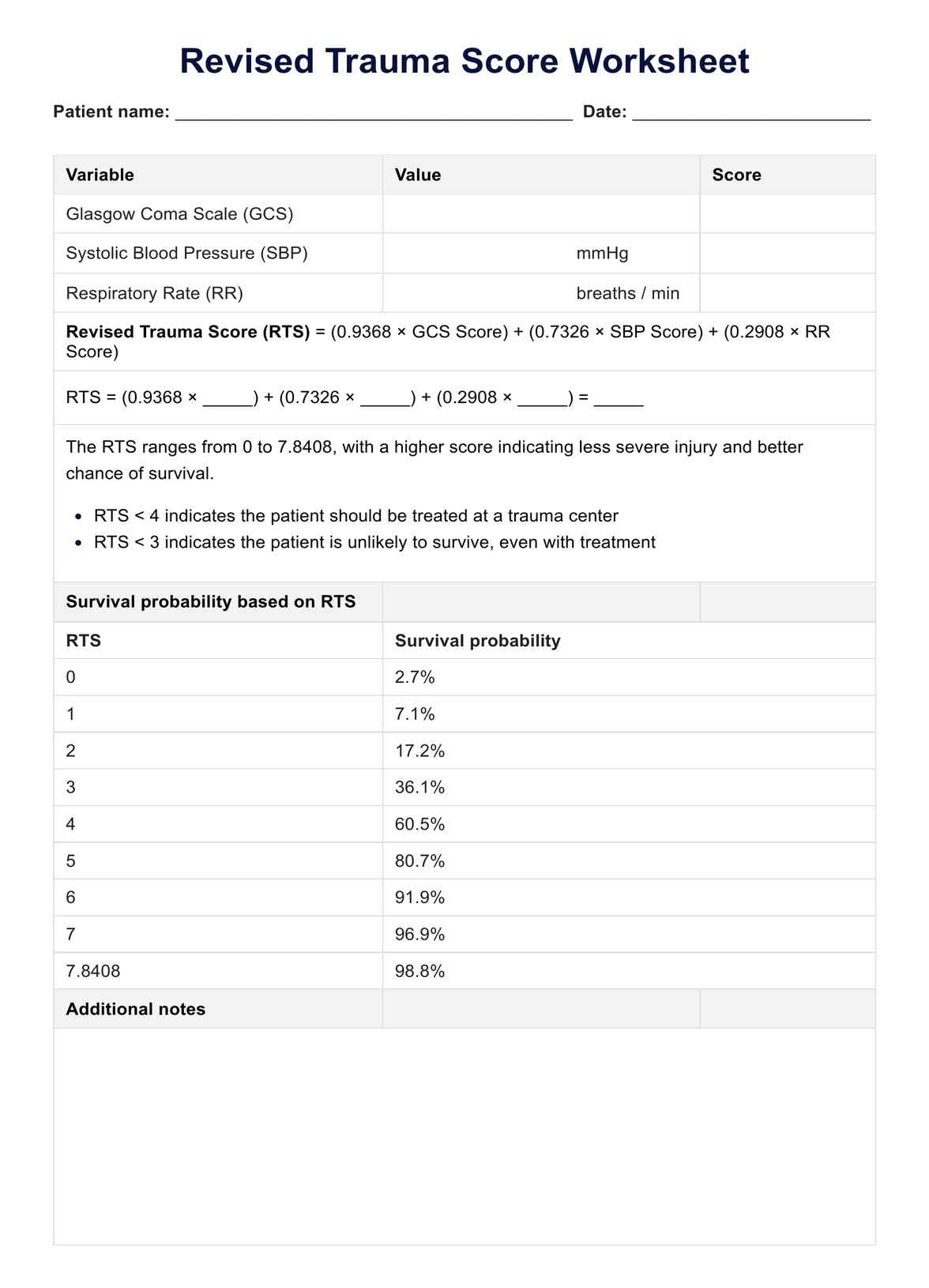
The RTS is a tool for quickly assessing the severity of trauma patients based on physiological parameters such as the Glasgow Coma Scale, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
Revised Trauma Score Worksheet
Learn about the significance of Revised Trauma Score in clinical practice, aiding triage, treatment decisions, and predicting patient outcomes.
Use Template
Revised Trauma Score Worksheet Template
Commonly asked questions
The RTS is calculated by assigning points to the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate and then summing these points to obtain an overall score.
The RTS helps healthcare providers triage trauma patients, guiding decisions on treatment priority and predicting patient outcomes. It also aids in resource allocation and improves patient care.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











