Schizoid Personality Disorder Test
Discover if your patient exhibits traits of Schizoid Personality Disorder with our comprehensive test. Tailor your treatment plan and achieve positive clinical outcomes.


What is a Schizoid Personality Disorder Test?
A Schizoid Personality Disorder Test is a self-assessment tool designed to help individuals identify potential traits or symptoms associated with schizoid personality disorder (SPD). SPD is a mental health condition characterized by limited emotional expression, social detachment, and a preference for solitary activities. The test typically consists of questions about emotional expression, social interactions, close relationships, and personal history.
While these tests can provide valuable insights into other personality disorders, they are not a substitute for a clinical diagnosis by a qualified mental health professional. A mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, can conduct a comprehensive evaluation using diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) to determine whether an individual meets the criteria for SPD or any other personality disorder.
SPD may co-occur with other mental health conditions, such as depression or autism spectrum disorder, making accurate diagnosis crucial for proper treatment. Treatment options include talk therapy, coping mechanisms, and medication to address symptoms and improve overall well-being.
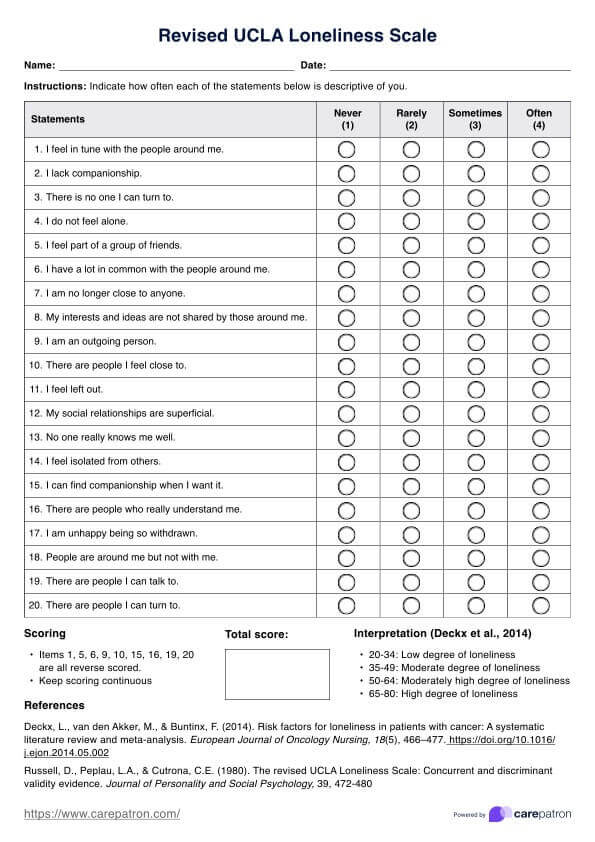
Schizoid Personality Disorder Test Template
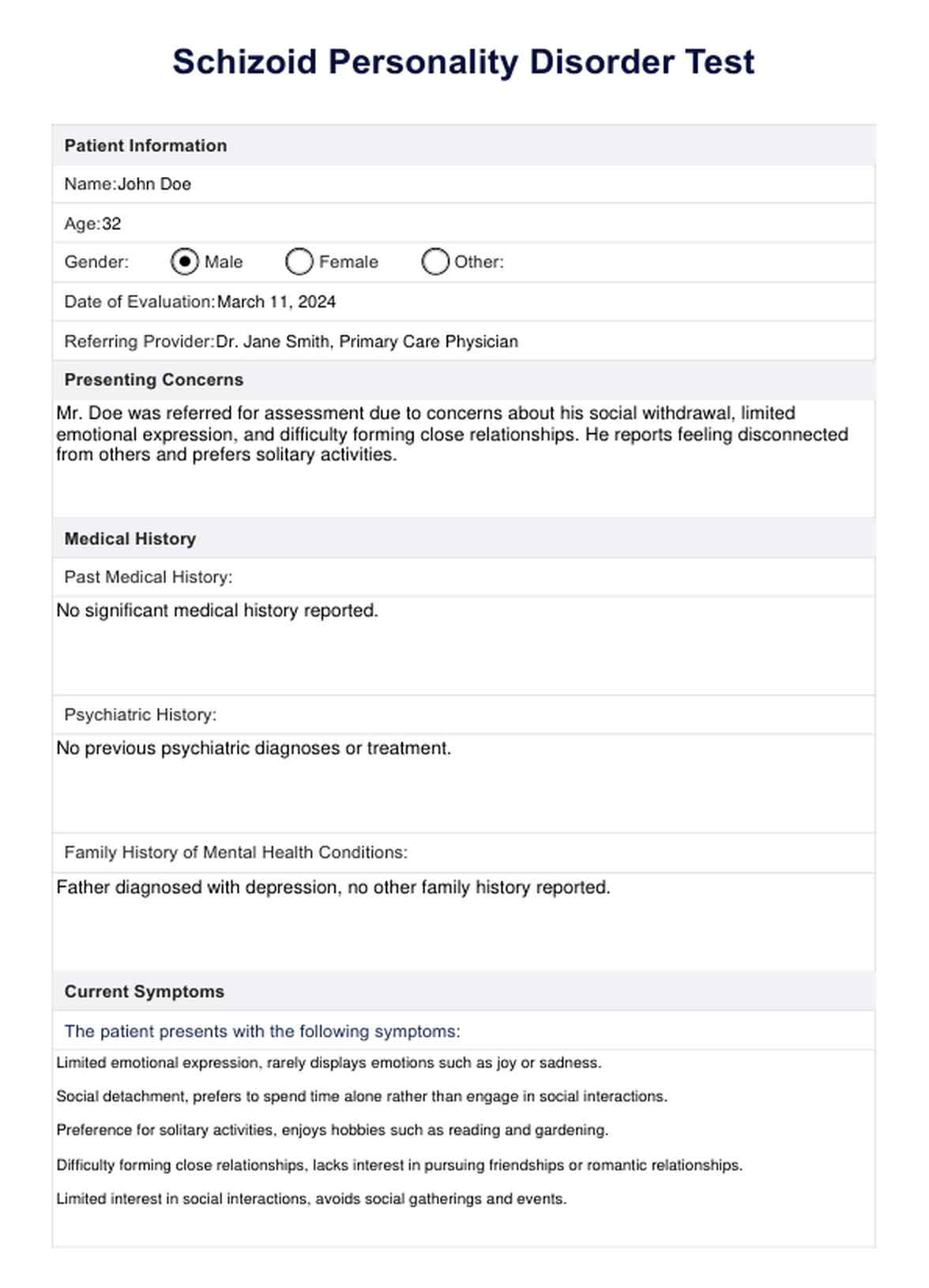
Schizoid Personality Disorder Test Example
Schizoid Personality Disorder symptoms
A Schizoid Personality Disorder Test typically assesses various symptoms associated with the condition, also referred to as schizoid traits. Some common symptoms that this test detects include:
Emotional expression
Individuals with schizoid personality disorder often exhibit difficulties in expressing and experiencing emotions. They may have limited emotions, appear emotionally detached in social interactions, and struggle to express their feelings to others.
Social interactions and relationships
Social detachment and a lack of interest in forming close relationships are hallmark features of schizoid personality disorder. Those affected may find it challenging to engage in social interactions, have little desire for intimacy with friends, struggle with social skills such as initiating or maintaining conversations, and show difficulty expressing criticism or praise.
Preferential behaviors
Individuals with Schizoid Personality Disorder typically also prefer solitude and solitary activities and may spend a significant amount of time alone. They may have little interest in seeking out social interactions or forming close friendships, but instead, they tend to find solace and fulfillment in solitary hobbies or pursuits.
Different Schizoid Personality Disorder Test types
There are several types of Schizoid Personality Disorder tests, each designed to assess different aspects of the condition. Here are some common types:
- Self-report questionnaires: These tests consist of a series of questions that individuals answer based on their experiences and perceptions. They typically assess symptoms associated with schizoid personality traits, social detachment, emotional expression, and interpersonal relationships.
- Structured interviews: Conducted by mental health professionals, structured interviews involve a systematic assessment of symptoms and behaviors associated with schizoid personality disorder. Clinicians ask specific questions to gather information about the individual's social and emotional functioning, personal history, and behavior patterns.
- Projective tests: Projective tests, such as the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) or the Rorschach Inkblot Test, involve presenting individuals with ambiguous stimuli and asking them to interpret or respond to what they see. These tests can provide insights into underlying psychological processes and may reveal aspects of schizoid personality traits or interpersonal dynamics.
- Diagnostic criteria assessment: Mental health professionals may use standardized diagnostic criteria, such as those outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), to assess whether an individual meets the criteria for schizoid personality disorder. This assessment evaluates the presence and severity of specific symptoms and behaviors associated with the disorder.
- Online assessments: There are various online tests and quizzes available that claim to assess schizoid personality traits. These assessments may provide a preliminary indication of potential symptoms or tendencies associated with the disorder but are not substitutes for a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional.
What's included in a Schizoid Personality Disorder Test?
A Schizoid Personality Disorder Test typically includes various components to assess different aspects of the condition. Here are some common elements that may be included:
- Symptom assessment: Evaluation of symptoms associated with schizoid personality traits, such as limited emotional expression and social detachment.
- Emotional expression: Exploration of the individual's ability to express and experience emotions, including the range and intensity of emotional responses.
- Social interaction: Assessment of the individual's comfort level, engagement in social interactions, and interest in forming close relationships.
- Preference for solitude: Examining the individual's tendency to engage in solitary activities and their feelings towards spending time alone versus in social settings.
- Social skills: Evaluation of the individual's social skills, including their ability to initiate and maintain conversations and interpret social cues.
- Personal history: Inquiry into the individual's unique history, including childhood experiences, family dynamics, and past relationships.
- Diagnostic criteria: Comparison of the individual's symptoms against the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM to determine if they meet the criteria for schizoid personality disorder.
Process for interpreting the results
Interpreting the results of a Schizoid Personality Disorder Quiz involves several steps to understand the implications of the findings accurately:
- Review results objectively: Review the test results objectively, considering each response and score without bias or preconceived notions.
- Identify patterns: Look for patterns or clusters of responses that indicate specific symptoms or tendencies associated with schizoid personality traits. Pay attention to consistent responses across different sections of the test.
- Consider severity: Assess the severity of symptoms indicated by the test results. Determine whether symptoms are mild, moderate, or severe based on the individual's responses and scoring.
- Compare to diagnostic criteria: Compare the test results to the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM for schizoid personality disorder. Determine if the individual's symptoms align with the requirements for diagnosis, considering factors such as the presence and duration of symptoms and their impact on functioning.
- Contextualize findings: Consider the individual's history, current life circumstances, and relevant contextual factors when interpreting the results. Consider environmental influences, cultural norms, and past experiences that may contribute to presenting symptoms.
- Consult with a professional: If interpreting the results independently, consider seeking input from a qualified mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist. They can provide expertise in understanding the significance of the findings and offer guidance on the next steps.
- Provide support and resources: Offer support and resources to the individual based on the interpretation of the results. This may include psychoeducation about schizoid personality disorder, recommendations for further evaluation or treatment, and referrals to mental health professionals or support groups.
- Monitor progress: If the individual receives a diagnosis of schizoid personality disorder, continue to monitor their symptoms and progress over time. Adjust treatment strategies as needed and provide ongoing support to promote their well-being and functioning.
Ethical considerations when administering or interpreting the test
When administering or analyzing the Schizoid Personality Disorder Test, it is crucial to consider the ethical challenges of treating personality disorders. Personality disorders, including schizoid personality disorder, present unique challenges that give rise to various ethical concerns for physicians.
One critical moral principle is the conflict between beneficence and nonmaleficence when involuntarily hospitalizing a patient. Additionally, the ethical responsibility of clinicians treating patients with personality disorders involves weighing risks versus benefits for individual patients, especially considering the severity, higher prevalence, chronicity, and complexity of these disorders.
Ethical considerations in the treatment of personality dysfunction emphasize the need for clinicians to navigate challenges such as self-harm, suicidality, and complex decision-making due to the severity of personality disorders.
Despite limited empirical data guiding treatment decisions for schizoid and other personality disorders, clinicians are urged to consider ethical issues and carefully assess the risks versus benefits of seeking treatment for each patient.
Tracking progress and changes in symptoms over time
When monitoring progress and changes in symptoms over time of mental health condition for individuals with Schizoid Personality Disorder, it is essential to consider various factors and strategies to manage the condition effectively. Here are some critical points based on the search results provided:
- Symptoms monitoring: Monitoring symptoms such as emotional detachment, lack of interest in developing close relationships, and solitary activities is crucial to track any changes or improvements over time.
- Treatment plan adherence: Individuals with Schizoid Personality Disorder need to adhere to their treatment plans, which often involve psychotherapy (talk therapy) to address social challenges and emotional detachment.
- Healthy coping mechanisms: Engaging in hobbies, seeking social support, joining groups, and prioritizing self-care can help individuals manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
- Expect setbacks: Setbacks are common when dealing with personality disorders, so it is essential to anticipate them and have strategies in place to overcome obstacles and stay on track with treatment goals.
- Professional guidance: Seeking help from mental health professionals specializing in personality disorders can provide valuable insights, support, and guidance in managing Schizoid Personality Disorder effectively.
Commonly asked questions
Symptoms of Schizoid Personality Disorder include a lack of interest in forming relationships, not enjoying close relationships with close friends often, showing little emotion, lacking the drive to reach goals, and not reacting to praise or criticism.
The exact causes of Schizoid Personality Disorder are not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors likely play a role. Having a family history of schizoid personality disorder, schizotypal personality disorder, or schizophrenia can increase the person at risk.
Diagnosing Schizoid Personality Disorder can be challenging as it involves a long-standing pattern of behaviors. Mental health professionals typically assess a person's history, relationships, and behaviors to diagnose correctly. Questionnaires may also aid in self-assessment tools and the diagnostic process.

















-template.jpg)