Anxiety Coping Skills Handout
Discover effective Anxiety Coping Skills and strategies to manage and reduce anxiety. Learn the signs, causes, and treatments to improve mental well-being.


What are anxiety coping skills?
Anxiety coping skills are strategies designed to help individuals manage anxiety, reduce stress, and regulate emotional responses. These coping strategies are essential for handling anxiety disorders, as they allow individuals to address both the mental and physical aspects of anxiety. It also allows individuals feeling anxious to identify triggers in stressful situations. When anxious feelings occur to an individual, coping strategies such as relaxation techniques, including breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation (Touissaint et. al., 2021), can provide immediate relief by calming the body and mind.
According to the Anxiety & Depression Association of America (2019), here are some effective anxiety management techniques to lower anxiety:
Relaxation techniques
Relaxation is essential for managing anxiety. Breathing exercises, such as slow, deep breaths, can help calm your mind and body. A simple method involves inhaling for 4 counts, holding for 4 counts, and exhaling for 4 counts. Mindfulness and meditation practices can also bring your focus to the present moment, reducing overwhelming thoughts. Additionally, yoga or gentle stretching routines promote physical relaxation, which can positively impact mental well-being.
Healthy habits
Maintaining healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce anxiety. Start by eating well-balanced meals, as skipping meals or consuming unbalanced diets may increase anxiety. Incorporate daily physical activities like walking, cycling, or yoga to boost endorphin levels and improve mood. It's equally important to avoid substances like alcohol and caffeine, which can exacerbate anxiety and trigger panic episodes. Finally, prioritize sleep hygiene by aiming for 7-9 hours of rest each night with an established bedtime routine.
Cognitive techniques
Cognitive strategies empower you to challenge negative thoughts and maintain a positive outlook. When anxiety arises, practice replacing self-critical or catastrophic thoughts with realistic affirmations. For instance, instead of thinking, "I can’t do this," reframe it as: "I’ll do my best, and that’s enough." Perspective-taking is another helpful tool—pause and ask yourself, "Is this situation really as bad as it seems?" This approach can make challenges feel more manageable and reduce emotional overwhelm.
Building support
Building and maintaining social connections is a powerful way to cope with anxiety. Openly sharing your feelings with trusted friends or family members fosters emotional support and reassurance. Additionally, consider engaging in community activities or volunteering.
Emergency coping tools
When anxiety feels overwhelming, grounding techniques can help you regain control. One effective strategy is the “5-4-3-2-1” technique, which involves engaging your senses by identifying 5 things you see, 4 you can touch, 3 you hear, 2 you smell, and 1 you taste. Another quick method is to count slowly to 10 (or 20 if needed) to calm your mind and bring yourself back to the present moment.
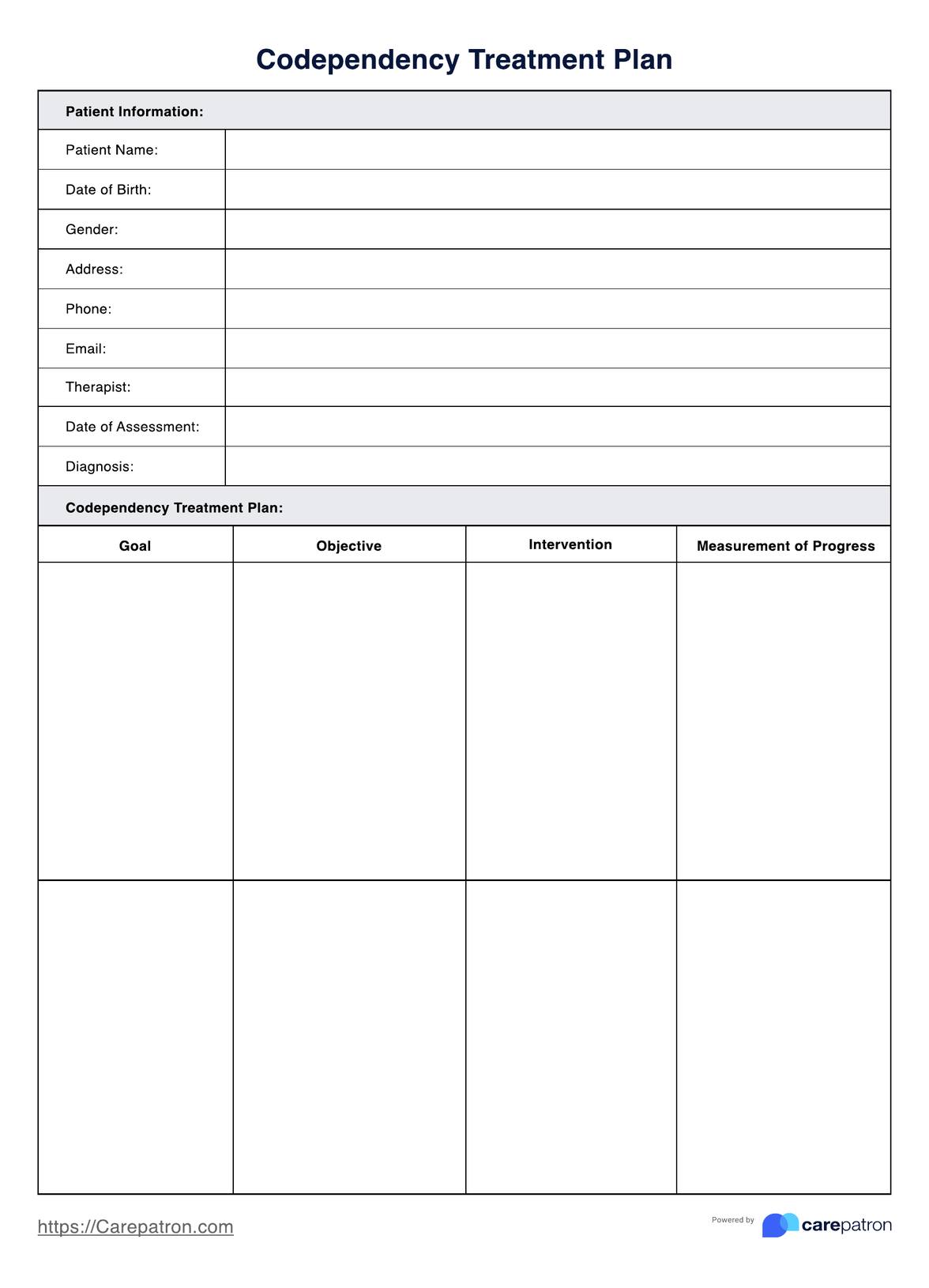
Anxiety Coping Skills Handout Template
Anxiety Coping Skills Handout Example
How does our Anxiety Coping Skills Handout work?
Carepatron's Anxiety Coping Skills Handout is a valuable resource designed to help healthcare practitioners and individuals manage anxiety through proven coping strategies. By following a simple, step-by-step approach, this handout allows for effective assessment and provides practical tools to integrate into daily routines for anxiety management.
Step 1: Access the template
You can find the Anxiety Coping Skills Handout template within this guide. It is easy to download and customize for use with your patients or for personal use. This template helps guides patients in managing anxiety.
Step 2: Use the template during a session
During a session, use the handout as a guide to help your patient alleviate anxiety symptoms and triggers. The template offers many options, so you can easily find which ones work for your patient and tailor a strategy for effective anxiety management. Make sure to hand the patient a copy of the handout.
Step 3: Discuss each coping skill in the handout with the patient
Take time to go through each coping skill listed in the handout with the patient. Explain how each strategy, such as breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, and physical activity, can help manage anxiety. This discussion ensures that the patient understands how to use these skills in real-life situations to alleviate anxiety.
Step 4: Provide further patient education and next steps
After discussing the coping skills, offer additional education on how to integrate these techniques into daily routines. Guide the patient in setting realistic goals for managing anxiety and discuss the next steps, such as scheduling follow-up appointments or seeking added support from a mental health professional, to ensure long-term success.
What are the benefits of having Anxiety Coping Skills?
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (2024), several effective treatments are available for managing anxiety disorders, including psychotherapy, medication, and stress management techniques.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), helps individuals experiencing anxiety identify and change negative thought patterns. Exposure therapy, a CBT method, gradually confronts feared situations to reduce avoidance. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) uses mindfulness to address negative thoughts, providing an alternative to traditional therapies.
Medication
Medications like antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs, and beta-blockers can help manage anxiety symptoms. Antidepressants improve brain chemical balance, while benzodiazepines offer quick relief for acute anxiety. Beta-blockers control physical anxiety symptoms, such as trembling and rapid heart rate, especially during performance situations.
Support groups
Support groups allow individuals with anxiety disorders to share experiences and find encouragement. These groups provide emotional support and can help reduce feelings of isolation. However, group advice should complement, not replace, professional treatment.
Stress management techniques
Techniques like physical exercise, mindfulness, and mindful meditation reduce anxiety symptoms. These practices promote relaxation, ease anxiety, and enhance mental well-being, often complementing other treatments such as psychotherapy for more effective long-term anxiety management.
What are other forms of anxiety treatment?
In addition to standard psychotherapy and medications, there are other forms of anxiety treatment that can be beneficial. These include psychological therapies, physical treatments like medications, and self-help or alternative therapies (Black Dog Insititute, 2021).
Psychological therapies
Psychological therapies, also known as “talking therapies,” can help individuals manage anxiety by changing thought patterns and behaviors. These therapies include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and mindfulness-based treatments. They address the root causes of anxiety and prevent its recurrence. Therapy can be conducted in person, online, or in groups, and often proves to be highly effective for long-term anxiety management.
Physical treatments (medication)
Medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and can complement psychological therapies. Common options include anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, and beta-blockers. Anti-anxiety drugs, such as benzodiazepines, provide quick relief for anxiety, while antidepressants help regulate mood. Beta-blockers control physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
Self-help and alternative therapies
Self-help techniques and alternative therapies can significantly support anxiety management. Practices like exercise, meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques help reduce stress. Good nutrition, omega-3 supplements, and avoiding alcohol and drugs are also essential for mental health. Although self-help therapies can be effective, they are typically more beneficial when used alongside professional treatments for moderate to severe anxiety.
References
Anxiety & Depression Association of America. (2019). Tips. https://adaa.org/tips
Black Dog Institute. (2021). Treatments for anxiety disorders. https://www.blackdoginstitute.org.au/resources-support/anxiety/treatment/
Toussaint, L., Nguyen, Q. A., Roettger, C., Dixon, K., Offenbächer, M., Kohls, N., Hirsch, J., & Sirois, F. (2021). Effectiveness of progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and guided imagery in promoting psychological and physiological states of relaxation. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2021, Article 5924040, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5924040
National Institute of Mental Health. (2024, April). Anxiety disorders. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders
Commonly asked questions
The best coping skills for anxiety include deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, and physical activities like exercise or yoga. These techniques help manage stress, calm the mind, and reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety.
The 3-3-3 rule for anxiety is a grounding technique where you identify three things you can see, three things you can hear, and three things you can touch. This practice helps bring your focus to the present moment and reduces overwhelming feelings of anxiety.
To cope with bad anxiety, try engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation to calm your body. It’s also helpful to challenge anxious thoughts by focusing on positive, realistic perspectives and seeking support from loved ones or a therapist.























-template.jpg)