Procrastination Worksheets PDF
Help clients access a practical tool for better time management and productivity with our Procrastination Worksheets.


What is procrastination?
Procrastination is the habitual delay of tasks or decisions, often resulting in stress, reduced productivity, and a sense of guilt. This behavior extends beyond simple time management issues and is frequently linked to deeper psychological factors, such as low self-esteem, perfectionism, fear of failure, or a lack of motivation. Often referred to as a quintessential self-regulatory failure, procrastination serves as a temporary escape from challenging emotions or tasks but ultimately increases long-term stress and negative consequences.
The causes of procrastination are multifaceted, encompassing both personal and situational factors. Psychologically, negative self-beliefs, uncertainty about tasks, or overwhelming expectations can hinder task initiation and progress. Additionally, uncomfortable feelings such as anxiety or frustration may contribute to avoidance, reinforcing the cycle of procrastination.
Our Procrastination Worksheets are designed as a professional resource to help individuals understand procrastination, address procrastination excuses, and develop strategies to overcome it. These evidence-based tools provide health professionals with structured activities, including reflection prompts and task initiation techniques, to identify triggers and patterns. By fostering self-awareness and implementing tailored, actionable strategies, the worksheets help individuals stop procrastinating and build productive habits, ultimately enhancing their well-being and productivity.
Procrastination Worksheets PDF Template
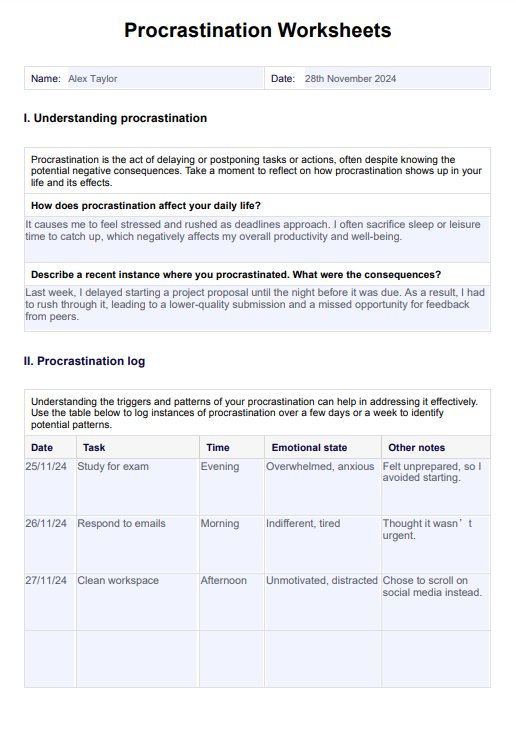
Procrastination Worksheets PDF Example
How to use our Procrastination Worksheets
The Procrastination Worksheets are a versatile and evidence-based tool designed to help individuals reflect on procrastination habits, identify triggers, and develop practical strategies to improve productivity. Follow this step-by-step guide to effectively integrate these worksheets into your professional practice:
Step 1: Access and download the worksheets
You can access the Procrastination Worksheets directly from this guide. Click “Use Template” to open the worksheets with Carepatron and customize them to meet your client’s needs. Alternatively, download a fillable PDF version for manual use.
Step 2: Introduce the worksheets to clients
Explain the purpose of the worksheets to your clients, emphasizing how they foster self-awareness and actionable behavior change. Highlight their role in complementing your therapeutic or coaching strategies.
Step 3: Complete the reflection section
Guide clients through the reflection questions to explore procrastination habits and understand their impact. This section helps identify the tasks they commonly delay and the consequences of procrastination.
Step 4: Log procrastination triggers and patterns
Use the procrastination log to help clients document tasks, emotional states, and potential triggers. Identifying patterns allows for tailored intervention planning.
Step 5: Develop an action plan
Work with clients to complete the Action Plan, incorporating strategies like task prioritization, setting deadlines, and creating accountability systems. This section ensures that clients have clear, actionable steps to address procrastination.
Step 6: Review and adjust strategies
During follow-up sessions, review the completed worksheets with clients, discuss their progress, and make necessary adjustments to refine strategies and ensure continued improvement.
Step 7: Store and document worksheets securely
Ensure completed worksheets are stored securely, respecting client confidentiality. Use secure, encrypted patient record software for digital forms. Physical copies should be kept in locked, restricted-access locations.
By integrating these worksheets into your professional practice, you provide clients with structured, evidence-based tools to overcome procrastination and achieve their goals effectively.
Understanding the psychological roots of procrastination
Procrastination is a complex behavior influenced by both psychological and environmental factors. Recognizing the underlying causes can guide effective and collaborative interventions, helping individuals address procrastination with greater self-awareness and confidence.
The role of emotional avoidance
Procrastination is often driven by the need to avoid uncomfortable emotions such as anxiety, fear of failure, or frustration. While delaying tasks may provide temporary relief, it can increase long-term stress. Exploring these emotional responses can help uncover healthier coping methods, such as mindfulness or emotional regulation strategies.
The impact of negative thought patterns
Cognitive distortions, including perfectionism and self-doubt, are common contributors to procrastination. Avoidance often stems from fears of inadequacy or failing to meet high expectations. Identifying and reframing these thought patterns can promote a more compassionate and realistic perspective, enabling individuals to approach tasks with greater confidence.
Motivation and belief in ability
A lack of motivation or confidence in one’s ability to succeed can hinder task initiation. Aligning tasks with personal values and goals can enhance engagement. Additionally, building self-efficacy—fostering a sense of capability—can empower individuals to approach challenges with greater control.
Procrastination and self-regulation
Difficulties with self-regulation, such as managing time, prioritizing tasks, or maintaining focus, often play a significant role in procrastination. These challenges may stem from difficulties in executive functioning or aligning actions to long-term goals. Personalized strategies, such as structured routines, time management techniques, and prioritization frameworks, can effectively overcome these barriers.
Environmental and situational factors
External influences, such as a disorganized workspace or unclear expectations, can exacerbate procrastination. Identifying and modifying environmental barriers, such as creating focused workspaces or minimizing distractions, can significantly improve task initiation and completion.
Key benefits of our Procrastination Worksheets
Using our Procrastination Worksheets PDF can offer the following benefits:
Enhances client self-awareness
The worksheets guide clients to reflect on their procrastination habits, helping them identify triggers, emotional patterns, and the consequences of their behaviors. This self-awareness provides a foundation for deeper understanding and meaningful change.
Supports evidence-based interventions
With strategies rooted in psychological research—such as task breakdowns, time blocking, and accountability—the worksheets allow professionals to implement practical, evidence-based solutions tailored to each client’s needs.
Encourages goal setting and progress tracking
The planners and action plans included in the worksheets help clients establish clear goals and track their progress over time. This structured approach makes it easier for professionals to monitor improvements and adjust interventions as needed.
Promotes active client engagement
By actively completing the worksheets, clients take ownership of their journey, fostering a sense of responsibility and motivation. This engagement helps bridge the gap between sessions and real-world application of strategies.
Versatile and easy to use
Available in printable and digital formats, the worksheets are adaptable for various settings, including in-person therapy, telehealth sessions, and group interventions. This flexibility allows professionals to seamlessly integrate them into their practice.
These benefits make the Procrastination Worksheets a valuable resource for mental health professionals. They help clients address procrastination effectively while supporting their overall mental well-being and productivity.
Commonly asked questions
Procrastination activity worksheets provide a structured approach to understanding procrastination and addressing its root causes. They include reflection exercises, reading passages, and actionable strategies to improve task initiation and help individuals stop procrastination. By identifying triggers, breaking down tasks, and setting achievable goals, these worksheets encourage the development of healthier habits and support long-term progress.
Chronic procrastination can result in heightened stress levels, contributing to physical health issues like headaches, fatigue, or weakened immunity. Procrastination Worksheets help mitigate these risks by promoting better self-regulation and time management. Through guided exercises and focusing on task prioritization, individuals can reduce stress and regain control over their responsibilities, improving mental and physical well-being.
How can procrastination activity worksheets help students stay on track?
Students often procrastinate due to difficulty managing tasks or understanding their priorities. Procrastination activity worksheets are particularly helpful for students by fostering reflection on why people procrastinate and providing tools to align their actions with their intended course. Through task breakdowns, time management exercises, and reading passages, students learn how to stay organized, improve task initiation, and develop habits that support long-term success.



















-template.jpg)