IADLS Assessment
Download our free IADLS Assessment template to evaluate daily living skills for better care and independence planning. Ideal for professionals and families.


What are instrumental activities of daily living?
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs) encompass complex activities necessary for independent living, extending beyond basic self-care to meal and food preparation, medication management, and managing finances. These activities require cognitive and physical abilities, reflecting a person’s ability to live independently and sustain a higher quality of life. Unlike basic activities of daily living (ADLs), which cover fundamental self-care tasks like eating and dressing, IADLs focus on more nuanced skills that enable community-dwelling older adults to manage their households, engage in social adjustments, and navigate community spaces effectively.
Why are these activities important?
IADLs are critical because they comprehensively measure an individual’s functional status, particularly among community-dwelling older adults. These activities indicate a person's ability to perform complex tasks, providing insights into their cognitive and physical health. Being able to carry out IADLs correlates with a person's ability to live independently, maintain social relationships, and participate fully in society. Issues with IADLs can often signal the onset of cognitive impairment or physical decline, necessitating interventions to prevent further deterioration.
What would prevent a person from performing and accomplishing these activities?
Various factors can impede an individual's ability to perform IADLs, including cognitive impairment, physical disabilities, and chronic health conditions. Cognitive issues, such as dementia, can make it difficult for individuals to plan meals, manage medications, or handle finances. Physical limitations stemming from conditions like arthritis or stroke can impair one's ability to perform tasks requiring manual dexterity or mobility, such as food preparation and housekeeping. Environmental barriers and lack of social support can also play significant roles in limiting an individual’s capacity to perform IADLs.
IADLS Assessment Template
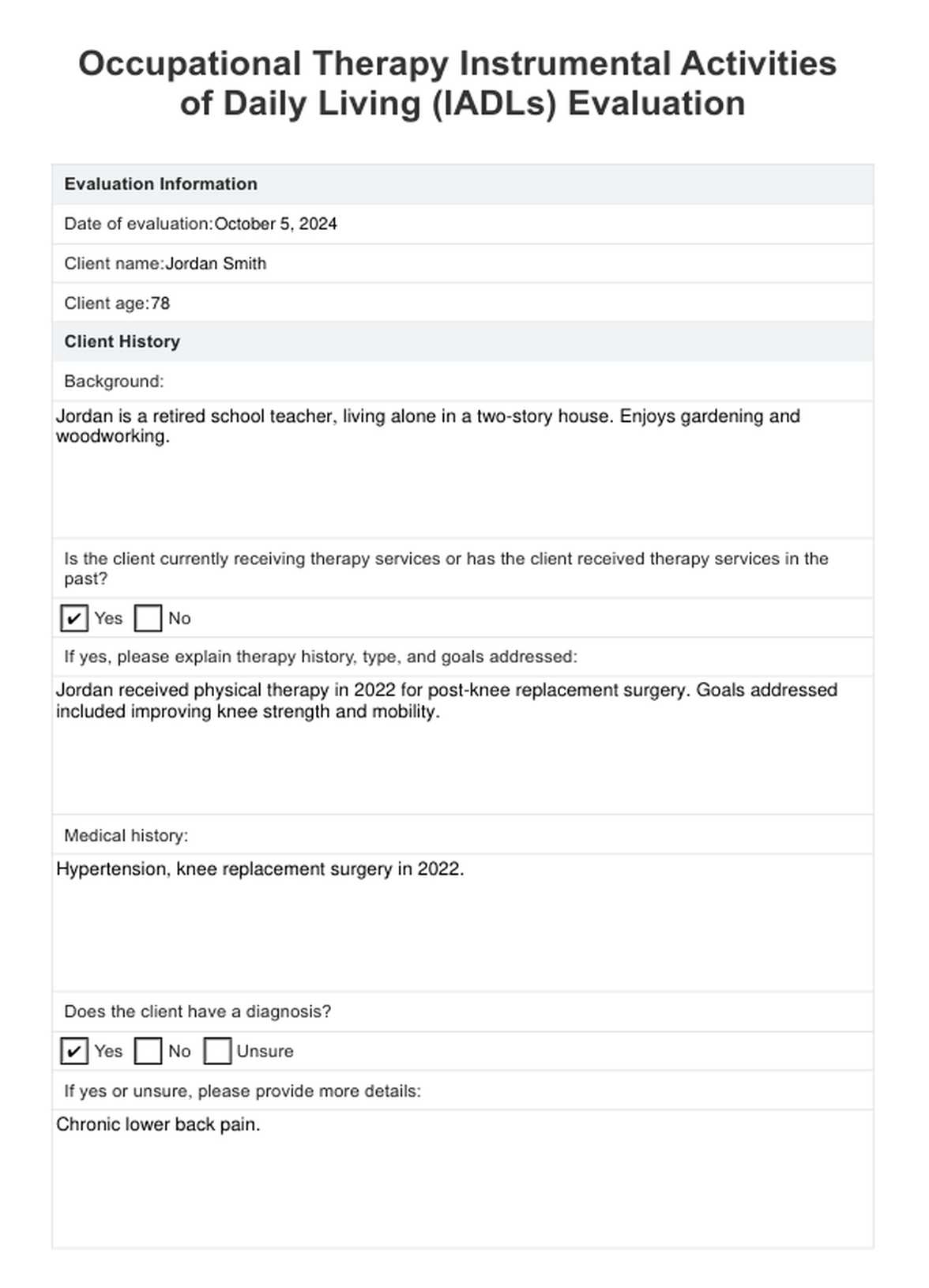
IADLS Assessment Example
What is the IADLS Assessment?
Occupational Therapy Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs) Assessment is a process used by occupational therapists to assess an individual's ability to perform daily activities that are necessary for independent living. These activities, also known as IADLs, are tasks that require more advanced skills and coordination compared to basic activities of daily living (ADLs).
IADLs Assessment evaluates an individual's functional abilities and performance in tasks such as meal preparation, housekeeping, managing finances, using transportation, and shopping. These activities are crucial for maintaining independence and overall quality of life.
As people age or experience a decline in physical or cognitive abilities due to injury or illness, they may struggle with these tasks. An IADL s assessment helps occupational therapists to identify any difficulties an individual may have and develop a personalized treatment plan to improve their ability to perform these tasks.
Next steps after this assessment
After conducting the IADL assessment, the next steps typically involve developing a tailored intervention plan to address identified needs. This may include occupational therapy to improve specific skills, modifications to the home environment to enhance safety and accessibility, and connecting individuals with community resources. For those with cognitive impairments or chronic conditions, interventions might also focus on medication management strategies and cognitive rehabilitation to maintain or improve functional abilities.
How does our IADLS Assessment template work?
Our IADLS Assessment template provides a structured format to systematically evaluate an individual's ability to perform instrumental activities of daily living. It guides the assessor through each activity, offering a consistent method for scoring and documenting the individual's level of independence. This template simplifies the assessment process, ensuring that all relevant areas are covered and facilitating the identification of specific needs for intervention.
When is this assessment usually conducted?
The timing of an IADL assessment is critical for maximizing its benefits and ensuring appropriate care. This assessment is commonly utilized:
- During routine check-ups: Healthcare providers may incorporate the IADL assessment into regular health evaluations for older adults or those with known chronic conditions. This proactive approach helps in early identification of potential declines in functional abilities.
- Upon admission to rehabilitation facilities: An IADL assessment is often conducted to establish a baseline of functional abilities for individuals admitted to rehabilitation facilities. This aids in creating a personalized rehabilitation plan to restore or enhance the patient’s independence in daily activities.
- Following hospitalization: After a hospital stay due to surgery or acute illness, an IADL assessment can be crucial in planning the transition back to home life. It helps determine the level of care and support the individual will need.
- Observation of decline: Family members, caregivers, or individuals may notice difficulties in performing daily tasks. Such observations can prompt an IADL assessment to understand the underlying issues and adjust care accordingly.
- Annual wellness visits: For older adults, incorporating IADL assessments into annual wellness visits can track changes over time, helping to identify subtle declines that might not be immediately obvious.
By conducting the IADL assessment at these strategic times, healthcare professionals can ensure that individuals receive the suppo
Benefits of using this assessment
The IADL assessment is more than just a tool for evaluating an individual's ability to perform daily tasks; it is integral to holistic care planning. The benefits of utilizing this assessment include:
Holistic understanding of patient needs
The IADL assessment offers a comprehensive view of an individual’s capabilities and challenges by evaluating various daily activities. This holistic understanding is essential for creating personalized care plans.
Early intervention
Identifying difficulties in performing IADLs can signal the onset of physical or cognitive decline. Early detection allows for interventions that can slow progression, maintain current levels of function, or even improve abilities.
Tailored care plans
The detailed insights gained from an IADL assessment enable healthcare professionals to tailor care plans to the individual's specific needs, whether that involves home modifications, occupational therapy, or other supportive measures.
Empowering individuals
The assessment can empower individuals and their families to make informed decisions about their care and living arrangements by identifying areas where support is needed.
Facilitates communication among the care team
The IADL assessment results can facilitate communication among various care team members, including doctors, therapists, and family members, ensuring that everyone is aligned in the care approach.
Baseline for monitoring
Establishing a baseline allows ongoing monitoring of an individual's function over time. This is crucial for adjusting care plans in response to changes in individual abilities, ensuring that interventions remain appropriate and effective.
Enhances quality of life
Ultimately, using the IADL assessment aims to enhance individuals' quality of life by ensuring they have the support they need to perform daily activities, remain independent, and participate in their community as fully as possible.
Incorporating the IADL assessment into care practices not only aids in the early detection and intervention of functional declines but also supports creating a more responsive and personalized healthcare system that adapts to the evolving needs of older adults and those with chronic conditions.
Commonly asked questions
IADLs involve more complex activities necessary for independent living, while ADLs are basic self-care tasks.
Yes, targeted interventions, such as occupational therapy, can improve an individual's ability to perform IADLs.
Regular assessments are recommended to update care plans and interventions as needed, especially after significant health changes.

.jpg)

















-template.jpg)