Coping Strategies for Stress PDF
Check out our Coping Strategies for Stress PDF and use it for patients dealing with stress constantly or for yourself!


What is stress?
Stress is a natural response that manifests physiologically and psychologically. We all experience it now and then, especially when dealing with things we deem challenging, like juggling several types of work, preparing for a wedding, and having financial troubles.
We also experience stress when we go through something threatening (especially traumatic experiences), like being ganged up by bullies, getting a subpoena, and being told you'll be fired if you make a mistake.
Other examples of stressful situations include losing a loved one, going through a divorce, getting into an accident, and losing your home to a fire. All of these situations can be referred to as stressors.
Whenever we get stressed, our bodies release cortisol and adrenaline hormones.
The former helps regulate our stress response and our blood pressure, helps our metabolism, and helps manage our sleep-wake cycle, but too much of it can lead to weight gain, muscle weakness, a spike up in blood sugar (which can lead to diabetes), and weaken our bones.
The latter can help us focus on what we're dealing with, but too much of it can cause anxiety and nervousness. We might even start shaking and feel tingles in our bodies. It can even prevent us from sleeping when we're supposed to, which can lead to insomnia. Those with pre-existing heart problems become more at risk of heart damage, too.
Given the adverse effects of having too much of these hormones, we can say that stress can lead to a wide variety of mental and physical health problems. For the benefit of our mental health and physical health, we need to develop healthy coping methods for managing stress.
By effectively managing stress, we can prevent it from leading to mental health issues like anxiety disorders and depression, as well as physical health issues like hypertension, stroke, and diabetes.
Coping Strategies for Stress PDF Template
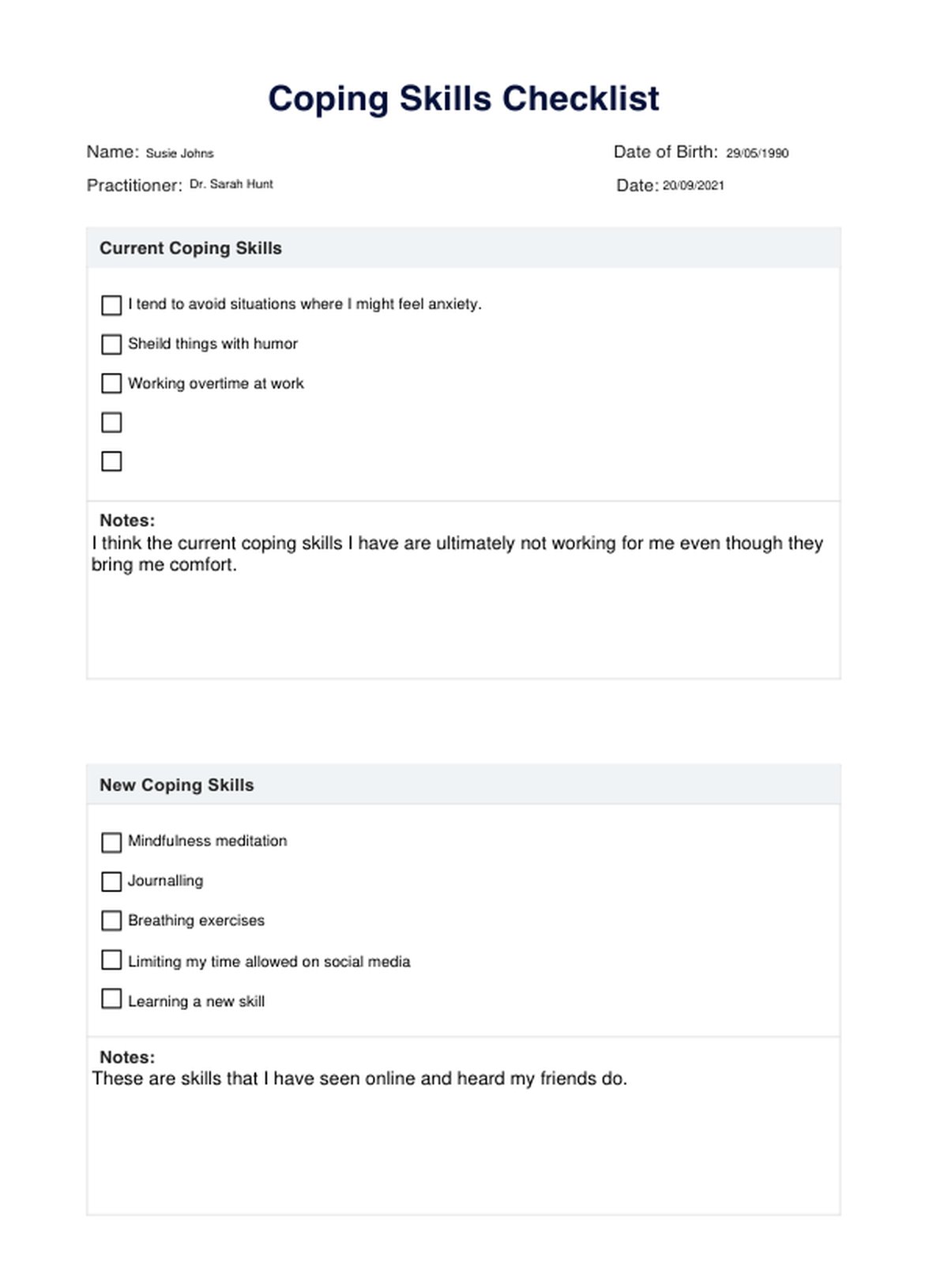
Coping Strategies for Stress PDF Example
How does one manage stress effectively?
Whether the stress experienced is academic stress, stress in the work environment, stress due to interpersonal conflict, psychological stress, or any stress, healthily coping with stress is essential. We can do so by having a coping strategy composed of various coping skills and mechanisms to help us regulate our emotional responses, fortify our psychological resilience, and help us soothe ourselves to calm down.
To manage stress effectively, a person must first identify and understand their specific stressors (these can change over time) because understanding them is half the battle. They can do so by seeing a specialist to discuss their stressors. Specialists who focus on mental health can help guide people to unpack what they feel when faced with stressors, and they can issue assessments like the Perceived Stress Test to evaluate a person's stress levels.
Once the person adequately identifies these stressors and understands how they affect their overall well-being, they can determine what coping mechanisms and skills they can add to their coping strategy.
What are examples of such coping skills?
Learning time management.
Schoolwork and office work are everyday stressors, and depending on their school or employer, the demands might be higher than others, leading to increased stress levels. If that is the case for a person, what they can do is learn time management. Time management can teach a person to set realistic goals and personal deadlines.
They can learn how to break down their work into manageable steps and determine what they should prioritize first instead of becoming flustered and overwhelmed by the amount of work they must do.
Make the necessary lifestyle adjustments.
Some people cope with stress in unhealthy ways. Some end up committing substance abuse or alcohol abuse as a way to manage. Some overeat. These are just examples of unhealthy ways of coping and can lead to various health issues on top of the adverse effects of stress they might already be dealing with.
Suppose this is the case for a person. In that case, they can attend counseling or therapy programs that focus on getting rid of addiction-related behaviors so they can unlearn these addictive behaviors and adopt healthy lifestyles to help them recover and maintain excellent overall physical well-being.
Even if they don't have addiction-related behaviors or negative psychological responses, making healthy lifestyle adjustments can still help. Having a healthy, hearty meal, especially one with vegetables and food that gives omega-3 fats, can regulate cortisol levels.
Regular exercise can also reduce stress because exercising can distract us from our stressors.
Practice deep breathing exercises and mindfulness.
Deep breathing exercises and mindfulness can help people calm down whenever their stress makes them anxious. These are exercises that they can do when they have free time, especially after doing something stressful. They can think more clearly and determine how to work through the stress by calming down.
Mindfulness is another exercise they can do because it's known for its anti-depressant and anti-anxiety effects. It lessens stress response and lowers our blood pressure. It can even combat specific stress responses like overeating and taking substances.
How does this Coping Strategies for Stress PDF work?
Now that you know the gist of stress and what examples of coping skills and strategies people can adopt to combat the effects of stress and navigate themselves around the challenges they face, we'd like you to know that we created a Coping Strategies for Stress PDF handout.
This PDF contains a list of exercises and instructions people can try and adopt to combat varying stress levels. Here are the coping skills listed in the PDF:
- The 4-7-8 Breathing Method (taking deep breaths can help lower stress)
- Counting from 1 to 10
- Mindfulness Meditation
- Lifestyle Changes List
- Finding Humor (because laughing at a problem sometimes helps)
- Positive Self-Talk
- Positive Thinking
- Journaling
If you happen to be a mental healthcare professional (psychologist, counselor, cognitive behavioral therapist, etc.), you can use this PDF as a handout to give to patients so they can have a list of coping strategies to refer to when dealing with stress.
If you're not a mental healthcare professional and stumbled upon this guide, you can use it if you need ideas on coping with stress.
What are the benefits of coping methods for stress management?
They can enhance a person's resilience and emotional well-being.
Coping methods for stress management can teach people how to manage their emotions and emotional responses to stress through thought exercises that can boost their emotional resilience. These exercises can improve a person's overall mood, happiness, and confidence to properly examine their stressors and develop ways to work around them.
Being more resilient means that, when they get stressed, they won't immediately panic or turn to unhealthy coping habits like drinking, substance use, or shut down. Instead, they can step back and think about working around their stressors. This also means that they become better at problem-solving skills.
It can help people maintain their focus.
If one is stressed, depending on the severity, their day might get disrupted, and they will shut down mentally. This isn't good, especially if they have a lot of responsibilities, like activities of daily living and work deliverables.
Having coping mechanisms for stress management can allow people to practice time management and categorize what they must do for the day. Instead of buckling under pressure in a stressful situation involving responsibilities, they can determine what they should prioritize first and then structure their daily responsibilities, beginning with what's urgent and ending with the least urgent task, then direct their focus to what requires the most before doing something else.
They can enhance our psychological health and reduce the physiological impact of stress.
As mentioned earlier, high levels of stress can lead to adverse effects on our psychological health and physical health. It can result in high blood pressure (hypertension), anxiety, depression, palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, insomnia, muscle pains, mood swings, and even diabetes.
Deep breathing exercises can help calm people down, regulate blood pressure, and lessen anxiety. Adopting healthy lifestyle changes such as regularly exercising to de-stress can have health benefits like shaving excess weight and improving immunity.
Other resources for stress management:
The Perceived Stress Scale
Earlier, we mentioned that specialists can assess people using a Perceived Stress Test. They will use the Perceived Stress Scale to do just that. This scale will be answered by the person being evaluated. They only have to answer the following questions:
- In the last month, how often have you been upset because of something that happened unexpectedly?
- In the last month, how often have you felt you could not control the important things?
- In the last month, how often have you felt nervous and stressed?
- How often have you felt confident about handling your personal problems in the last month?
- In the last month, how often have you felt that things were going your way?
- In the last month, how often have you found that you could not cope with everything you had to do?
- In the last month, how often have you been able to control irritations in your life?
- In the last month, how often have you felt that you were on top of things?
- In the last month, how often have you been angered because of things that happened outside your control?
- In the last month, how often have you felt difficulties were piling up so high that you could not overcome them?
The scale has a set of answer options:
- 0 = never
- 1 = almost never
- 2 = sometimes
- 3 = fairly often
- 4 = very often
The fourth, fifth, seventh, and eighth questions are reverse-scored.
Here are the designations that perceived stress scores fall under:
- Scores ranging from 0-13 would be considered low stress.
- Scores ranging from 14-26 would be considered moderate stress.
- Scores ranging from 27-40 would be considered high perceived stress.
Stress Management Worksheets
If you're a therapist or counselor specializing in treating patients with high-stress levels, having an extensive roster of clinical tools, including assessments like the Perceived Stress Scale above and stress management worksheets, would be best.
Stress management worksheets can help people think about their stress, which they might not have had the opportunity to do if they're always overwhelmed by stress. Some worksheets will have people unpack their stress and identify what causes them. They also ask patients how they plan on tackling these stressors or what they can do to cope.
Some even have goal-setting portions to remind themselves about what they're striving for, which gives them an excellent reason to combat stress.
Commonly asked questions
Acute stress is a type of stress that happens suddenly as a response and should go away in a short while. Chronic stress is a type of stress that lasts for a long time or becomes recurring, and the stress gets worse, mainly when not addressed.
Yes. Drinking herbal teas can soothe people. Aromatherapy is another option because some scents have calming effects.
When the stress has negatively (significantly) impacted a person's daily life and interpersonal relationships, plus has resulted in physical health problems, it would be best to get checked to address stress's mental and physical effects.



















-template.jpg)