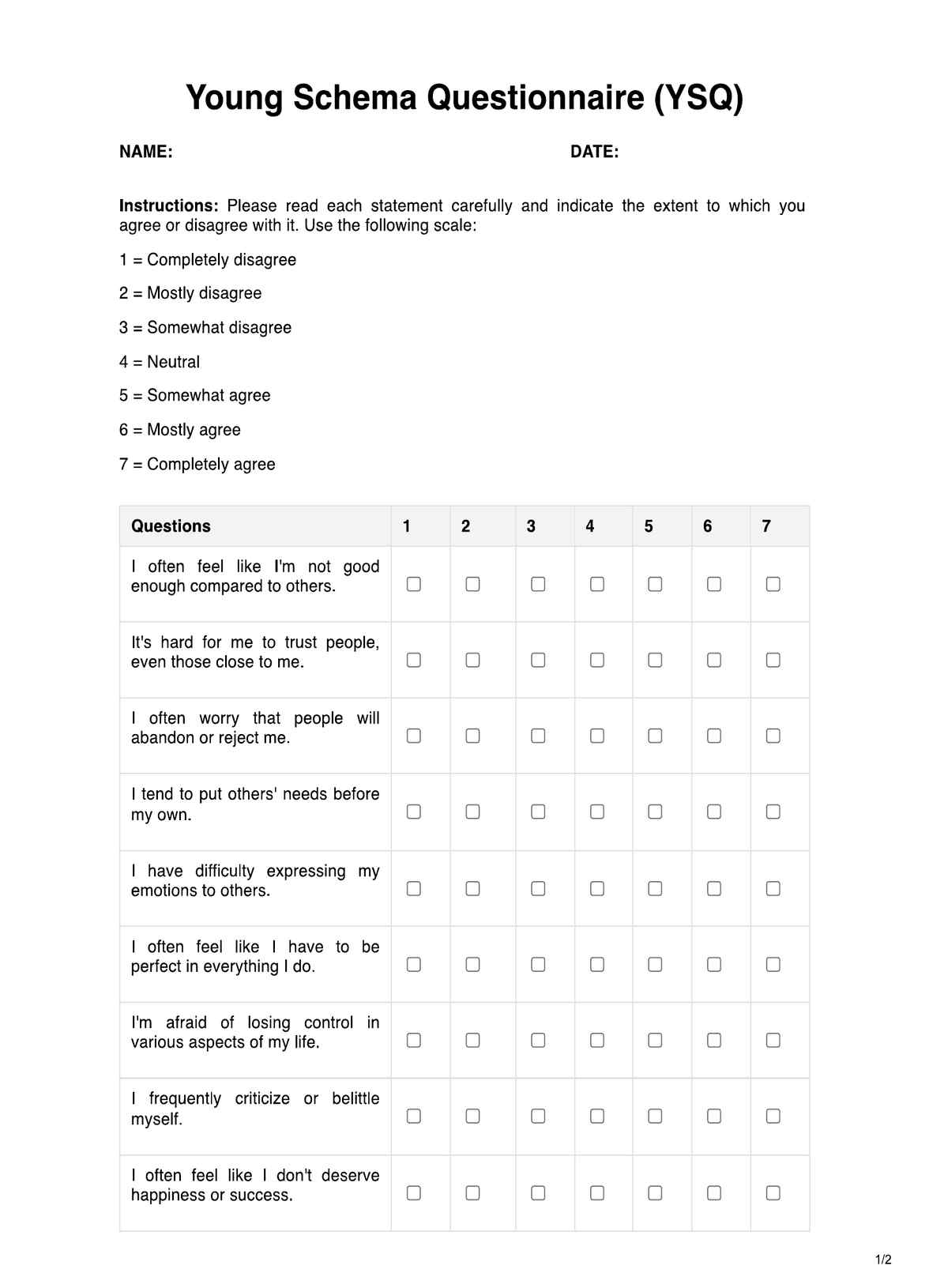
Respondents answer statements indicating their level of agreement or disagreement with each item. Scores are then calculated to determine the presence and intensity of various schemas.
Young Schema Questionnaire
Assess your mental health with the Young Schema Questionnaire. Identify underlying patterns to guide effective healthcare strategies.
Use Template
Young Schema Questionnaire Template
Commonly asked questions
Schemas include abandonment, emotional deprivation, perfectionism, and fear of losing control, among others.
YSQ results guide schema therapy interventions, targeting specific maladaptive schemas to promote emotional healing and personal growth.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











