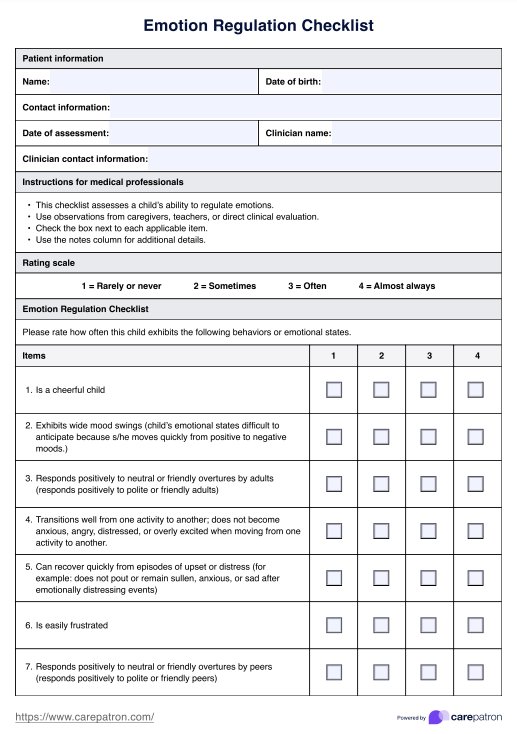
Emotion Regulation Checklist
Download Carepatron's free Emotion Regulation Checklist PDF to effectively manage and regulate patients' emotions.


What is emotion regulation?
Emotion regulation is the process of managing emotions for personal and social purposes. It is essential for social competence, psychological well-being, and mental health stability (Thompson et al., 2008). It is a critical function in developmental psychology, influencing mental well-being, decision-making, and dyadic and family relations. Effective emotion regulation helps individuals control negative emotions, reducing impulsive reactions and fostering thoughtful responses.
In clinical child psychology, emotion regulation is significant in school-age children, as it supports emotional self-awareness and the ability to handle stress. As children grow into young adults, emotion regulation becomes vital for interpersonal competence, allowing them to navigate social interactions and relationships effectively. Deficits in this skill, known as emotion dysregulation, are linked to behavioral challenges and mental health disorders.
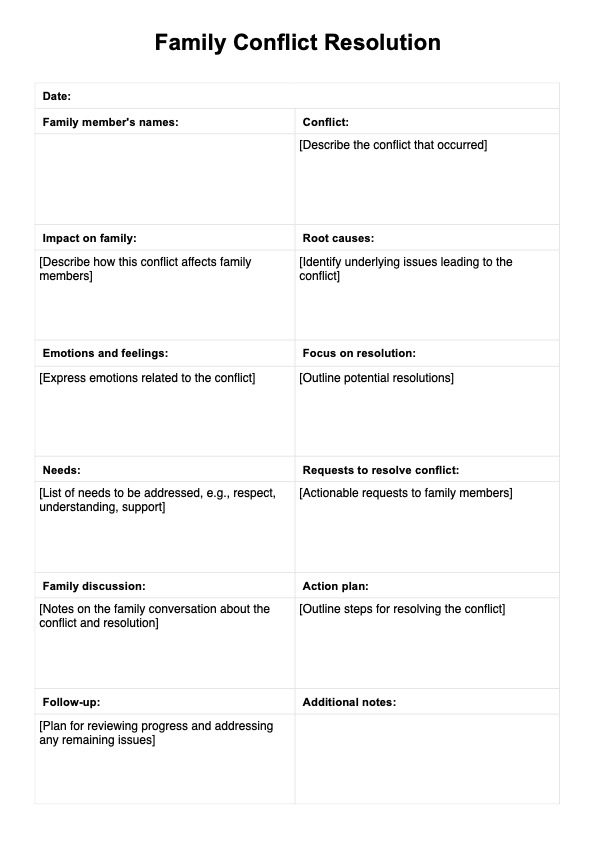
Emotion Regulation Checklist Template
Emotion Regulation Checklist Example
What is an Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC)?
The Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) is a structured emotion regulation assessment battery used to evaluate children’s self-regulation and ability to manage positive emotions and negative emotional responses (Shields & Cicchetti, 1997). The ERC provides measurable insights into emotional regulation skills through informant-based ratings and is designed primarily for child development research and clinical assessment.
The ERC consists of 24 items categorized into two subscales: Emotional Lability/Negativity (L/N) and Emotion Regulation (ER). The L/N subscale assesses emotional instability, mood shifts, and difficulties controlling negative affect, while the ER subscale evaluates adaptive emotional responses, young adults’ interpersonal competence, and situational appropriateness.
Unlike self-reported tools like the emotion regulation scale or criterion Q-sort scale, the ERC relies on external observations from caregivers, educators, or clinicians. This ensures an objective perspective on a child’s emotional adaptability in different environments.
How does it work?
The Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) by Carepatron is designed to streamline emotion regulation assessments in clinical settings. It helps medical professionals evaluate emotional regulation skills, interpret findings, and guide interventions effectively. Below are the key steps to integrating the ERC into your workflow.
Step 1: Access the template
Click “Use template” to open and customize the Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) in the Carepatron app. This digital format ensures efficiency, allowing you to assess patients in real time and store data securely for future reference.
Step 2: Introduce the checklist to the patient
Explain the ERC’s purpose to caregivers, educators, or relevant professionals involved in the child’s assessment. Clarify that the checklist evaluates emotion regulation abilities based on observed behaviors rather than self-reporting. Establishing clear expectations ensures accurate and reliable responses from informants.
Step 3: Use the checklist in your assessment workflow
Incorporate the ERC into standard emotion regulation assessments by rating each item based on observed behaviors. The checklist covers positive and negative emotions, comprehensively evaluating the patient’s emotional stability, adaptability, and responsiveness to different situations.
Step 4: Gather and interpret data
Once the checklist is completed, analyze the emotion regulation abilities across subscales. Identify patterns of greater emotion dysregulation or adaptive responses. Compare findings with other assessment tools like the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire to develop a well-rounded understanding of the patient’s emotional strengths and challenges.
Step 5: Provide patient education and next steps
Use the ERC results to inform treatment planning, intervention strategies, or caregiver guidance. Discuss findings with the patient’s support network, recommending evidence-based approaches for improving emotional self-awareness and regulation. Provide follow-up resources or interventions tailored to the patient’s developmental stage and specific regulatory needs.
Scoring and interpretation
Scores are typically calculated by summing the ratings for each subscale. Additionally, an average score can be computed by dividing the total score by the number of items in each subscale.
- Emotion Regulation (ER) Subscale (8 items: 1, 3, 7, 15, 16, 18, 21, 23; range: 8–32) assesses emotional self-awareness, empathy, and appropriate affective responses. Items 16 and 18 are reverse-scored. Higher scores reflect stronger regulatory abilities.
- Emotional Lability/Negativity (L/N) Subscale (15 items: 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 17, 19, 20, 22, 24; range: 15–60) measures mood instability, emotional inflexibility, and frequent negative emotions. Items 4, 5, 9, and 11 are reverse-scored. Higher scores indicate increased emotional dysregulation.
Item 12 does not load onto either subscale but provides insight into other child behaviors.
Interpreting the ERC involves comparing subscale scores. Higher ER scores suggest effective emotional regulation and positive socio-emotional functioning. Conversely, higher L/N scores may indicate difficulty managing emotional responses, impacting childhood social competence and early school adjustment. The ERC helps clinicians identify risk factors and develop targeted interventions to support an individual’s emotional regulation abilities.
Benefits of using this checklist
The Emotion Regulation Checklist is a valuable tool for medical professionals assessing a child’s ability to manage emotions. It provides structured data on affective stability and emotional responsiveness, aiding clinical decision-making. The checklist’s internal consistency ensures reliable assessments across different age ranges, from early childhood through adolescence.
The regulation checklist helps clinicians identify emotional dysregulation patterns by systematically evaluating negative emotions, such as angry outbursts, and positive emotional regulation strategies. This allows for targeted interventions that promote adaptive behavior and social-emotional development. The ERC also assesses responses to neutral or friendly overtures, providing insights into children's social interactions.
Integrating the ERC into routine assessments enhances accuracy in diagnosing emotional difficulties and tracking progress over time. Its structured format saves time by offering a clear framework for evaluating emotional control, making it a practical and efficient tool for medical professionals.
References
Boelens, E., Van Beveren, M.-L., De Raedt, R., Verbeken, S., & Braet, C. (2021). Are emotion regulation strategies associated with visual attentional breadth for emotional information in youth? Frontiers in Psychology, 12, Article 637436. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.637436
Jiménez-Picón, N., Romero-Martín, M., Ponce-Blandón, J. A., Ramirez-Baena, L., Palomo-Lara, J. C., & Gómez-Salgado, J. (2021). The relationship between mindfulness and emotional intelligence as a protective factor for healthcare professionals: Systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(10), Article 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18105491
Shields, A., & Cicchetti, D. (1997). Emotion regulation among school-age children: The development and validation of a new criterion Q-sort scale. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 906–916. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.33.6.906
Thompson, R. A., Meyer, S., & Jochem, R. (2008). Emotion regulation. In M. M. Haith & J. B. Benson (Eds.), Encyclopedia of infant and early childhood development (pp. [page range if available]). Academic Press. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780123708779000554
Troy, A. S., Shallcross, A. J., Brunner, A., Friedman, R., & Jones, M. C. (2018). Cognitive reappraisal and acceptance: Effects on emotion, physiology, and perceived cognitive costs. Emotion, 18(1), 58–74. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000371
Commonly asked questions
The Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) is a structured assessment tool medical professionals use to evaluate a child’s ability to regulate emotions. It measures negative emotions, affective stability, and adaptive behavior, helping clinicians identify emotional regulation challenges across different age ranges.
The five steps of emotional self-regulation include recognizing emotions, understanding emotional triggers, developing coping strategies, applying regulation techniques, and evaluating outcomes. These steps help individuals manage angry outbursts, respond appropriately to neutral or friendly overtures, and build emotional resilience.
The four emotional regulation Rs are Recognize, Reflect, Regulate, and Respond. This framework helps individuals identify emotional states, assess their impact, implement adaptive behavior strategies, and adjust responses to maintain affective stability.
Effective emotion regulation strategies include mindfulness meditation, cognitive reappraisal, attentional deployment, and journaling. These techniques enhance internal consistency, improve emotional control, and reduce negative emotions across developmental stages.





















-template.jpg)