Look for patterns of behavior that consistently hinder your progress towards goals, accompanied by negative self-talk and fear of success.
Self-Destructive Behavior Test
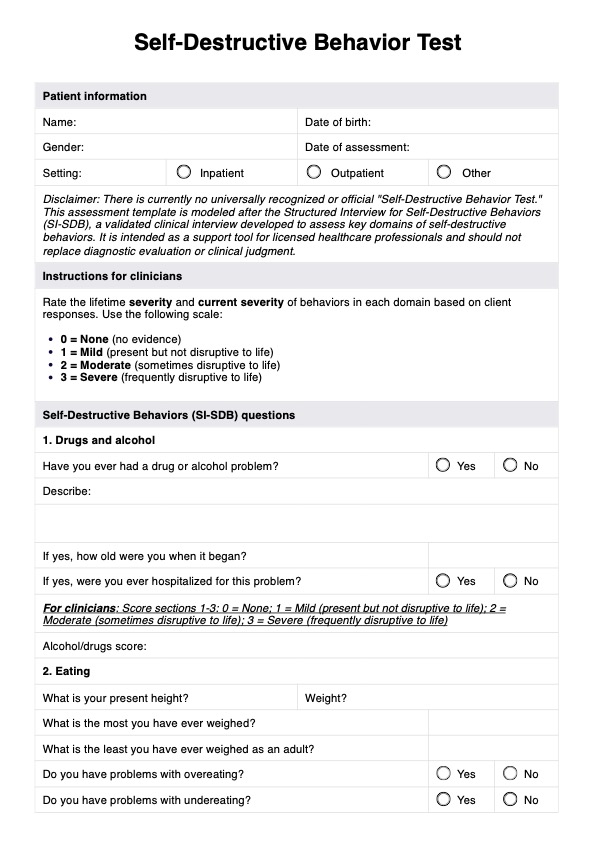
Uncover patterns of self-destructive behavior with our comprehensive test. Identify self-sabotage, understand its causes, and take steps toward healing with our free PDF download.
Use Template
Self-Destructive Behavior Test Template
Commonly asked questions
It often stems from deep-seated beliefs about unworthiness, fear of failure or success, and unresolved emotional trauma.
Underlying mental health issues, negative conditioning from past experiences, and protective mechanisms against perceived threats to one's self-image.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











