Counseling Supervision Form
Gain insight into your counseling practice with our Supervision Form. Elevate your healthcare journey today.


What is counseling supervision?
Counseling supervision is a cornerstone of counselor education and professional development within mental health services. It is a structured process where experienced clinicians, known as supervisors, guide, and mentor practicing school counselors or other mental health professionals in their clinical work. This process aims to enhance their counseling skills, promote ethical practice, and ultimately improve client outcomes.
At its core, clinical supervision provides a safe space for counselors to reflect on their therapeutic interactions, explore challenging cases, and receive constructive feedback from their supervisors. Through regular meetings and case discussions, supervisors help counselors navigate complex ethical dilemmas, adhere to professional standards, and maintain the highest level of integrity in their practice.
One of the key objectives of counseling supervision is to foster continuous professional growth. By engaging in reflective dialogue and receiving guidance from seasoned supervisors, counselors can expand their repertoire of therapeutic techniques, deepen their understanding of theoretical frameworks, and refine their clinical judgment. This ongoing learning process benefits individual practitioners and contributes to the overall advancement of the counseling profession.
Moreover, counseling supervision plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and effectiveness of mental health services. Supervisors help safeguard clients' well-being and uphold the ethical principles of confidentiality, respect, and cultural competence by providing oversight and accountability. Through collaborative supervision models, counselors also have the opportunity to learn from their peers, share best practices, and contribute to a culture of continuous improvement within their organizations.
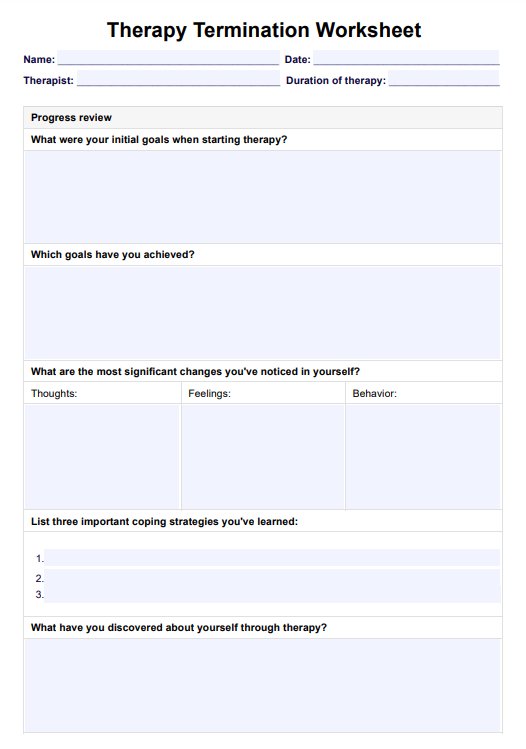
Counseling Supervision Form Template
Counseling Supervision Form Example
Why would a counselor need to be supervised?
Counselors seek supervision for multifaceted reasons, each pivotal to their professional advancement and the caliber of care dispensed in mental health services:
Professional advancement
Supervision furnishes counselors with continual learning opportunities and skill refinement. Regular feedback and mentorship from seasoned supervisors empower counselors to hone their counseling proficiency, deepen their grasp of theoretical underpinnings, and remain abreast of burgeoning best practices in the field.
Ethical integrity
Supervision guarantees counselors' adherence to ethical benchmarks outlined by esteemed organizations such as the American Counseling Association. Counselors uphold the highest ethical standards by deliberating ethical quandaries, receiving direction on apt interventions, and scrutinizing the influence of personal values on practice.
Client well-being
Supervision is a bulwark for clients' welfare, ensuring effective and culturally sensitive care. Counselors deliberate on cases, treatment modalities, and client progress with supervisors, navigating intricate scenarios involving issues like substance abuse, child welfare, or diverse clientele adeptly.
Personal nurturance
Given the emotional toll inherent in counseling, supervision affords counselors a nurturing haven to explore their responses, manage stressors, and embrace self-care practices. Supervisors collaboratively devise coping strategies, fostering counselors' resilience and fortitude in managing the emotional rigors of their vocation, thereby bolstering their job satisfaction and longevity.
Quality assurance
Supervision fosters the overarching excellence of mental health services by vigilantly monitoring counselors' performance and outcomes. Through meticulous evaluation and ongoing feedback, supervisors ascertain counselors' adherence to treatment protocols, efficacy in achieving client objectives, and continual professional growth, ensuring the perpetuation of superlative care delivery.
What is a Counseling Supervision Form?
A Counseling Supervision Form is an essential tool in mental health practice management software, fostering structured communication between clinical supervisors and supervisees, whether seasoned counselors or students in practicum programs.
It provides a comprehensive framework for goal-setting, evaluation, and discussion, ensuring a systematic approach to professional development. The form encompasses crucial elements such as assessing the supervisory relationship, reviewing clinical practice, and addressing ethical considerations. The in-depth exploration of the supervisee's decisions and interventions creates a supportive environment for reflection and growth.
Ethical considerations are paramount in Counseling Supervision Forms, with dedicated sections for examining ethical dilemmas, ensuring adherence to standards, and navigating challenging situations responsibly.
The form also emphasizes professional development, collaboratively identifying goals for skill enhancement, multicultural competence, and self-awareness. Feedback and evaluation serve as integral components, offering specific insights into the supervisee's performance and prompting discussions on areas for improvement.
How does our Counseling Supervision Form work?
Our Counseling Supervision Form facilitates effective communication, reflection, and growth between supervisors and supervisees in mental health counseling. Here's how it works:
Step 1: Schedule a supervision session
The first step involves scheduling a supervision session between the supervisor and supervisee. This can be done using our integrated scheduling feature, allowing both parties to select a convenient time and date for the session.
Step 2: Complete pre-session preparation
Before the supervision session, the supervisee completes any necessary pre-session preparation, such as reviewing client cases, identifying discussion points, and reflecting on personal challenges and successes.
Step 3: Conduct a supervision session
During the session, the supervisor and supervisee engage in open and collaborative discussions about clinical cases, ethical considerations, professional goals, and self-care strategies. The supervisor provides feedback, guidance, and support to help the supervisees navigate challenges and enhance their counseling skills.
Step 4: Document discussion points
Throughout the session, both parties document key discussion points, insights gained, and action steps for follow-up. Our Counseling Supervision Form provides structured fields for recording session details, client information, goals for supervision, and discussion points.
Step 5: Set goals for the next session
At the end of the session, the supervisor and supervisee collaboratively set goals for the next supervision session. These goals may include specific areas for skill development, ethical considerations, or personal growth objectives.
Step 6: Implement feedback and strategies
Following the session, the supervisee implements feedback and strategies discussed during supervision into their counseling practice. The supervisor may provide additional resources or referrals to support the supervisee's ongoing professional development.
Step 7: Monitor progress and adjust as needed
As supervision sessions progress, both parties monitor progress toward goals, evaluate outcomes, and adjust as needed. Regular supervision sessions ensure ongoing support, growth, and quality improvement in the provision of counseling services.
By following these steps and utilizing our Counseling Supervision Form, supervisors and supervisees can foster a supportive and collaborative supervisory relationship, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided to clients.
What are the benefits of getting counseling supervision?
Here are the benefits of counselor supervision:
Improvement in clinical skills
Counseling supervision presents an avenue for supervisees to glean feedback, direction, and assistance from seasoned clinical supervisors. Through deliberations on cases, treatment strategies, and intervention approaches, supervisees can refine their clinical acumen, cultivate a deeper grasp of theoretical frameworks, and hone their proficiency in catering to a myriad of diverse client demographics.
Fostering professional development
Participation in counseling supervision nurtures professional development by fostering introspection, a culture of reflective practice, and perpetuating a culture of continual learning. Supervisees can introspect on their strengths and areas necessitating improvement, establish objectives for honing their skills, and garner backing in realizing their professional aspirations.
Promotion of ethical conduct
Counseling supervision is integral in championing ethical conduct and adherence to professional benchmarks among supervisees. Supervisors navigate supervisees through ethical conundrums, guarantee informed consent, uphold confidentiality, and assist supervisees in navigating intricate ethical predicaments that may arise during counseling practice.
Personalized support and nurturing well-being
Counseling supervision provides a nurturing sanctuary for supervisees to address personal tribulations, cope with stressors, and prioritize self-preservation. Supervisors extend encouragement, validation, and perspective, assisting supervisees in sustaining their emotional equilibrium and resilience amidst arduous circumstances.
Upholding standards of excellence
Counseling supervision fuels the overarching amelioration of mental health services by certifying that counseling services adhere to a lofty echelon of quality and efficacy. Supervisors oversee supervisees' performance, dispense insights on client outcomes, and identify domains necessitating enhancement to ensure that clients receive superlative care.
Commonly asked questions
The goals include improving clinical skills, enhancing self-awareness, promoting ethical practice, supporting professional development, and ensuring quality client care.
Seek supervisors through professional organizations, academic institutions, or networking with colleagues, ensuring they have relevant experience and credentials.
Seek supervisors through professional organizations, academic institutions, or networking with colleagues, ensuring they have relevant experience and credentials.





















-template.jpg)