High-Functioning Autism in Adults Checklist
Streamline the evaluation of high-functioning autism in adults using our concise checklist template for effective assessment and monitoring.


What is an autism spectrum disorder (ASD)?
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how individuals communicate and interact with others and how they experience and process sensory stimuli. It is characterized by difficulties in social communication and interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
It's important to understand that ASD is a spectrum disorder, meaning that individuals with ASD can exhibit a wide range of symptoms, abilities, and autistic traits. Some individuals may have more severe impairments, while others may have milder symptoms and above-average intelligence (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
While ASD is typically formally diagnosed in childhood, many adults with milder forms of the disorder may not receive an autism diagnosis until later in life. This can lead to challenges with their mental health, navigating social situations, and managing sensory sensitivities in everyday life (Henninger & Taylor, 2013).
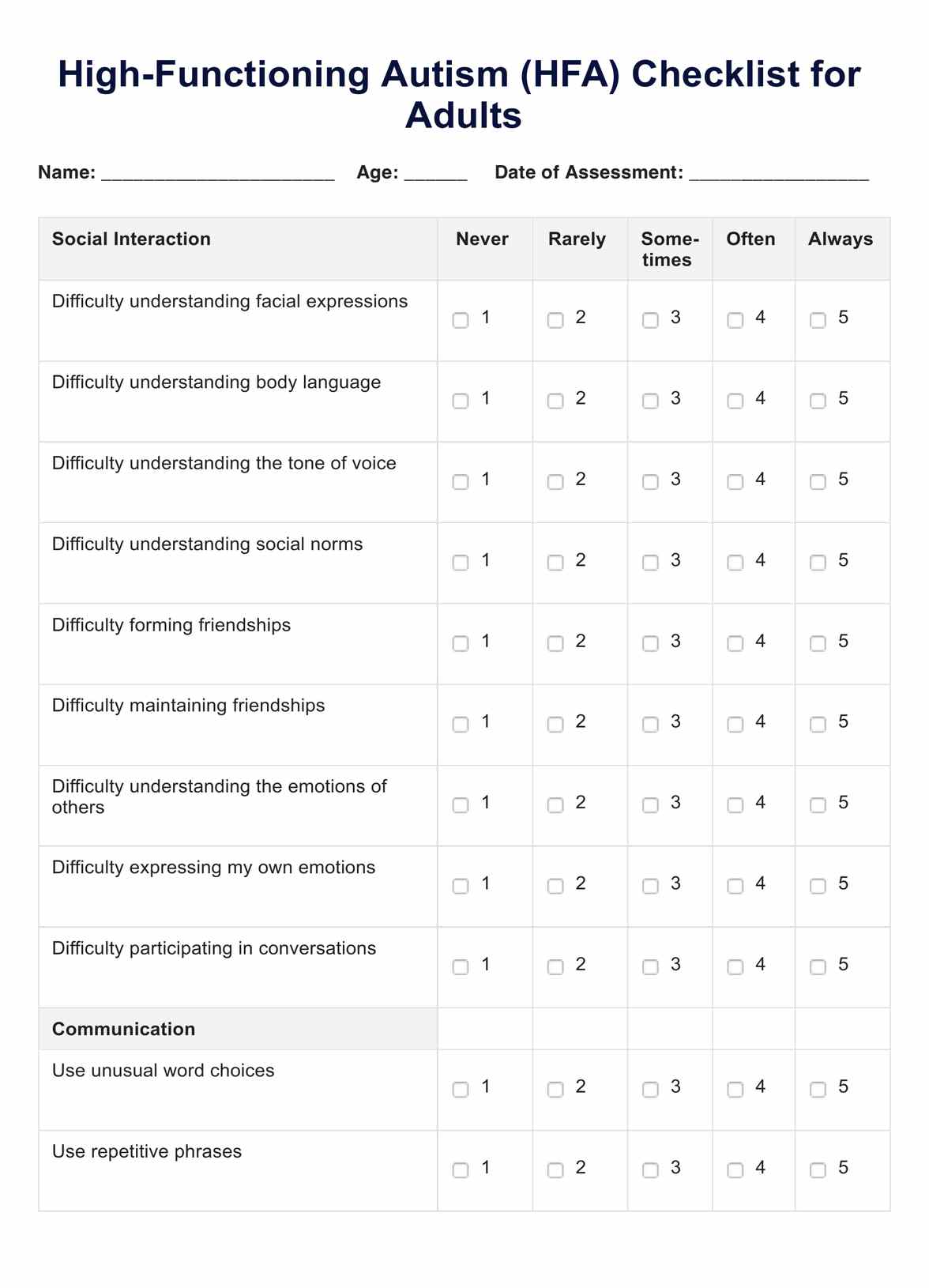
High-Functioning Autism in Adults Checklist Template
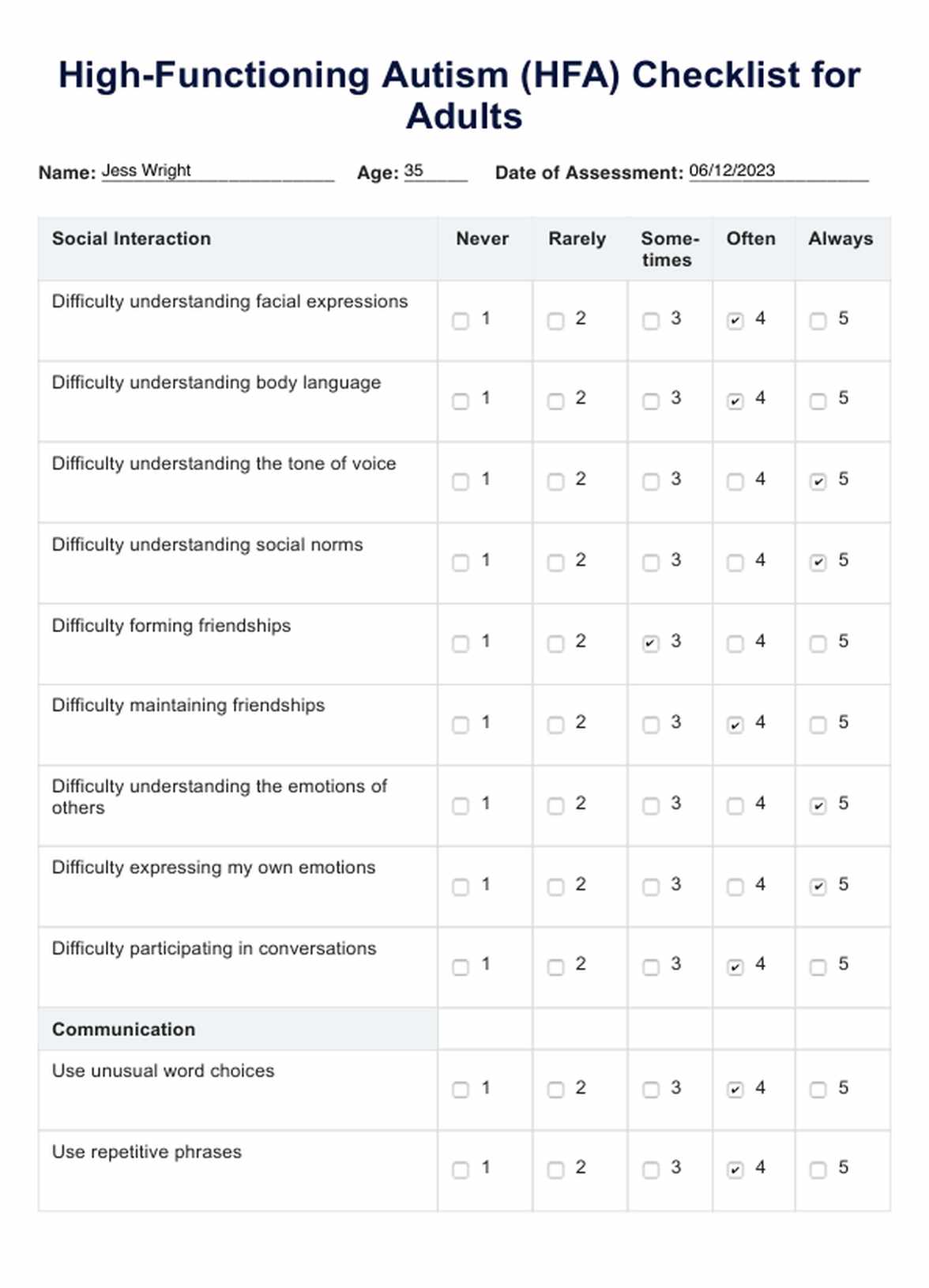
High-Functioning Autism in Adults Checklist Example
Autism symptoms in adults checklist
The following checklist of common signs can help identify potential signs of autism in adults (Barlow et al., 2022). However, only a qualified professional can provide a formal diagnosis.
Social interactions and communication
Individuals with autism often experience challenges in understanding and navigating social situations and communication. Some common signs include:
- Difficulty understanding social cues, facial expressions, and body language
- One finds it difficult to maintain eye contact
- Struggles with back-and-forth conversation
- Use of overly formal language or own unique phrases
- Difficulty initiating or maintaining close friendships and meaningful relationships
Restrictive interests and repetitive behaviors
Restricted interests and repetitive behaviors are core characteristics of ASD. These may manifest in the following ways:
- Fixation on specific interests to an excessive degree
- Need for routines and dislike of change
- Repetitive body movements like rocking or hand-flapping
- Repetitive language
- Highly focused interests that dominate conversations
Sensory processing differences
Individuals with autism often experience sensory input differently from neurotypical individuals, which can lead to:
- Over or under-sensitivity to lights, sounds, smells, textures
- Very strong reaction to sensory input that others ignore
- Sensory overload in everyday environments
Additional traits
In addition to the core symptoms, some other potential indicators of autism in adults include:
- Exceptional skills in a particular area
- Difficulty multitasking
- Literal interpretation of language
- Trouble regulating emotions
While having some autistic traits does not necessarily mean an autism diagnosis, if an adult is experiencing significant challenges, they should seek an evaluation from a qualified health professional. An early diagnosis can help individuals develop coping strategies and build meaningful social relationships.
How does it work?
This adult autism checklist is a valuable tool that a health professional can use to identify potential signs of high-functioning autism spectrum disorder in adults. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use this checklist effectively:
Step 1: Administer the checklist
Provide the client with the High-Functioning Autism in Adults Checklist and ask them to rate each item based on the frequency with which they experience or exhibit the described behavior or trait. The checklist covers three main areas: social interaction, communication, and restricted interests/repetitive behaviors. This can also be used during a clinical interview.
Step 2: Evaluate the responses
Once the checklist is completed, review the individual's responses carefully. Pay particular attention to items rated as "often" or "always," as these may indicate potential areas of concern. It's important to note that not all items need to be endorsed for a diagnosis of high-functioning ASD, as the condition presents differently in each individual.
Step 3: Gather additional information
Use the checklist as a starting point for further assessment and evaluation. Conduct a comprehensive interview with the individual, gathering more detailed information about their experiences, challenges, and strengths. It may also be helpful to involve close family members or friends who can provide additional insights and observations.
Step 4: Consider a formal assessment
If the checklist and additional information gathered suggest a strong possibility of high-functioning ASD, recommend a formal assessment by a qualified professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist specializing in autism spectrum disorders.
When would you use this template?
The High-Fuctioning Autism in Adults Checklist can be a valuable tool for healthcare practitioners to consider utilizing in various situations when assessing or supporting individuals who may be on the autism spectrum. Here are some scenarios where this checklist could be beneficial:
Screening tool for healthcare professionals
Healthcare professionals, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, or primary care physicians, can use the checklist as a screening tool during initial assessments. The checklist helps identify potential high-functioning autism traits and guides further evaluation.
Identifying comorbid conditions
The checklist can help identify potential comorbid conditions associated with high-functioning autism, such as anxiety, depression, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Recognizing these conditions allows for comprehensive treatment and management.
Guiding treatment planning
The checklist findings can inform treatment planning decisions, ensuring that individuals with high-functioning autism receive appropriate interventions tailored to their specific needs. This may include psychotherapy, medication, learning coping strategies, or healthier emotional responses.
Monitoring treatment effectiveness
The checklist can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment interventions, assessing whether symptoms are improving or if adjustments to the treatment plan are needed.
Providing psychoeducation
The checklist can also be a valuable resource for psychoeducation and awareness-raising efforts. By reviewing the items on the checklist, individuals and their families can gain in-depth knowledge of the various characteristics and challenges associated with high-functioning autism.
Strategies in managing an autism diagnosis among adults
Receiving an autism spectrum disorder diagnosis as an adult can bring a range of emotions and challenges. However, with the right strategies and support, individuals can learn to embrace their unique strengths and find ways to manage the associated difficulties.
Seek professional support
Working with professionals who specialize in ASD can be invaluable. Therapists, counselors, and support groups can guide on coping mechanisms, communication strategies, and practical tools for navigating daily life with autism.
Build a support network
Connecting with others who understand the experience of being an autistic adult can be incredibly empowering. Having a support network, whether an in-person or online autism community, can offer a sense of belonging, validation, and a wealth of shared knowledge.
Develop self-advocacy skills
Learning to develop strategies to communicate one's needs and advocating for appropriate accommodations is crucial. Self-advocacy skills can help individuals take control and create more inclusive environments.
Embrace special interests
Rather than viewing intense interests or hyperfocus as a limitation, many adults might find that specific traits or signs of ASD can positively impact life. Embracing special interests can lead to personal growth, career opportunities, and a sense of purpose.
Practice self-care
Individuals with autism often experience sensory sensitivities, anxiety, and emotional dysregulation. Developing self-care strategies, such as mindfulness techniques, exercise routines, or sensory accommodations, can help manage overwhelming situations and promote overall well-being.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Pearson.
Barlow, D. H., Durand, V. M., & Hofmann, S. G. (2022). Psychopathology: An integrative approach to mental disorders (9th ed.). Wadsworth.
Henninger, N. A., & Taylor, J. L. (2013). Outcomes in adults with autism spectrum disorders: a historical perspective. Autism, 17(1), 103–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362361312441266
Commonly asked questions
Adults with autism may exhibit various behaviors, including difficulties with social interactions, communication, and repetitive behaviors. They may have trouble understanding social cues, initiating or maintaining conversations, and reading nonverbal signals. They may also exhibit repetitive behaviors like hand flapping or rocking and have vital interests or fixations on specific topics.
The diagnostic criteria for autism in adults are based on the DSM-5, which defines autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple contexts, as manifested by deficits in social-emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communicative behaviors, and developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships.
Autism in adults can be confused with other conditions, such as social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, or intellectual disability. Some individuals may be misdiagnosed with a different condition due to the overlap in symptoms.


















-template.jpg)