automatic thoughts related to the trauma and to find healthier alternative thoughts.
A specific example to use as a template could be the Stuck Point Log, designed to help clients recognize areas in their lives where they feel stuck due to their trauma and to begin developing alternative, healthier perspectives.
How does our Cognitive Processing Therapy Worksheet work?
Our printable Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) Worksheet is a cornerstone of CPT, designed to facilitate a deep and transformative engagement with one's thoughts and beliefs surrounding traumatic experiences. This tool is meticulously structured to guide clients through a therapeutic journey of self-discovery, reflection, and cognitive restructuring. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how the CPT Worksheet operates to foster healing and growth:
Active engagement with trauma-related thoughts
The initial step in utilizing the CPT Worksheet involves clients actively engaging with their trauma-related thoughts. This engagement is not a passive recall but a deliberate and focused introspection. Clients are encouraged to articulate and document the specific thoughts and narratives that emerge when they recall or are reminded of their traumatic event. This process lays the groundwork for the following therapeutic work, ensuring that the thoughts and beliefs under scrutiny impact the client’s emotional well-being.
Systematic challenge of maladaptive beliefs
Once these thoughts are identified, the CPT Worksheet facilitates a systematic challenge to these beliefs. Clients are guided to question the validity and helpfulness of their current beliefs about the trauma. This might involve dissecting the thought to understand its origins, evaluating the evidence that supports or contradicts this belief, and considering the potential biases that might influence their perspective. This critical examination helps clients see that many of their distressing beliefs about the trauma may not be as accurate or immutable as they once thought.
Exploration of alternative viewpoints
A crucial aspect of the CPT Worksheet is its encouragement of exploring alternative viewpoints. This exploration is not about denying the trauma or its impact but about understanding it in a more nuanced and less distressing way. Clients are prompted to consider different interpretations of the event, other possible outcomes, and the perspectives of others involved or aware of the trauma. This broadens the client’s cognitive landscape, allowing for a more flexible and less harmful interpretation of their experiences.
Construction of new, adaptive beliefs
The culmination of working through the CPT Worksheet is the construction of new, more adaptive beliefs about the trauma. This involves synthesizing the insights gained through challenging and exploring thoughts to form a revised narrative of the traumatic event. Clients are encouraged to develop beliefs more aligned with reality and conducive to their emotional healing and growth. This new understanding fosters a sense of closure, empowerment, and resilience, enabling clients to move forward with their lives with a healthier perspective on their past trauma.
Continuous support and reflection
Finally, the CPT Worksheet is designed to be revisited and reflected upon. As clients progress through their therapy and continue to grow and evolve, their understanding and perceptions of their trauma may also change. Re-engaging with the worksheet at different points in their recovery journey allows for ongoing refinement of their beliefs and emotional healing.
The CPT Worksheet is more than just a paper-and-pencil exercise; it is a dynamic tool that facilitates a critical part of the therapeutic process in CPT. By providing a structured framework for engaging with, challenging, and ultimately transforming trauma-related thoughts, the CPT Worksheet plays an integral role in helping clients recover from the impact of traumatic events and rebuild their lives with newfound strength and resilience.
What are the benefits of using CPT worksheets?
Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) worksheets offer a structured way for individuals to navigate their path toward healing after experiencing trauma. These tools are integral to the therapeutic process, providing a framework for understanding and processing traumatic events. Here's a closer look at the benefits of using CPT worksheets:
Active role in recovery
CPT worksheets empower clients to take a pivotal role in their healing journey. By engaging with these structured exercises, clients are provided with a clear and focused approach to address the complex array of thoughts and beliefs related to their trauma. This active participation is crucial, fostering a sense of agency and control over one's recovery process and encouraging a proactive stance toward healing.
Challenging unhelpful beliefs
One of the primary benefits of utilizing our Free CPT worksheets is their ability to help clients identify and challenge unhelpful beliefs. These beliefs often serve as barriers to recovery, holding individuals back from fully processing their trauma. Clients learn to question and reassess these beliefs through targeted exercises, gradually replacing them with more balanced and constructive perspectives.
Targeting trauma-related cognitive distortions
CPT worksheets are instrumental in helping clients target and dismantle trauma-related cognitive distortions. These distortions can skew a person's perception of the traumatic event, themselves, and the world around them, leading to increased distress and dysfunction. By systematically addressing these distortions, clients can begin to see their experiences in a more accurate and less harmful light.
Finding healthier alternative thoughts
A key objective of CPT worksheets is to guide clients toward finding healthier alternative thoughts. This process involves moving away from black-and-white thinking, overgeneralizations, and catastrophic predictions toward a more nuanced and positive way of interpreting their experiences. As clients practice generating alternative thoughts, they often experience a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms, including decreased anxiety, reduced avoidance behaviors, and an overall improvement in mood. By working through these worksheets, individuals can make meaningful strides in their recovery, ultimately leading to a more hopeful and empowered outlook.
Is cognitive processing therapy effective?
Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) has garnered substantial empirical support for its effectiveness in treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and other trauma-related mental health issues. Research evidence demonstrates that CPT significantly reduces PTSD symptoms, enhances overall mental health, and improves the quality of life for individuals impacted by trauma.
One pivotal study by Monson et al. (2006) explored CPT's efficacy within a veteran population, revealing remarkable reductions in PTSD symptoms when compared to a waitlist control group. This study underscores CPT's potential for addressing the complex needs of veterans, who often face unique challenges related to military-related traumatic events.
Further supporting CPT's broad applicability, Resick et al. (2002) conducted a randomized controlled trial comparing CPT to prolonged exposure therapy and a waiting condition among female rape victims. The findings indicated that CPT not only significantly reduced PTSD symptoms but also outperformed the other treatment modalities, highlighting its effectiveness across different types of trauma.
Additionally, Galovski et al. (2012) investigated the flexibility of CPT's structured approach, affirming its adaptability and sustained effectiveness in treating PTSD symptoms. This study emphasizes CPT's capacity to be tailored to meet individual client needs, further solidifying its status as a gold-standard treatment.
These studies attest to CPT's robust efficacy in the therapeutic landscape. By focusing on identifying and reframing maladaptive beliefs related to trauma, CPT offers a structured and effective approach to treating PTSD, with benefits that extend well beyond symptom reduction to include significant improvements in overall mental health and quality of life.
References
Galovski, T. E., Blain, L. M., Mott, J. M., Elwood, L., & Houle, T. (2012). Manualized therapy for PTSD: Flexing the structure of cognitive processing therapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80(6), 968–981. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23106761/
Monson, C. M., Schnurr, P. P., Resick, P. A., Friedman, M. J., Young-Xu, Y., & Stevens, S. P. (2006). Cognitive processing therapy for veterans with military-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74(5), 898–907. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.74.5.898
Resick, P. A., Nishith, P., Weaver, T. L., Astin, M. C., & Feuer, C. A. (2002). A comparison of cognitive-processing therapy with prolonged exposure and a waiting condition for the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder in female rape victims. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70(4), 867–879. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.70.4.867
Commonly asked questions
Structured clinical interviews combined with validated questionnaires are considered the gold standard for PTSD diagnosis.
CPT is highly effective in individual and group therapy settings, allowing clients to benefit from shared experiences and support.
CPT usually consists of 12 to 16 sessions, though the duration can vary based on the individual's needs and progress.

.jpg)























-template.jpg)