Anxiety Thermometer
Download our Anxiety Thermometer template to track anxiety levels. Ideal for young people, parents, and educators. Free PDF example included.


What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a mental health condition characterized by excessive worry, fear, or nervousness that is persistent and can interfere with daily activities. It involves emotional and physical sensations that may include feelings of dread, heightened alertness, rapid heartbeat, and rapid breathing. Anxiety is common among individuals of all ages. It can manifest in various forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic attacks, and social anxiety, impacting one's ability to function effectively in everyday life.
Anxiety symptoms
Anxiety symptoms can manifest in various physical and emotional forms and significantly affect daily life. Common physical symptoms include restlessness, rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and fatigue. Emotional symptoms often feature dread, nervousness, and a constant sense of impending danger or panic. People may also experience difficulty concentrating, irritability, and trouble sleeping. The severity and frequency of these symptoms can vary widely among individuals, making personalized assessment and treatment essential for effective management.
Causes of anxiety
Anxiety can arise from many things, a complex interplay of factors that can vary greatly from person to person. Key triggers include:
- Genetic predisposition: Just as with other traits, the likelihood of experiencing anxiety can be inherited, influencing one's susceptibility to anxiety disorders.
- Environmental stressors: Everyday life events such as job pressures, family issues, or ongoing financial worries are common sources of stress that can escalate into anxiety.
- Life changes or trauma: Major life transitions, whether positive or negative—like moving to a new city, starting a new school, or experiencing a loss—can induce significant anxiety.
- Learned behaviors: From a young age, individuals may learn to become anxious as a response to specific situations based on observed behaviors from parents or significant others.
Understanding these causes is crucial for developing strategies to manage anxiety effectively, particularly in environments involving young people and educational settings where social workers and educators play pivotal roles. A variety of factors, including genetics, environmental stressors, and significant life changes or trauma, can trigger anxiety.
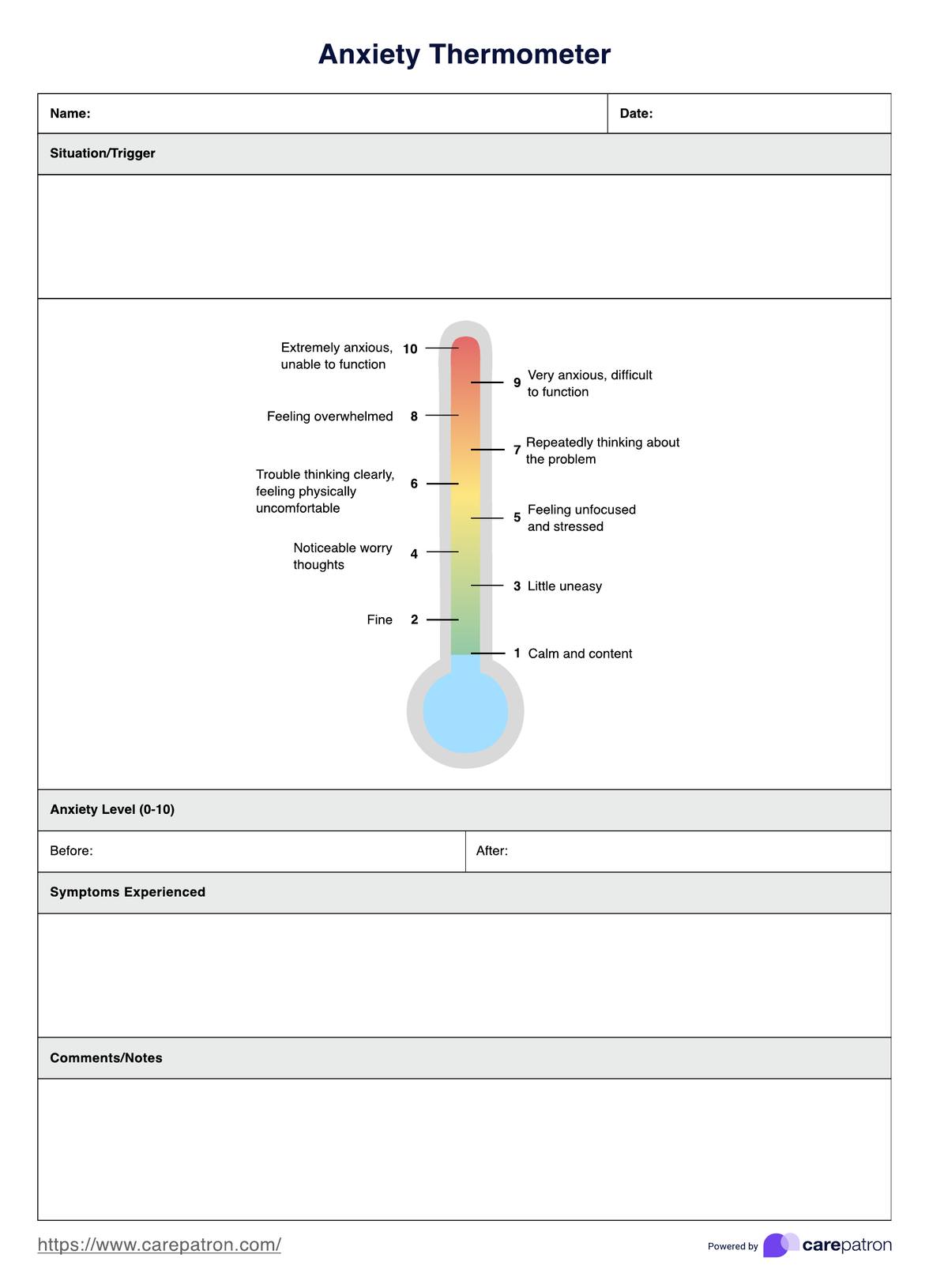
Anxiety Thermometer Template
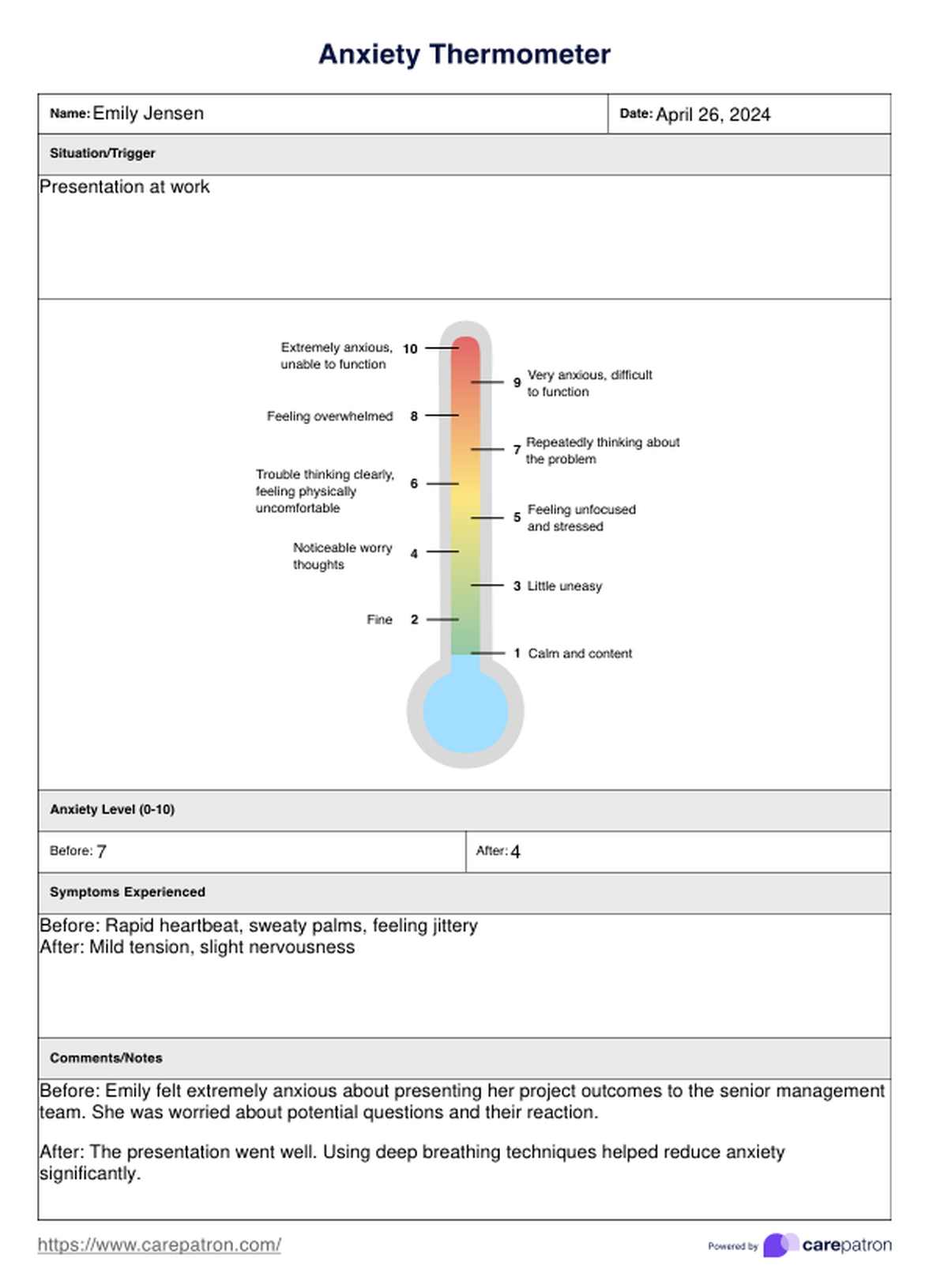
Anxiety Thermometer Example
What is an Anxiety Thermometer?
An Anxiety Thermometer is a therapeutic tool designed to help individuals, particularly children and young adults, quantify their level of anxiety. It features a scale, usually from 0 (indicating no anxiety) to 10 (indicating extreme fear or anxiety), allowing users to express how anxious they feel at any given moment of the day visually.
How is this used?
The Anxiety Thermometer is employed in various settings such as therapy sessions, classrooms, or at home to assist individuals in identifying and communicating their anxiety levels. By regularly marking their current level of anxiety on the thermometer, individuals can facilitate more effective discussions about their emotional state with therapists, teachers, or family members.
What information does it convey?
The Anxiety Thermometer provides a simple yet effective way to measure emotional distress. It offers a clear, numerical representation of how anxious a person feels, making it easier for caregivers and mental health professionals to track anxiety trends over time and adjust intervention strategies accordingly. This tool is particularly valuable in helping young people and those with difficulty verbalizing their emotions to communicate their feelings more clearly.
How to use our Anxiety Thermometer template
Here are the steps as to how you can maximize the use of our printable Anxiety Thermometer template:
Step 1: Download the template
Begin by downloading our free Anxiety Thermometer template from our website. This easy-to-use tool is designed to help monitor and discuss anxiety levels effectively.
Step 2: Customize for individual needs
Adapt the template content to suit the individual's specific needs. This might involve personalizing the format of the scales' content to reflect unique triggers or the most common symptoms experienced by the user.
Step 3: Implement regularly
Incorporate the Anxiety Thermometer into daily or weekly routines to consistently assess anxiety levels. This tool is especially useful in educational settings, therapy sessions, or at home. It provides a visual measure of anxiety that facilitates open discussions between children, teens, students, parents, and educators or counselors.
Step 4: Record and analyze
Record the results over time to identify patterns or triggers of anxiety. This sort of data collection can be invaluable for healthcare providers, social workers, or educators in developing more effective coping strategies and interventions.
Step 5: Review and adjust
Review the effectiveness of the Anxiety Thermometer regularly and make necessary adjustments to the tool or change the management strategies based on feedback and observed outcomes. This ongoing adjustment helps ensure the tool remains relevant and useful in managing anxiety.
By following these steps, users can make the most out of the Anxiety Thermometer template to manage and reduce anxiety in various social and personal contexts.
When is this fear thermometer used?
The Anxiety Thermometer is a valuable resource in various contexts, particularly in educational settings and mental health discussions, aimed at nurturing emotional intelligence among young people. By incorporating items from the Anxiety Thermometer into classroom activities or therapy sessions, educators and mental health professionals can create opportunities for students to develop a deeper understanding of their emotions and how to manage them effectively.
In schools, the Anxiety Thermometer can be integrated into social-emotional learning (SEL) programs to help students constructively recognize and express their feelings of fear. Teachers can use it during group discussions or one-on-one interactions to encourage students to articulate their fear and anxiety and explore coping strategies together.
Similarly, the Anxiety Thermometer is a great visual aid in therapy or counseling sessions to facilitate communication between therapists and young clients. It provides a tangible way for children and adolescents to convey their emotional states, fostering greater self-awareness and enabling therapists to tailor interventions to meet their needs.
Overall, the Anxiety Thermometer offers a practical and accessible tool for promoting emotional intelligence and supporting the mental well-being of young people across various educational and therapeutic settings.
Anxiety treatments and management strategies for developing emotional intelligence
Some treatments used to manage anxiety include:
Therapy
Psychotherapy, particularly Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), is one of the most effective treatments for managing anxiety. It helps individuals identify and challenge the negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety symptoms.
Medication
For some, medication may be necessary to manage symptoms effectively. Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and beta-blockers are commonly prescribed to help reduce the physiological symptoms of anxiety.
Lifestyle adjustments
Incorporating lifestyle changes such as regular physical activity, a healthy diet, sufficient sleep, and mindfulness practices can significantly impact anxiety levels. These adjustments help improve overall well-being and resilience against stress.
Using an anxiety thermometer
An Anxiety Thermometer is a valuable tool in supporting these treatments. It allows individuals and healthcare providers to identify specific triggers and monitor fluctuations in anxiety levels over time. By regularly recording anxiety levels, therapists and patients can see the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments. This ongoing monitoring can also encourage individuals to engage more actively in their treatment plans, fostering a sense of control and empowerment over their anxiety.
Support systems
Developing a strong support network of family, friends, and support groups can also play a crucial role in managing anxiety. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can provide comfort and practical advice for daily challenges.
By combining these treatments, resources, and strategies, individuals dealing with anxiety can find comprehensive support that addresses both the symptoms and the underlying causes of their condition, leading to more effective management and improved quality of life.
Commonly asked questions
Developing emotional intelligence enables better recognition, regulation, and management of emotions, reducing anxiety levels over time.
It provides a simple, effective way to communicate with and support children dealing with anxiety, promoting better management strategies in social and educational environments.

.jpg)

















-template.jpg)