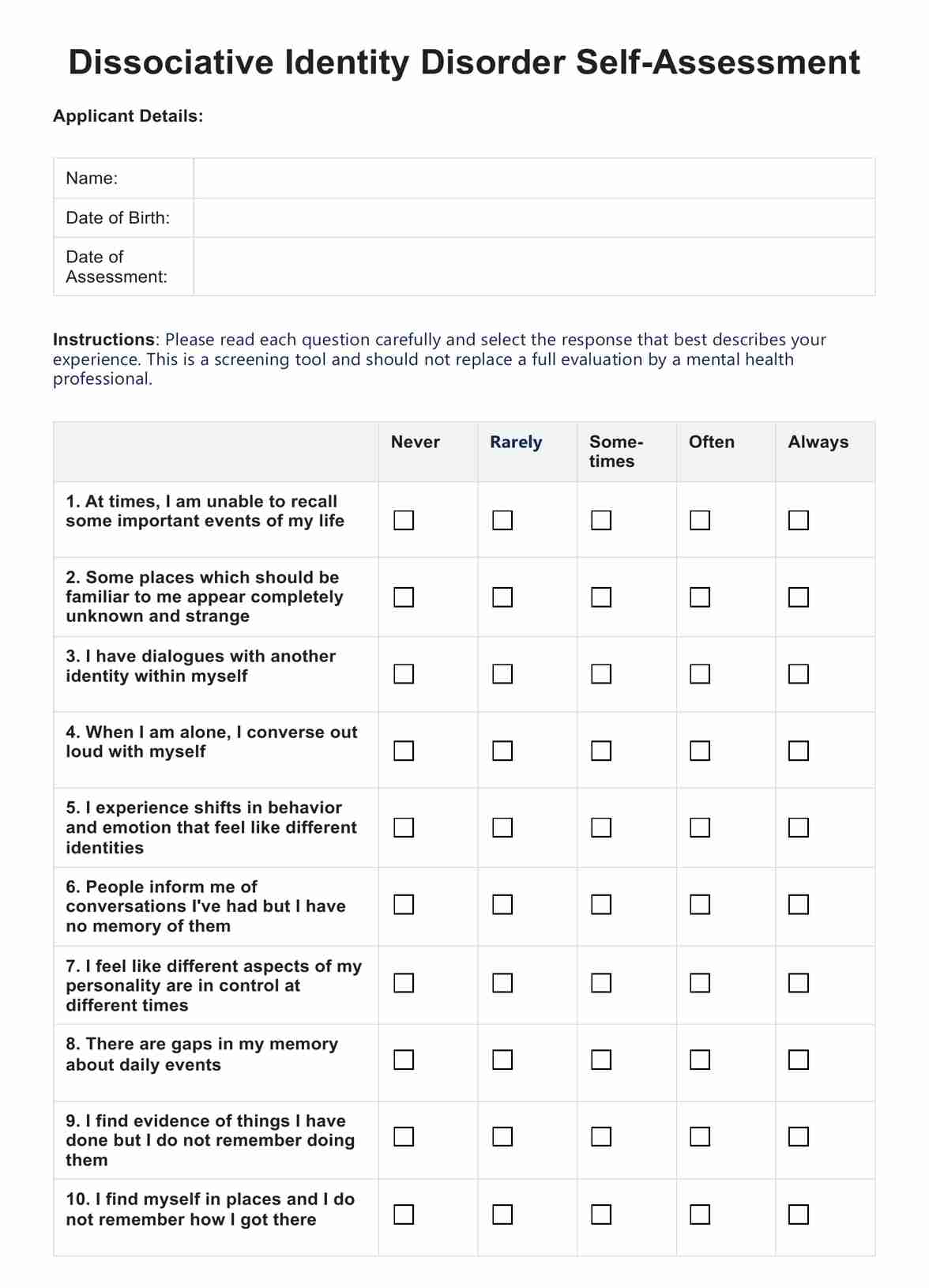
What are dissociative disorders?
Dissociative disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by disruptions or breakdowns in different areas of psychological functioning. This affects memory, identity, consciousness, and perception of the self and the environment (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
The main dissociative disorders include:
Dissociative identity disorder (DID)
This mental illness, formerly known as Multiple Personality Disorder, involves the presence of two or more distinct personality states or separate identities that recurrently take control of the individual's behaviors through everyday events.
Dissociative amnesia
This form of dissociative disorder is characterized by memory loss. Dissociative amnesia involves an inability to recall important personal information, usually associated with a highly stressful or traumatic past event that is inconsistent with ordinary forgetting.
Depersonalization/derealization disorder
This mental health condition involves persistent or recurrent experiences of feeling detached or disconnected from one's mind, self, body, or reality.
Dissociative symptoms can also occur in other mental health conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and as a result of certain medical conditions or substance use (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).