Neurological Vital Signs
Understanding neurological vital signs is crucial for assessing a patient's brain function. Get Carepatron's free PDF download with examples to deepen your knowledge.


What is a neurological assessment?
A neurological assessment is a crucial component of healthcare that focuses on evaluating the function and health of the nervous system. This intricate examination allows healthcare professionals to gather valuable insights into the functioning of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. By assessing neurological vital signs, clinicians can identify abnormalities or changes in neurological status, aiding in the early detection of potential health issues.
The primary goal of a neurological assessment is to comprehensively evaluate cognitive function, sensory perception, motor skills, and reflexes. Such assessments also include a neurological examination checklist, which involves a series of structured tests and observations to assess the patient's mental status, cranial nerves, coordination, and muscle strength. Through these evaluations, healthcare providers can comprehensively understand the patient's neurological health and identify deviations from the norm.
Neurological assessments are crucial in various medical scenarios, such as traumatic injuries, neurological disorders, and specific medical emergencies. Timely and accurate assessments enable healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding treatment plans, interventions, and the overall management of neurological conditions.
Understanding the significance of neurological assessments is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals. Regular assessments can contribute to the early detection of neurological issues, allowing for prompt intervention and improved patient outcomes. Moreover, for individuals interested in monitoring their neurological health, a basic understanding of the components of a neurological assessment can empower them to recognize potential signs of concern and seek timely medical attention.
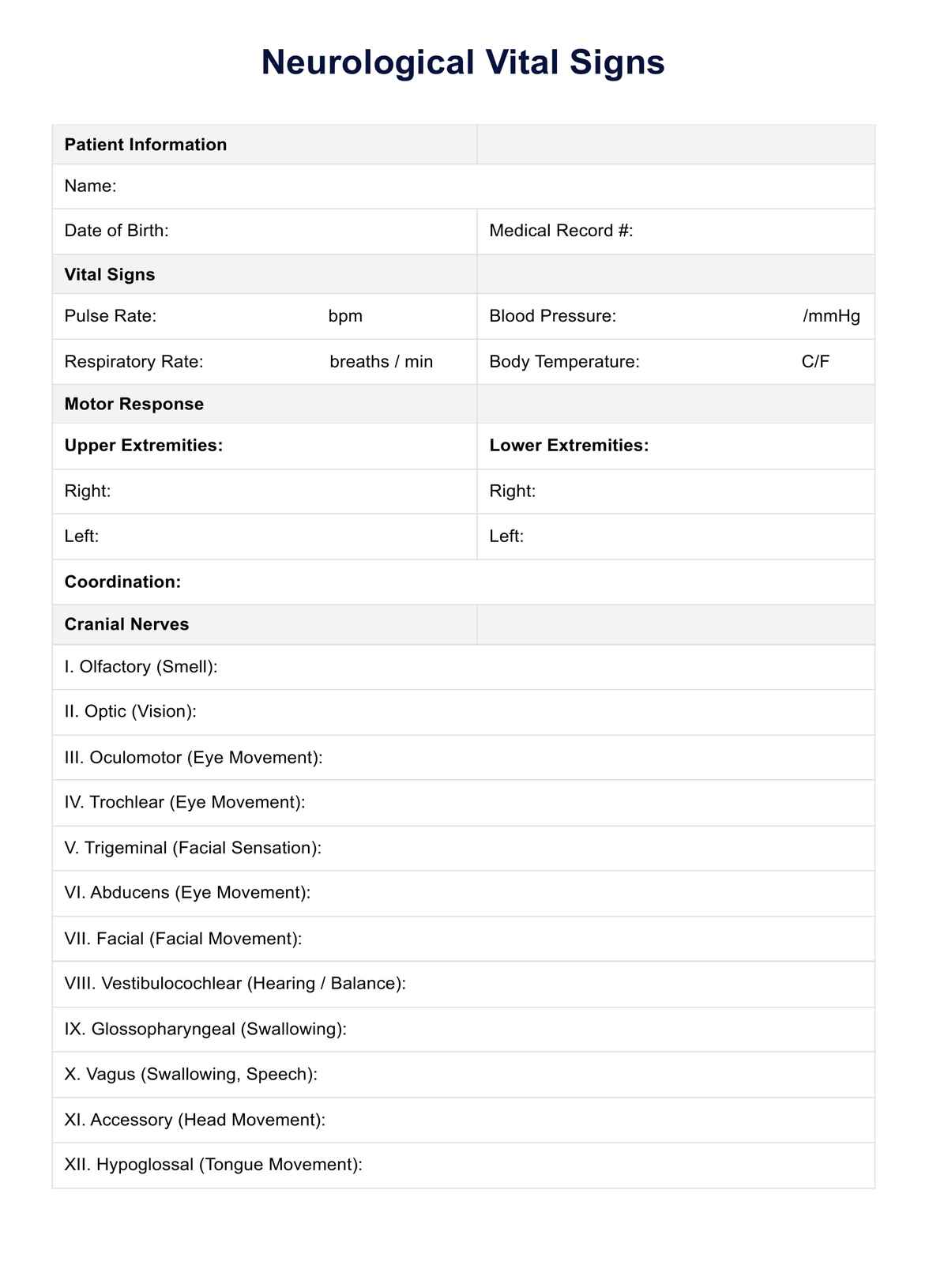
Neurological Vital Signs Template
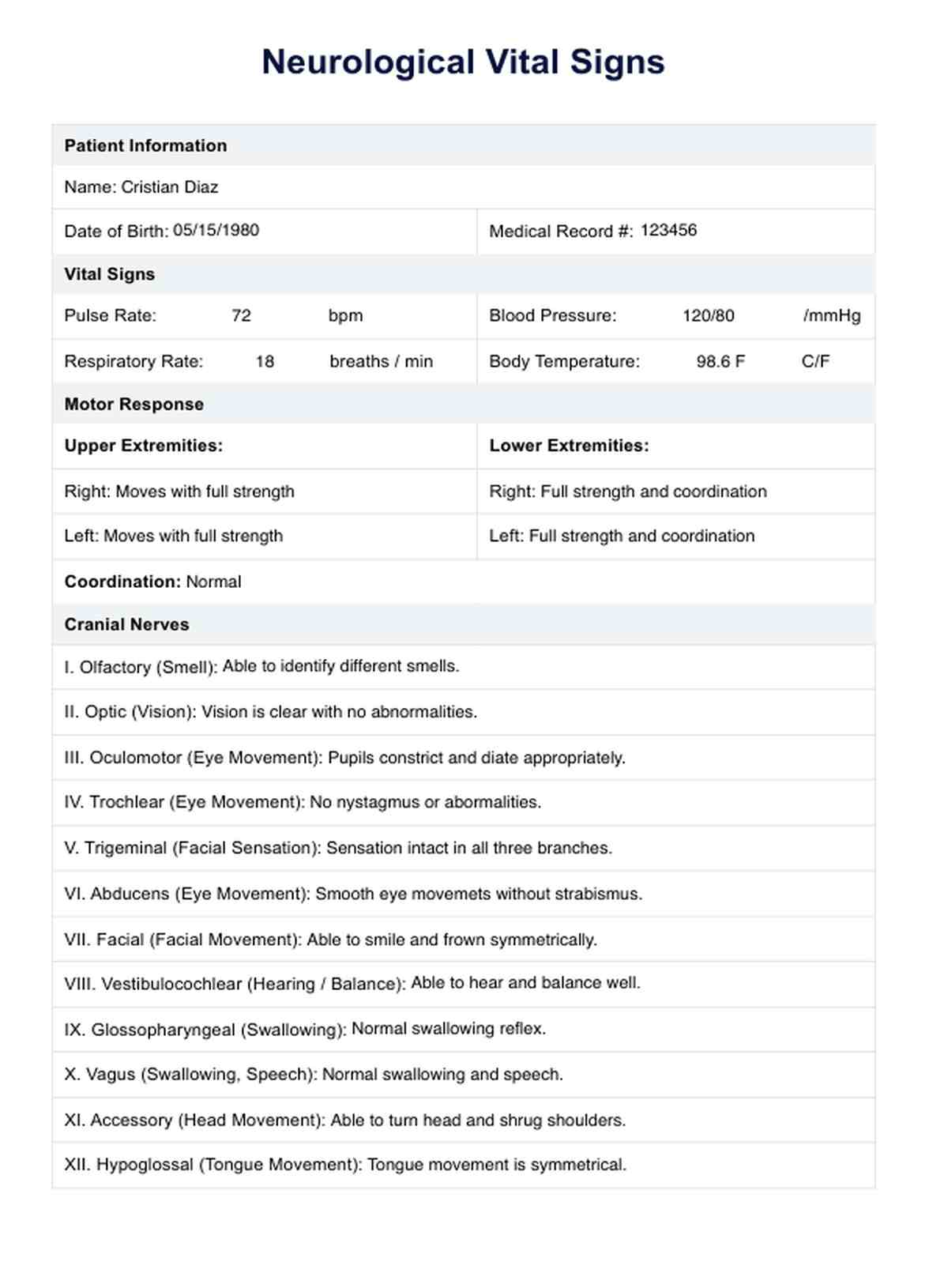
Neurological Vital Signs Example
When to check the patient's neurological status?
Ensuring a timely and thorough evaluation of a patient's neurological status is paramount in various healthcare scenarios. The frequency and necessity of these assessments depend on specific situations and medical conditions.
Head injuries and trauma
One critical instance that warrants the immediate checking of neurological status is in cases of head injuries or trauma. Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) resulting from a head injury can lead to severe complications if not promptly addressed. Regular neurological examinations, including assessing pupillary reactions, motor responses, and cranial nerves, are crucial in monitoring and managing patients with head injuries.
Post-surgery and critical care
Patients undergoing surgeries, especially those involving the central nervous system, require close monitoring of their neurological status postoperatively. Critical care settings demand vigilant attention to vital signs, including blood pressure and neurological examinations, to detect any signs of complications or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Neurological disorders
Individuals with known neurological disorders or conditions that affect the central nervous system may require regular neurological assessments as part of their ongoing care. This helps healthcare providers track disease progression, adjust treatment plans, and address emerging symptoms.
Altered mental status
Any unexplained alteration in mental status, such as sudden confusion, disorientation, or loss of consciousness, should prompt an immediate neurological assessment. This evaluation helps identify potential underlying causes, such as neurological issues or disruptions in blood flow to the brain.
Emergency situations
Checking neurological status is essential in emergencies, where rapid decision-making is crucial. This is particularly true for cases involving strokes, seizures, or other acute neurological events. Assessing motor responses, cranial nerves, and vital signs becomes pivotal in determining the appropriate course of action.
What vital signs are checked during the assessment?
Ensuring a comprehensive neurological assessment involves evaluating specific vital signs and responses to various stimuli. Each of these vital signs provides valuable information about the patient's neurological function and overall well-being.
Motor response
Motor responses play a crucial role in assessing the integrity of the central nervous system. During a neurological assessment, healthcare professionals evaluate the patient's ability to move limbs purposefully, assessing motor function and identifying abnormalities. This examination aids in determining the extent of neurological impairment and guiding appropriate interventions.
Cranial nerves
Assessing cranial nerves is a fundamental aspect of a neurological examination. These nerves, responsible for various sensory and motor functions of the head and neck, provide essential information about the patient's overall neurological health. Testing cranial nerves involves evaluating functions such as vision, hearing, and facial movements.
Assessing pupillary reaction
Examination of pupillary reactions is a key indicator of neurological function, particularly related to the brain stem. Changes in pupillary size and response to light can reveal critical information about the patient's neurological status. Anisocoria (unequal pupil size) or sluggish pupillary reactions may suggest underlying neurological issues.
Motor nerves
The assessment of motor nerves involves evaluating the patient's ability to move specific muscle groups in response to stimuli. This examination helps identify any disruptions in the communication between the brain and muscles, providing insights into the functioning of the motor nervous system.
Brain stem function
The brain stem plays a vital role in regulating essential functions such as breathing, heart rate, and consciousness. Assessing brain stem function during a neurological examination involves testing reflexes, facial movements, and responses to various stimuli. Changes in brain stem function can indicate severe neurological impairment.
Patient's level of consciousness
The patient's level of consciousness is a critical vital sign that reflects overall neurological function. Using standardized scales, healthcare professionals assess the patient's responsiveness to stimuli, including verbal response, motor response, and reactions to painful stimuli. Changes in consciousness levels may signal neurological deterioration or improvement.
Verbal response
Evaluating verbal responses is integral to understanding higher cognitive function and communication abilities. The patient's ability to respond coherently and appropriately to verbal stimuli provides insights into the functioning of the cerebral cortex and language centers.
How to use this template
Effectively utilizing the neurological vital signs template is essential for conducting thorough assessments and gaining valuable insights into a patient's neurological well-being. Follow the steps outlined below to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
Review vital signs and patient history
Start by reviewing the patient's vital signs, including pulse rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. Gather relevant information from the patient's history, including any known neurological conditions, recent injuries, or changes in sensory perception. Understanding the baseline vital signs helps establish a reference point for the assessment.
Conduct motor response evaluation
Initiate the assessment by evaluating the patient's motor responses. Assess the ability to move limbs purposefully, checking for any abnormalities in motor function. Observe coordination, strength, and any signs of weakness or paralysis. Motor responses provide crucial insights into the integrity of the central nervous system.
Examine cranial nerves
Perform a detailed examination of cranial nerves to assess various sensory and motor functions of the head and neck. Test vision, hearing, facial movements, and eye movements. Document any abnormalities, as cranial nerve findings can aid in the diagnosis of specific neurological conditions.
Evaluate pupillary reaction and eye movement
Focus on the assessment of pupillary reactions and eye movements, as these provide key information about brain stem function. Use a penlight to observe pupil size, symmetry, and responsiveness to light. Assess eye movements for coordination and any deviations from normal patterns.
Assess brain stem function
Include specific tests to evaluate brain stem function, such as reflexes, facial movements, and responses to stimuli. Abnormalities in brain stem function may indicate severe neurological issues and require immediate attention, especially in emergency department settings.
Document sensory and verbal responses
Evaluate sensory responses by testing the patient's ability to feel and respond to stimuli. Additionally, verbal responses should be assessed to gauge cognitive function and communication abilities. Document findings accurately to comprehensively overview the patient's neurological status.
Compile assessment findings
Compile all assessment findings into a coherent summary. This may include abnormalities observed during motor response testing, cranial nerve examinations, pupillary reactions, eye movements, and brain stem function assessments. A clear and concise compilation aids in effective communication with other healthcare professionals and supports accurate diagnosis.
Use findings for diagnosis and treatment planning
Utilize the compiled findings to support the diagnosis of neurological conditions or issues. The information gathered through this template serves as a valuable tool for healthcare professionals in determining appropriate treatment plans and interventions tailored to the patient's specific needs.
Importance of checking vital signs
Regularly checking vital signs is a fundamental aspect of healthcare that holds paramount importance in monitoring and ensuring the well-being of individuals. Vital signs encompass various physiological parameters that provide critical information about the body's functions.
The significance of routinely assessing these signs extends across different medical settings, contributing to early detection, intervention, and overall patient care.
Early detection of health issues
Monitoring vital signs, including pulse rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and body temperature, enables healthcare professionals to identify subtle changes in a patient's health status. Early detection of deviations from normal values can indicate underlying health issues, allowing for timely intervention and preventive measures.
Assessment of cardiovascular health
Vital signs serve as key indicators of cardiovascular health. Blood pressure and pulse rate, for example, provide insights into the efficiency of the heart's pumping action and the overall health of the circulatory system. Abnormalities in these vital signs may signal conditions such as hypertension or cardiovascular diseases, prompting further investigation and management.
Monitoring neurological well-being
In the context of neurological vital signs, regular assessments are crucial for evaluating the health of the nervous system. Changes in motor responses, cranial nerve function, and pupillary reactions can indicate neurological disorders, traumatic injuries, or other critical conditions. Timely identification of such changes allows for prompt intervention and improved outcomes.
Indicators of respiratory function
Respiratory rate is a vital sign that provides valuable information about a person's respiratory health. Abnormalities in respiratory rate may suggest respiratory distress, infections, or other pulmonary conditions. Monitoring this vital sign is particularly crucial in emergency situations and critical care settings.
Guide for treatment adjustments
Vital signs serve as a guide for healthcare professionals in adjusting treatment plans. Changes in vital signs may necessitate modifications in medication dosages, fluid management, or other interventions. Regular monitoring ensures treatment strategies are tailored to the individual patient's needs and response.
Overall patient safety
Routine vital sign assessments contribute to the overall safety of patients. Regular monitoring enables healthcare providers to promptly identify and address potential complications, reducing the risk of adverse events. This is especially critical in postoperative care, emergencies, and during the management of chronic illnesses.
Next steps
After reviewing the neurological vital signs, individuals and healthcare professionals alike should take specific next steps to ensure a comprehensive assessment and appropriate actions. Here's a quick overview of what to do next:
1. Interpret findings
Begin by interpreting the findings from the neurological vital signs assessment. Consider the observed motor responses, cranial nerve function, pupillary reactions, and any noted abnormalities. This interpretation lays the foundation for further investigation and targeted interventions.
2. Conduct additional assessments
Consider the need for additional evaluations depending on the initial neurological vital signs assessment. Conduct more detailed examinations, such as imaging studies, laboratory tests, or neurological specialized assessments, to gather more specific information about the underlying causes or contributing factors.
3. Consult with specialists
For complex or challenging cases, it's essential to consult with specialists. Neurologists, neurosurgeons, or other relevant healthcare professionals can provide expertise in diagnosing and managing specific neurological conditions. Collaborative decision-making ensures a comprehensive approach to patient care.
4. Implement treatment plans
Based on the neurological vital signs and additional assessments, develop and implement tailored treatment plans. Depending on the diagnosed neurological conditions, these may include medications, rehabilitation therapies, surgical interventions, or other targeted approaches.
5. Monitor progress
Regularly monitor the patient's progress throughout the treatment and recovery process. Adjust treatment plans as necessary based on changes in neurological status or responses to interventions. Monitoring ensures the chosen strategies are practical and aligned with the patient's evolving needs.
6. Educate patients and caregivers
Provide clear and concise information to patients and their caregivers regarding the neurological findings, diagnosis, and recommended treatments. Education empowers individuals to participate in their care actively, understand the importance of follow-up appointments, and adhere to prescribed treatment plans.
7. Coordinate follow-up care
Coordinate and schedule follow-up appointments to track ongoing neurological health. Regular check-ins enable healthcare providers to assess long-term progress, address any emerging issues, and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
8. Foster holistic well-being
Recognize the interconnectedness of neurological health with overall well-being. Encourage lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, to promote optimal neurological function and support the individual's holistic health.
Commonly asked questions
To monitor neurological status, regularly assess vital signs like pulse rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. Additionally, conduct neurological examinations, evaluating motor responses, cranial nerves, and pupillary reactions to identify any changes or abnormalities promptly.
Vital signs are integral to the neurological assessment as they provide crucial information about the overall health and functioning of the nervous system. Changes in pulse rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate can indicate neurological issues or distress, guiding healthcare professionals in timely interventions.
Document a neurological assessment in nursing by recording detailed observations and findings. Include vital signs, motor responses, cranial nerve assessments, and any abnormalities observed during the assessment. Use clear and concise language to facilitate effective communication among healthcare providers and ensure comprehensive patient care.





















-template.jpg)